STEMM opportunity alliance announces more than 100 partners
2023-04-19
Washington, D.C. – The STEMM Opportunity Alliance (SOA), a national effort galvanizing stakeholders to achieve equity and excellence in science, technology, engineering, mathematics, and medicine (STEMM) by 2050, announced a milestone of more than 100 partners since its launch at the White House Summit on STEMM Equity and Excellence in December 2022.
Some highlights from SOA’s newest partners and their commitments include:
Johnson & Johnson will continue growing multiple projects ...
Model that uses machine learning methods and patient data at hospital arrival predicts strokes more accurately than current system
2023-04-19
Stroke is among the most dangerous and commonly misdiagnosed medical conditions. Black and Hispanic people, women, older people on Medicare, and people in rural areas are less likely to be diagnosed in time for treatment to be effective. In a new study, researchers used machine learning methods and data available when patients enter the hospital to develop a model that predicts strokes with more accuracy than current models.
The study, by researchers at Carnegie Mellon University (CMU), Florida International University (FIU), and Santa Clara University (SCU), appears in the Journal of Medical Internet ...
Organic beekeeping rivals conventional methods for bee health, productivity
2023-04-19
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Honey bee colonies managed using organic methods were as healthy and productive as those managed in conventional systems, while avoiding the use of synthetic pesticides to control pests and pathogens inside the hive, according to newly published research led by Penn State entomologists.
The researchers said they believe that their study, which compared the performance of honey bees under three types of management systems, is the first to show that organic beekeeping management is sustainable and supports high honey-bee survival and honey production.
The methods beekeepers use to manage honey ...
Tribal water rights underutilized in U.S. West
2023-04-19
A new North Carolina State University study shows that Indigenous groups in the western United States are – for various reasons – having difficulty turning water they have a legal right to, under water rights settlements, into actual water that can generate revenue through leases to other groups or through direct uses such as agriculture.
Western tribal water rights are a longstanding, yet underpublicized, component of a large and seemingly intractable problem: how to satisfy all water-rights holders when available ...
Stronger paper bags, reused repeatedly then recycled for biofuel could be future
2023-04-19
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — As the world searches for ways to reduce the use of plastics such as single-use plastic bags, a novel study by Penn State researchers demonstrates a process to make paper bags stronger — especially when they get wet — to make them a more viable alternative.
The study suggests a process for creating paper bags durable enough to be used multiple times and then broken down chemically by an alkaline treatment to be used as a source for biofuel production, according to researcher Daniel Ciolkosz, associate ...
NSF grant to investigate the role of macrobiota in carbon cycling in estuaries
2023-04-19
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A Penn State-led interdisciplinary team of researchers across six institutions was awarded a $3.5 million grant from the National Science Foundation to investigate the role that macrobiota, such as clams, salt marshes and seagrasses, play in carbon cycling in estuaries.
“Estuaries are highly productive and diverse ecosystems and hence deserve study in their own right,” said Raymond Najjar, professor of oceanography and lead investigator on the project. “But estuaries ...
New blue light technique could enable advances in understanding nanoscale technologies
2023-04-19
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — With a new microscopy technique that uses blue light to measure electrons in semiconductors and other nanoscale materials, a team of Brown University researchers is opening a new realm of possibilities in the study of these critical components, which can help power devices like mobile phones and laptops.
The findings are a first in nanoscale imaging and provide a workaround to a longstanding problem that has greatly limited the study of key phenomena in a wide variety of materials that could one day lead to more energy-efficient semiconductors and electronics. ...
Study finds that child victims of violence face long-term psychological effects
2023-04-19
A study of young adults who were victims of violent injuries as children found significantly higher levels of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in this group than the general population.
The study – conducted by University of Rochester Medical Center (URMC) researchers – surveyed 24 respondents who were victims of gunshot, stab, or assault wounds as children between the years of 2011 and 2020. Of the participants, 15 suffered a gunshot wound, eight suffered a stab wound, and one was assaulted. Respondents were primarily teenagers at the time of injury, with a median age of 16.6 years. An average of six years had passed from the initial injury to the time ...
Association for Chemoreception Sciences (AChemS) 45th Annual Meeting
2023-04-19
Bonita Springs, FL— Smell, taste, and chemesthesis are vital chemical senses that contribute to the multidimensional sensation of flavor. Together with other sensory inputs, they allow us to enjoy eating and drinking. Understanding the fundamental mechanisms underlying these sensations is a primary focus of the annual conference of the Association for the Chemoreception Sciences, AChemS XLV. Other key areas include factors that modulate these mechanisms and their impact on fundamental behavior in a wide array of species. Attendees and members of AChemS are leading scientific and biomedical researchers dedicated to better understanding the function ...
As pandemic prison populations fell, proportion of Black prisoners rose
2023-04-19
New Haven, Conn. — The U.S. prison population plummeted during the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic but the percentage of incarcerated Black people rose, according to a new analysis of prison data published April 19 in the journal Nature.
The higher percentage of incarcerated Black people by mid-2020 was found in almost all states, and temporarily reversed a decades-long decrease in the percentage of Black people in the national prison population, researchers from Yale and Northeastern Universities and the Santa Fe Institute found.
While several factors contributed to the increase in percentage of incarcerated Black people during the height of the pandemic, researchers ...
Cannabis exposures in suspected suicide attempts are on the rise
2023-04-19
VANCOUVER, Wash. – Suspected suicidal cannabis exposures have increased 17% annually, over a period of 12 years, according to a Washington State University-led analysis of U.S. poison center data.
The vast majority of the attempts, more than 92%, involved other substances in addition to cannabis, and the data cannot show a direct causal link between cannabis and suicide attempts. Still, the findings are cause for concern, the researchers said, especially since the increase was more pronounced among children and women ...
Mind-body connection is built into brain, study suggests
2023-04-19
Calm body, calm mind, say the practitioners of mindfulness. A new study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis indicates that the idea that the body and mind are inextricably intertwined is more than just an abstraction. The study shows that parts of the brain area that control movement are plugged into networks involved in thinking and planning, and in control of involuntary bodily functions such as blood pressure and heartbeat. The findings represent a literal linkage of body and mind ...
Race, ethnicity–adjusted age recommendation for initiating breast cancer screening
2023-04-19
About The Study: This study of 415,000 breast cancer deaths in female patients in the U.S. from 2011 to 2020 provides evidence-based race-adapted starting ages for breast cancer screening. The findings suggest that health policy makers and clinicians could consider an alternative, race and ethnicity–adapted approach in which Black female patients start screening earlier.
Authors: Mahdi Fallah, M.D., Ph.D., of the German Cancer Research Center in Heidelberg, Germany, and Tianhui Chen, M.D., Ph.D., of the Zhejiang Cancer Hospital in Hangzhou, China, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Cognitive function in people with familial risk of depression
2023-04-19
About The Study: Depression in prior generations was associated with lower cognitive performance in offspring, whether assessed by family history or genetic data. There are opportunities to generate hypotheses about how this arises through genetic and environmental determinants, moderators of brain development and brain aging, and potentially modifiable social and lifestyle factors across the life span.
Authors: Breda Cullen, Ph.D., of the University of Glasgow in Glasgow, United Kingdom, is the corresponding author.
To ...
Nature publication on loops, flags and tension in DNA
2023-04-19
1 Cohesin loops DNA
It has been known for more than a century that the long DNA strands in cell nuclei are neatly folded into the characteristic shape of chromosomes, resembling bottlebrushes , in preparation for cell division. And also between divisions, chromosomes are organised into loops that are important for regulating the processing genetic information. In 2018, Dekker and his group were the first to visualise how SMC protein complexes such as condensin and cohesin extrude loops in DNA.
#2 CTCF flags have a direction and determine where a ...
Nature-study reveals new mechanism for DNA folding
2023-04-19
A hitherto unknown mechanism for DNA folding is described in a study in Nature published by researchers from Karolinska Institutet and the Max Planck Institute for Biophysics. Their findings provide new insights into chromosomal processes that are vital to both normal development and to prevent disease.
The DNA in our cells is organised into chromosomes, which are highly dynamic structures that are altered when genes are transcribed, when DNA damage is repaired or when chromosomes are compacte in preparation for cell division. These processes are affected by so called SMC protein complexes (SMC, Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes), which by mediating chromosomal interactions ...
New findings pave the way for stable organic solar cells that may enable cheap and renewable electricity generation
2023-04-19
Due to the recent improvements in the efficiency with which solar cells made from organic (carbon-based) semiconductors can convert sunlight into electricity, improving the long-term stability of these photovoltaic devices is becoming an increasingly important topic. Real-world applications of the technology demand that the efficiency of the photovoltaic device be maintained for many years. To address this key problem, researchers have studied the degradation mechanisms for the two components used in the light-absorbing layer of organic solar cells: the ‘electron donor’ and ‘electron ...
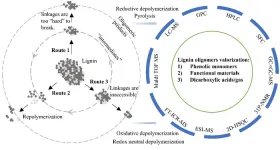
Perspective on oligomeric products from lignin depolymerization: their generation, identification, and further valorization
2023-04-19
Lignin depolymerization is playing a pivotal role in transforming the second most abundant biopolymers in nature into many valuable chemicals/fuels. This route could directly replace their petrol-based equivalents and therefore a great pathway to fight climate change and contribute to future sustainability. Interpretation of the reaction pathways is always desired to gain an insightful mechanic view in understanding the depolymerization chemistry and also paving new paths for lignin valorization at the industrial scale. However, such interpretation heavily relies on the state-of-art analytical capability since ...
UVA launches ambitious effort to reduce health disparities
2023-04-19
The University of Virginia School of Medicine has launched a new Center for Health Equity and Precision Public Health to improve the health and well-being of rural residents, the economically challenged and minority groups across Virginia and beyond.
The center will bring to bear expertise from across UVA to tackle many of today’s greatest public health issues. The goal: reduce health disparities and promote health equity to help people live longer, healthier lives.
“The pandemic has really taught us that, one, our public health infrastructure is not nearly as strong as it should be. And, two, we can't ...
Wonder drug-capsule may one day replace insulin injection for diabetics
2023-04-19
Scientists in Melbourne have designed a new type of oral capsule that could mean pain-free delivery of insulin and other protein drugs.
Co-lead researcher Professor Charlotte Conn, a biophysical chemist from RMIT University, said protein drugs had proven challenging to deliver orally as the drugs degrade very quickly in the stomach – until now.
“These types of drugs are typically administered with an injection – thousands of diabetics in Australia need insulin injections up to several times a day, which can be unpleasant for the patient and results in high healthcare costs,” said Conn, from RMIT’s School of Science.
She said the new technology could also be ...
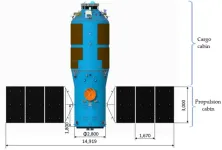
Scientists reviewed the research and development of Tianzhou cargo spacecraft
2023-04-19
Cargo spacecraft is robotic spacecraft designed to support space station operation by transporting food, propellant and other supplies. Tianzhou cargo spacecraft (The abbreviation is TZ) is a Chinese automated cargo spacecraft developed by the China Academy of Space Technology, as part of China's manned space Station program. The China Academy of Space Technology began to design TZ in 2010. Its main tasks are transporting and storing supplies for the space station, storing and descending waste materials for the space ...
SwRI launches the Global Decarbonized Mobility Summit Nov. 13-17
2023-04-19
SAN ANTONIO – 4.19.23 —Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) will host the inaugural Global Decarbonized Mobility Summit (GDMS) on Nov. 13-17. The multi-day summit will bring together key stakeholders in the transportation industry to discuss technology challenges associated with sustainable decarbonized mobility solutions for on-and-off-road applications.
The GDMS will assemble industry members from SwRI’s many automotive-related consortia and joint industry projects at its San Antonio headquarters. Throughout the summit, SwRI staff experts will hold sessions on the latest research and development advancements, pathways ...
Nebraska-led study first to define anxiety spiraling from national election
2023-04-19
Researchers are beginning to better understand the toll of polarized politics on mental and physical health, and a new study suggests that Americans’ political anxiety crescendos before a major election.
Led by University of Nebraska–Lincoln political scientist Kevin Smith, with Aaron Weinschenk of the University of Wisconsin–Green Bay and Costas Panagopoulos of Northeastern University, the study is the first to examine anxiety tethered to a specific political event — the 2020 presidential election, touted by both sides as the ...
A second chance for a healthy heart
2023-04-19
A recent study using mice has revealed a way to turn back the clock after heart attack. The researchers behind the work used RNAs to instruct cells in an injured heart to eliminate scar tissue and recreate cardiac muscle, allowing the heart to function like new again.
Cardiovascular disease, including heart attack, is the leading cause of death worldwide.
“Adult human hearts are not very good at repairing themselves,” said Conrad Hodgkinson, an associate professor of medicine and pathology at Duke University School of Medicine who oversaw the study. “Once they have a heart attack or any type of damage, ...
Study explores prosocial behavior within, between religious groups
2023-04-19
Does a commitment to one’s God facilitate altruistic behavior that benefits only members of the same religious group? Or does it extend to helping members of a different religion?
University of Illinois Chicago social psychologist Michael Pasek and colleagues examined this question through field and online experiments involving more than 4,700 people from diverse ethnoreligious populations in three political and cultural contexts.
Christians, Muslims, Hindus and Jews in the Middle East, Fiji and the United ...
[1] ... [1971]
[1972]
[1973]
[1974]
[1975]
[1976]
[1977]
[1978]
1979
[1980]
[1981]
[1982]
[1983]
[1984]
[1985]
[1986]
[1987]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.