HKU biologists determine the evolutionary age of individual cell types providing critical insights for animal development
2023-04-13
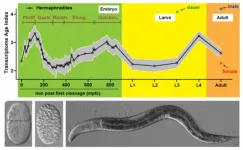
A research team led by Dr Chaogu ZHENG from the School of Biological Sciences at The University of Hong Kong (HKU) has recently made a significant discovery about the evolutionary age of different type of cells in a small animal called Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans). By using single-cell transcriptomic data and refined phylostratigraphy, the team determines the transcriptomic age of individual cells, which means they are able to estimate the evolutionary origin of different cells based on the age of the genes expressed in the ...
Coral-eating fish poo may act as ‘probiotics’ for reefs
2023-04-13
Until recently, fish that eat coral — corallivores — were thought to weaken reef structures, while fish that consume algae and detritus — grazers — were thought to keep reefs healthy. But scientists have discovered that feces from grazers leave large lesions on coral, possibly because they contain coral pathogens. By contrast, feces from corallivores may provide a source of beneficial microbes that help coral thrive.
“Corallivorous fish are generally regarded as harmful because they bite the corals,” said Dr Carsten Grupstra of Rice University, ...
New study demonstrates hospital safety climate and organizational characteristics predict healthcare-associated infections and occupational health outcomes
2023-04-13
Arlington, Va., April 13, 2023 – New data published today in the American Journal of Infection Control (AJIC) provide the first published evidence that a positive safety climate and adherence to standard precautions predict key healthcare-associated infection (HAI) and occupational health outcomes among patients and health care workers, respectively. The findings highlight features within hospitals’ organizations and safety climates that could be modified to improve these outcomes.
“Despite the infection prevention and safety benefits associated with standard precautions, generating consistent adherence in the healthcare setting has been ...
Selenium as a predictor of metabolic syndrome in middle age women
2023-04-12
“Recently, optimizing selenium intake in the population to prevent diseases [...] has been an important issue in modern health care worldwide.”
BUFFALO, NY- April 12, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 6, entitled, “Selenium as a predictor of metabolic syndrome in middle age women.”
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is a widespread clinical entity that has become almost a global epidemic. Selenium plays an important role in metabolic homeostasis. It has been suggested that it ...
A new vision for soybean meal: designer tempeh
2023-04-12
In a novel effort to create the next generation of plant-based, protein-rich environmentally sustainable and savory alternatives to animal meat, a University of Massachusetts Amherst food scientist has turned his attention to soybean meal.
Globally, this byproduct of soybean oil extraction is used almost exclusively for animal feed. In the U.S. alone, some 48 million metric tons of soybean meal was produced in 2022, according to the USDA.
“After the oil extraction, the majority of the protein is in the meal, not the oil,” says Hang ...
Riluzole and Sorafenib in patients with advanced solid tumors: a Phase I trial
2023-04-12
“Our phase I study determined the tolerable dose of this combination and investigated its biologic effects.”
BUFFALO, NY- April 12, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on April 10, 2023, entitled, “A phase I trial of riluzole and sorafenib in patients with advanced solid tumors: CTEP #8850.”
Overexpression of metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 (GRM1) has been implicated in the pathogenesis of multiple cancers. Riluzole, an inhibitor of glutamate release, showed synergistic antitumor activity in combination with the multi-kinase inhibitor sorafenib ...
COVID-19 increased weekday screentime for children: study
2023-04-12
The COVID-19 pandemic led to increased weekday screentime for school-aged children says a new study involving the University of Ottawa published in JAMA Pediatrics.
Researchers examined the change in children’s screen time from prior to the pandemic to three separate pandemic waves between 2020 and 2021. Researchers found a boost of up to 1.35 hours per day during the weekdays compared to prior to the pandemic, particularly with school closures at the onset of the pandemic.
While the weekend time was on par with pre-pandemic levels, ...
In search of a better semiconductor chip
2023-04-12
A University of Texas at Arlington materials science and engineering researcher is working on a project to determine when failure happens in electronic device circuits. The research ultimately will help manufacturers design better semiconductor chips.
Choong-Un Kim, professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, was awarded a $285,0000 grant from the Semiconductor Research Corporation (SRC) for the project “Enabling Electromigration Solver for Solder Joint With Various Packaging Structures and Alloys.” This is the latest in a series of grants he has received from SRC that aims to answer the demand for improved device reliability.
The SRC ...
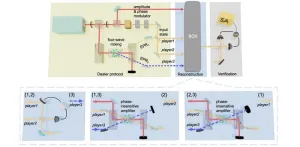
All-optical quantum state sharing via continuous variable system
2023-04-12
Quantum information is a powerful technology for increasing the amount of information that can be processed and communicated securely. Using quantum entanglement to securely distribute a secret quantum state among multiple parties is known as “quantum state sharing.” An important protocol in quantum networks and cryptography, quantum state sharing works like this (in simple terms): a secret quantum state is divided into n shares and given to n players. The secret state can only be reconstructed ...
Father’s alcohol consumption before conception linked to brain and facial defects in offspring
2023-04-12
According to the U.S. Surgeon General, women should not drink alcoholic beverages during pregnancy because of the risk of birth defects in their unborn child. Now, research at Texas A&M University demonstrates that a father’s alcohol consumption before conception also links to growth defects that affect the development of his offspring’s brain, skull and face.
Research investigating fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) exclusively examines maternal alcohol exposure. However, because men drink more and are more likely to binge drink than women, Dr. Michael Golding, an associate ...
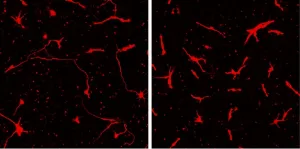
New technique allows researchers to dig into molecular causes of pediatric bipolar disorder
2023-04-12
It’s extremely difficult to study the biological basis of psychiatric disorders, in part because researchers can’t easily collect brain cells from living people to study in the laboratory. Now, University of Utah Health scientists have developed a way around that.
The researchers grew three-dimensional structures, called “organoids”, derived from blood cells donated by a patient with pediatric bipolar disorder and by several family members. The approach identified significant molecular changes linked to the psychiatric condition.
The results, reported in Molecular Psychiatry, suggest that structural changes in the ...
COVID-19 pandemic will disrupt cancer reporting for years to come
2023-04-12
Key takeaways:
American College of Surgeons research published in JAMA Surgery reveals the complexities and variations that occurred in cancer reporting in the National Cancer Database (NCDB) because of the pandemic.
The number of reported cancer cases in NCDB declined by 14.4% compared with prior years, representing more than 200,000 cancer cases that were not diagnosed and/or treated at accredited facilities.
Research offers guidance to centers across the country on how to interpret data from 2020 and onwards.
CHICAGO: New research from the American College of Surgeons (ACS) outlines significant ways that the COVID-19 pandemic destabilized usual patterns of cancer care as reported ...
Is the language you speak tied to outcome after stroke?
2023-04-12
MINNEAPOLIS – Studies have shown that Mexican Americans have worse outcomes after a stroke than non-Hispanic white Americans. A new study looks at whether the language Mexican American people speak is linked to how well they recover after a stroke. The study is published in the April 12, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
“Our study found that Mexican American people who spoke only Spanish had worse neurologic outcomes three months after having a stroke than Mexican American people who spoke only English or were bilingual,” said study author ...
Archaeological sites at risk from coastal erosion on the Cyrenaican coast, Libya
2023-04-12
Archaeological sites along the Libyan shoreline are at risk of being damaged or lost due to increasing coastal erosion, according to a study published April 12, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Kieran Westley and Julia Nikolaus of Ulster University, UK and colleagues.
The Cyrenaican coast of Eastern Libya, stretching from the Gulf of Sirte to the current Egypt-Libya border, has a long history of human occupation back to the Palaeolithic era, and it therefore hosts numerous important and often ...
Poor family cohesion is associated with long-term psychological impacts in bereaved teenagers
2023-04-12
The death of a parent can affect the health and well-being of children and adolescents, including higher risk of depression. A study published in PLOS ONE by Dröfn Birgisdóttir at Lund University, Lund, Sweden and colleagues suggests poor family cohesion is associated with long-term psychological symptoms among bereaved youth.
Parentally bereaved children are at increased risk for mental illness including depression, anxiety, suicide attempts, and self-injurious behaviors. However, the relationship ...
The stripes of the Lesser Pacific Striped Octopus are as unique as our own fingerprints, enabling scientists to track individuals as they grow
2023-04-12
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0265292
Article Title: Individually unique, fixed stripe configurations of Octopus chierchiae allow for photoidentification in long-term studies
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Most retail cannabis may be less potent than claimed, with THC being at least 15% less potent than reported on the label in around 70% of products sampled in Colorado
2023-04-12
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0282396
Article Title: Uncomfortably high: Testing reveals inflated THC potency on retail Cannabis labels
Author Countries: USA
Funding: Headspace Sensory LLC provided funding for purchase of 13 of the 23 Cannabis samples that were included as part of another study [47], but had no other involvement in this study. All other funding was provided by the McGlaughlin Lab at the University of Northern Colorado and by the first author. Mile High Labs provided support for this study in the form of salaries for VJ and JH. The specific roles of these authors are articulated in the ‘author contributions’ ...
New 52 million-year-old bat species discovered in Wyoming, US, is the oldest bat skeleton known
2023-04-12
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0283505
Article Title: The oldest known bat skeletons and their implications for Eocene chiropteran diversification
Author Countries: The Netherlands, USA
Funding: 1) Theodore Roosevelt Memorial Fund of the American Museum of Natural History (TBR) https://www.amnh.org/research/richard-gilder-graduate-school/academics-and-research/fellowship-and-grant-opportunities/research-grants-and-graduate-student-exchange-fellowships/roosevelt-memorial-fund 2) ...
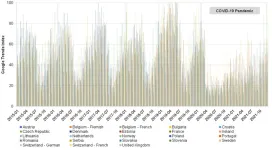
Google Trends reveal how the spread of chickenpox may have been suppressed during the COVID-19 pandemic
2023-04-12
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0283465
Article Title: Impact assessment of immunization and the COVID-19 pandemic on varicella across Europe using digital epidemiology methods: A descriptive study
Author Countries: Sweden, Lithuania, Ireland, USA, Spain
Funding: Funding for this research was provided by Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA (MSD). We confirm that the funder provided support in the form of salaries for Ugne Sabale, Ligita Jarmale, Janice Murtagh, Manjiri Pawaskar, and Goran Bencina, but did not have any additional ...
Got milk? The ancient Tibetans did, according to study
2023-04-12
New research into ancient populations that resided on the Tibetan Plateau has found that dairy pastoralism was being practiced far earlier than previously thought and may have been key to long-term settlement of the region’s extreme environment.
Professor Michael Petraglia, Director of Griffith’s Australian Research Centre for Human Evolution, was part of the international research team that set out to understand how prehistoric populations adapted to the vast, agriculturally poor highlands of the Tibetan Plateau.
The research, ...
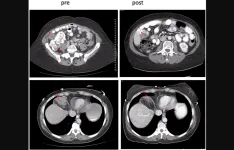
From tragedy, a new potential cancer treatment
2023-04-12
Diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG) is a lethal pediatric brain cancer that often kills within a year of diagnosis. Surgery is almost impossible because of the tumors’ location. Chemotherapy has debilitating side effects. New treatment options are desperately needed.
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Professor Adrian Krainer is best known for his groundbreaking research on antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs)—molecules that can control protein levels in cells. His efforts led to Spinraza®, ...
Dairy foods helped ancient Tibetans thrive in one of Earth’s most inhospitable environments
2023-04-12
The Tibetan Plateau, known as the “third pole”, or “roof of the world”, is one of the most inhospitable environments on Earth. While positive natural selection at several genomic loci enabled early Tibetans to better adapt to high elevations, obtaining sufficient food from the resource-poor highlands would have remained a challenge.
Now, a new study in the journal Science Advances reveals that dairy was a key component of early human diets on the Tibetan Plateau. The study reports ancient ...
Multifunctional patch offers early detection of plant diseases, other crop threats
2023-04-12
Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed an electronic patch that can be applied to the leaves of plants to monitor crops for different pathogens – such as viral and fungal infections – and stresses such as drought or salinity. In testing, the researchers found the patch was able to detect a viral infection in tomatoes more than a week before growers would be able to detect any visible symptoms of disease.
“This is important because the earlier growers can identify plant diseases or fungal infections, the ...
Predictive power of climate models may be masked by volcanoes
2023-04-12
Simulated volcanic eruptions may be blowing up our ability to predict near-term climate, according to a new study published in Science Advances.
The research, led by the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR), finds that the way volcanic eruptions are represented in climate models may be masking the models’ ability to accurately predict variations in sea surface temperatures in the tropical Pacific that unfold over multiple years to a decade.
These decadal variations in sea surface ...
Industry veteran Pablo Velez, RN, Ph.D., named CEO of El Centro Regional Medical Center
2023-04-12
In coordination with the El Centro Regional Medical Center (ECRMC) Board of Trustees, UC San Diego Health today announced that Pablo Velez, RN, PhD, has been appointed by UC San Diego Health as ECRMC’s chief executive officer effective April 17. Reporting to UC San Diego Health CEO Patty Maysent, Velez will oversee day-to-day operational, clinical and financial management of ECRMC, leading UC San Diego Health’s overall efforts to support the strategic and operational plan that was announced ...
[1] ... [1986]
[1987]
[1988]
[1989]
[1990]
[1991]
[1992]
[1993]
1994
[1995]
[1996]
[1997]
[1998]
[1999]
[2000]
[2001]
[2002]
... [8824]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.