Ancient DNA reveals the multiethnic structure of Mongolia’s first nomadic empire
2023-04-14
Long obscured in the shadows of history, the world’s first nomadic empire - the Xiongnu - is at last coming into view thanks to painstaking archaeological excavations and new ancient DNA evidence. Arising on the Mongolian steppe 1,500 years before the Mongols, the Xiongnu empire grew to be one of Iron Age Asia’s most powerful political forces - ultimately stretching its reach and influence from Egypt to Rome to Imperial China. Economically grounded in animal husbandry and dairying, the Xiongnu were famously nomadic, building their empire on the backs of horses. ...
2022 Tongan volcanic explosion was largest natural explosion in over a century, new study finds
2023-04-14
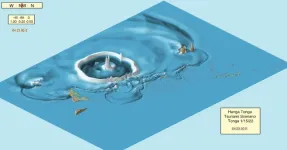
The 2022 eruption of a submarine volcano in Tonga was more powerful than the largest U.S. nuclear explosion, according to a new study led by scientists at the University of Miami Rosenstiel School of Marine, Atmospheric, and Earth Science and the Khaled bin Sultan Living Oceans Foundation.
The 15-megaton volcanic explosion from Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha'apai, one of the largest natural explosions in more than a century, generated a mega-tsunami with waves up to 45-meters high (148 feet) along the coast of Tonga’s Tofua Island and waves up to 17 meters (56 feet) on Tongatapu, ...
How does an aging-associated enzyme access our genetic material?
2023-04-14
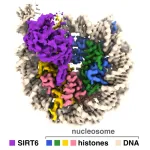
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — New research provides insight into how an enzyme that helps regulate aging and other metabolic processes accesses our genetic material to modulate gene expression within the cell. A team led by Penn State researchers have produced images of a sirtuin enzyme bound to a nucleosome—a tightly packed complex of DNA and proteins called histones—showing how the enzyme navigates the nucleosome complex to access both DNA and histone proteins and clarifying how it functions in humans and other animals.
A paper describing the results appears April 14 in the journal ...
Aston University develops software to untangle genetic factors linked to shared characteristics among different species
2023-04-14
Has potential to help geneticists investigate vital issues such as antibacterial resistance
Will untangle the genetic components shared due to common ancestry from the ones shared due to evolution
The work is result of a four-year international collaboration.
Aston University has worked with international partners to develop a software package to help scientists answer key questions about genetic factors associated with shared characteristics among different species.
Called CALANGO (comparative analysis with annotation-based genomic ...
Single-use surgical items contribute two-thirds of carbon footprint of products used in common operations
2023-04-14
A new analysis of the carbon footprint of products used in the five most common surgical operations carried out in the NHS in England shows that 68% of carbon contributions come from single-use items, such as single-use gowns, patient drapes and instrument table drapes. Published by the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, the analysis highlights significant carbon contributors were the production of single use items and their waste disposal, together with processes for decontaminating reusable products.
Researchers ...
Study: Anti-obesity medications could be sold for lower prices
2023-04-14
ROCKVILLE, Md.—New research shows that several anti-obesity medications could be manufactured and profitability sold worldwide at far lower estimated lower prices compared to their high costs, according to a new study in Obesity, The Obesity Society’s (TOS) flagship journal.
“Access to medicine is a fundamental element of the human right to health. While the obesity pandemic grows, especially amongst low-income communities, effective medical treatments remain inaccessible for millions in need. Our study highlights the inequality in pricing that exists for effective anti-obesity medications, ...
Offering medications for opioid addiction to incarcerated individuals leads to decrease in overdose deaths
2023-04-14
BOSTON – New research from Boston Medical Center concluded that offering medications to treat opioid addiction in jails and prisons leads to a decrease in overdose deaths. Published in JAMA Network Open, the study also found that treating opioid addiction during incarceration is cost-effective in terms of healthcare costs, incarceration costs, and deaths avoided.
Overdoses kill more than 100,000 people per year in America and this number continues to increase every year. People with addiction are more likely to be incarcerated than treated, with those from communities of color who use drugs more likely to be incarcerated than ...
SIAM Conference on Financial Mathematics and Engineering (FM23)
2023-04-14
The objective of the Activity Group on Financial Mathematics and Engineering is to advance fundamental research and implementation of practices in financial engineering, computation, and operations. The group aims at fostering collaborations among applied mathematicians, applied probabilists, statisticians, computer and data scientists, economists, as well as industry practitioners. The conference will expose state-of-art mathematical and computational tools in quantitative finance, including its uses in the public and private sector. The activity group promotes and supports the development of financial mathematics and engineering as an academic discipline. END ...
Ambrosia beetles can recognise their food fungi by their scents
2023-04-14
Certain ambrosia beetles species engage in active agriculture. As social communities, they breed and care for food fungi in the wood of trees and ensure that so-called weed fungi spread less. Researchers led by Prof. Dr. Peter Biedermann, professor of Forest Entomology and Forest Protection at the University of Freiburg, now demonstrate for the first time that ambrosia beetles can distinguish between different species of fungi by their scents. "The results can contribute to a better understanding of why beetles selectively colonise trees with conspecifics and how ...
Study snapshot: Following the letter of the law: 2020–2021 retention outcomes under Michigan’s Read by Grade Three Law
2023-04-14
Study: "Following the Letter of the Law: 2020–2021 Retention Outcomes Under Michigan’s Read by Grade Three Law"
Authors: Andrew Niel Utter (Michigan State University), John Westall (Michigan State University), Katharine O. Strunk (Michigan State University)
Embargoed until: 12:01 a.m. CT Friday, April 14
This study will be presented at the place-based component of the 2023 Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association.
Session: Minding the Gap in Accountability Policy Implementation
Date/Time: Friday, April 14, 2:50 p.m. – 4:20 p.m. CT
Main Findings:
Under Michigan’s “Read by Grade ...
The ACMG publishes statement on clinical, technical and environmental biases influencing equitable access to clinical genetics/genomics testing
2023-04-14
With the goal of fostering awareness and identifying strategies to reduce bias within the medical genetics field and to improve health equity, members of the ACMG’s Social, Ethical and Legal Issues (SELI) and Diversity, Equity and Inclusion (DEI) Committees collaborated to address factors in which bias can occur in clinical genetic testing in a just-published statement, “Clinical, technical, and environmental biases influencing equitable access to clinical genetics/genomics testing: A points to consider statement of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG)”.
This is the first joint statement of the ACMG’s ...
Improving community outreach and engagement
2023-04-14
As researchers continue to make advances in new cancer prevention and treatment methods, it will not have much impact if the community is unaware and not engaged. For this reason, community outreach and engagement (COE) efforts are an important pillar of the University of Cincinnati Cancer Center’s mission.
Cancer Center researchers will present research abstracts on several COE initiatives at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2023, held in Orlando, Florida, April 14-19.
Encouraging ...
Healing the unhealable: New approach helps bones mend themselves
2023-04-14
Young babies and newborn mice can naturally heal damage to the bones that form the top of the skull, but this ability is lost in adults. In a new study published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, University of Pittsburgh researchers developed a novel approach that promoted bone regeneration in mice without implantation of bone tissue or biomaterials.
The technique uses a device similar to an orthodontic wire used to realign teeth to carefully stretch the skull along its sutures, activating ...
Scientists narrow down pool of potential height genes
2023-04-14
When it comes to height, our fate is sealed along with our growth plates—cartilage near the ends of bones that hardens as a child develops. Research publishing April 14 in the journal Cell Genomics shows that cells in these plates determine the length and shape of our bones and can hint at our stature. The study identified potential "height genes" and found that genetic changes affecting cartilage cell maturation may strongly influence adult height.
"The study is really understanding ...
Finding the dream team to beat the heat
2023-04-14
Associate Professor Jonathan Boreyko leads a team at Virginia Tech that has built a strong portfolio of work with ice and water, exploring the possibilities for de-icing planes, building novel water harvesting devices, and creating snow globes out of bubbles. This familiarity with water has given the team a strong sense of its behavior in different states, leading to a new project that shows how ice quenches heat in comparison to water. The findings were published in Chem on April 14.
Mojtaba Edalatpour and master’s student Camryn ...
Analysis of health and prescription data suggests chronic health conditions in U.S. incarcerated people may be severely undertreated
2023-04-14
Chronic conditions such as type 2 diabetes, asthma, HIV infection, and mental illness may be greatly undertreated in the U.S. jail and prison population, suggests a new study from researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
For their analysis, the researchers used national health survey data covering 2018 to 2020 to estimate rates of chronic conditions among recently incarcerated people, and a commercial prescription database to estimate the distribution of medication treatments to the jail and prison population. Their analysis suggests ...
In-person vs virtual education and community COVID-19 case incidence following school re-openings
2023-04-14
About The Study: In a study of matched pairs of counties that reopened with in-person versus virtual instruction at the secondary school level in the 2020 to 2021 academic year, counties with in-person school instructional models early in the COVID-19 pandemic experienced increases in county-level COVID-19 incidence at six and eight weeks after in-person reopening, compared with counties with virtual instructional models.
Authors: Meredith Matone, Dr.P.H., of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The ...
Black representation in the primary care physician workforce and its association with population life expectancy
2023-04-14
About The Study: The findings of this study of survival outcomes for 1,618 U.S. counties suggest that greater representation of Black primary care physicians (PCPs) in the PCP workforce is associated with improved survival-related outcomes for Black individuals, although there was a dearth of U.S. counties with at least one Black PCP during each study time point. Investments to build a more representative PCP workforce nationally may be important for improving population health.
Authors: John E. Snyder, M.D., M.S., M.P.H., and Rachel D. Upton, Ph.D., of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services in Rockville, Maryland, are the corresponding ...
Racial, ethnic differences in barriers faced by medical college admission test examinees
2023-04-14
About The Study: In this study of 81,755 Medical College Admission Test examinees, American Indian or Alaska Native, Black, and Hispanic students reported lower parental educational levels, greater educational and financial barriers, and greater discouragement from pre-health advisers than white students. These barriers may deter groups underrepresented in medicine from applying to and matriculating at medical school.
Authors: Jessica Faiz, M.D., M.S.H.P.M., of the Veterans Affairs Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System and UCLA in Los Angeles, is the corresponding ...
Calling AI experts! Join the hunt for exoplanets
2023-04-14
Artificial Intelligence (AI) experts have been challenged to help a new space mission to investigate Earth’s place in the universe.
The Ariel Data Challenge 2023, which launches on 14 April, is inviting AI and machine learning experts from industry and academia to help astronomers understand planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets.
Dr Ingo Waldmann, Associate Professor in Astrophysics, UCL (University College London) and Ariel Data Challenge lead said:
“AI has revolutionised many fields of science and industry in the past years. The field of exoplanets has fully arrived in the era of big-data and cutting edge AI is needed to break ...
Estonian researchers developed a method for instant energy-performance label
2023-04-14
The researchers of the FinEst Centre for Smart Cities of Tallinn University of Technology (Estonia, Europe) developed the DigiAudit platform to monitor and analyse energy use and indoor climate indicators of buildings and large real estate portfolios in real time. Thinnect, an Estonian IoT start-up company, will help sell the solution and market it worldwide.
We can only reach zero-emission buildings when we have reliable data
The European Union has set a target for all buildings to be zero-emission, or near-zero energy, by 2050. However, there is no reliable data on the energy consumption of many buildings, so it is not possible to monitor the condition ...
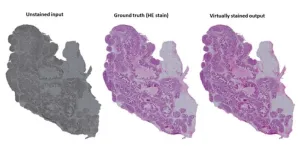
Researchers developed an AI-based method to replace chemical staining of tissue
2023-04-14
Researchers from the University of Eastern Finland, the University of Turku, and Tampere University have developed an artificial intelligence-based method for virtual staining of histopathological tissue samples as a part of the Nordic ABCAP consortium. Chemical staining has been the cornerstone of studying histopathology for more than a century and is widely applied in, for example, cancer diagnostics.
“Chemical staining makes the morphology of the almost transparent, low-contrast tissue sections visible. Without it, analysing tissue morphology is almost impossible for human vision. Chemical staining is irreversible, and in most ...
Rescuing corneal cells from death with the help of mitochondria
2023-04-14
Québec City, April 14, 2023 - Fuchs' endothelial corneal dystrophy, a degenerative eye disease, causes progressive vision loss that can induce blindness. It is the leading cause of corneal transplantation, but the scarcity of grafts hinders its treatment. A research team from Université Laval and Université de Montréal has identified a way to slow the disease and even avoid transplantation if diagnosed at an early stage.
In people with the disease, the endothelial cells at the back of the cornea die more quickly than in healthy people. "Everyone loses them at a slow rate, slow enough to make it to the end of our lives ...
New specimens and species of the Oligocene toothed baleen whale Coronodon from South Carolina and the origin of Neoceti
2023-04-14
A new study published in the journal PeerJ by Robert W. Boessenecker (CofC), Brian L. Beatty (NYIT), and Jonathan H. Geisler (NYIT) reports a wealth of new fossils of the early toothed baleen whale Coronodon from Oligocene (23-30 million years old) rock layers near Charleston, South Carolina. These include five new skulls, representing two new species: Coronodon planifrons and Coronodon newtonorum, and young juveniles of Coronodon havensteini – first named from a single skull by this team in 2017. Coronodon is one of the most primitive members ...
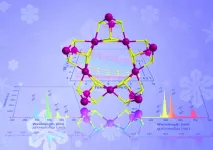
New family of wheel-like metallic clusters exhibit unique properties
2023-04-14
While the wheel does not need to be reinvented, there are benefits to the development of new nano-wheels, according to a multi-institute research team based in China. The group fabricated a novel family of metallic compounds, each of which exhibit unique properties desirable for next-generation technologies, such as advanced sensors.
Their findings were made available online on March 12 in Polyoxometalates.
“Polymetallic complexes are of great interest not only for their appealing molecular structure but also ...
[1] ... [1981]
[1982]
[1983]
[1984]
[1985]
[1986]
[1987]
[1988]
1989
[1990]
[1991]
[1992]
[1993]
[1994]
[1995]
[1996]
[1997]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.