Quantum random number generator sets benchmark for size, performance
2021-06-29
WASHINGTON, June 29, 2021 -- As pervasive as they are in everyday uses, like encryption and security, randomly generated digital numbers are seldom truly random.
So far, only bulky, relatively slow quantum random number generators (QRNGs) can achieve levels of randomness on par with the basic laws of quantum physics, but researchers are looking to make these devices faster and more portable.
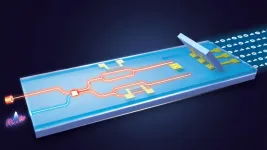
In Applied Physics Letters, by AIP Publishing, scientists from China present the fastest real-time QRNG to date to make the devices quicker and more portable. The ...
Patients with acute myocarditis following mRNA COVID-19 vaccination
2021-06-29
What The Study Did: This study describes four patients who presented with acute myocarditis after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination.
Authors: Raymond J. Kim, M.D., of the Duke Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Center in Durham, North Carolina, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2021.2828)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the articles for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflicts of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: ...
Myocarditis Following Immunization With mRNA COVID-19 vaccines in members of US military
2021-06-29
What The Study Did: Researchers describe myocarditis presenting after COVID-19 mRNA vaccination in 23 patients within the Military Health System.
Authors: Jay Montgomery, M.D., of Walter Reed National Military Medical Center in Bethesda, Maryland, and Margaret Ryan, M.D., M.P.H., of the Naval Medical Center San Diego, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2021.2833)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the articles for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflicts of interest and financial disclosures, and funding ...
Selection tool accurately predicts ovarian damage in girls with cancer
2021-06-29
This press release is in support of a presentation by Dr Ruth Howie presented online at the 37th Annual Meeting of ESHRE.
29 June 2021: Cancer treatments can cause premature ovarian failure (POI) including in girls who want to become mothers eventually. Ovarian tissue cryopreservation (OTC) provides a future fertility option but is invasive, has risks and evidence indicates that most girls don't develop POI. So, doctors face the dilemma of how to offer OTC appropriately.
Now, an assessment tool has been found to help predict correctly which female cancer patients aged under 18 years will develop POI and should therefore be offered OTC. Results from a long-term follow-up study of 423 girls and young women show nearly a quarter (24%; n = 9) of the 37 assessed as high ...
Pretreating nuisance green algae with lye, urea increases bacterial production of biogas
2021-06-29
WASHINGTON, June 29, 2021 - For more than 60 years, algae have been studied as a potential feedstock for biofuel production, but the cellulose in their cell wall makes it hard to access the critical molecules inside and convert them to biogas.
In the Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, from AIP Publishing, an international research team reports their success in using urea and sodium hydroxide (NaOH, commonly known as lye or caustic soda) as a pretreatment of algae, which breaks down cellulose and more than doubles biogas production under their initial experimental conditions.
"We were ...
Cancer neuroscientists identify a key culprit behind pediatric brain cancer's spread
2021-06-29
With advances in medical science driving progress against childhood brain tumors, today three out of four young patients survive at least five years beyond diagnosis. However, the outcomes look grim when malignant cells spread, or metastasize.
Such is the case with medulloblastoma, a type of brain cancer that arises in the cerebellum, at the back of the head. Although rare in absolute terms -- about 350 cases emerge each year, 60 percent of them in children -- medulloblastoma is the most common and deadliest form of pediatric brain cancer. Metastasis ...
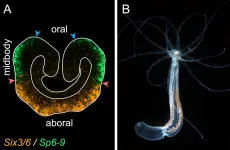
The evolution of axial patterning
2021-06-29
In a new article in Nature Communications, a research group led by Grigory Genikhovich at the University of Vienna has found that the way the main body axis of sea anemones is patterned by different intensities of β-catenin signaling is similar to that of sea urchins and vertebrates. This suggests that this axial patterning mechanism already existed about 650 million years ago.
The positioning of all anatomical structures in an embryo is determined by systems of molecular coordinates, which are called body axes. Different regulatory genes are activated at specific locations along the body axes to drive the development of all body parts in correct places.
This process is very ...
Cell biology -- Masters of synapse modulation
2021-06-29
Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich researchers have shown how RNA-binding proteins modulate synaptic responses that mediate the transmission of nerve cell impulses.
Cells in the central nervous system possess a high degree of flexibility, which enables them to adapt to fluctuating demands and respond to changing patterns of neuronal activity. This is achieved by modulating the connections between nerve cells, which are mediated by structures called synapses that determine how neighboring neurons respond to stimulation. These adjustments in turn require the intracellular transport of mRNAs. Consequently, the required proteins ...
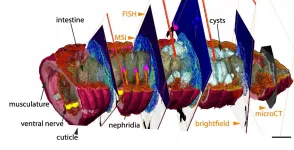
The earthworm in new light
2021-06-29
Earthworms experience constant chemical interactions with bacteria, fungi, plants and small invertebrates across soil ecosystems. Even within their tissues, earthworms harbor symbiotic microbes and small animal parasites that trigger internal metabolic responses such as innate immunity. To reveal the fundamental processes that enable animal-microbe symbioses to form and persist, we have to study their metabolic interactions in situ. By combining novel imaging techniques, a team of researchers around Benedikt Geier from the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology ...
New components for antisense gene therapy show promise in treating spinal muscular atrophy
2021-06-29
Skoltech researchers and their colleagues from Russia and the UK investigated the safety and efficacy of new chemistry in antisense oligonucleotides used to treat spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), a debilitating genetic disease. Their results may lead to the development of drugs with less toxicity and fewer injections needed thanks to prolonged action. The paper was published in the journal Nucleic Acid Therapeutics.
Antisense oligonucleotides are single stranded chemically modified fragments of DNA that target pre-messenger RNA, short bits of genetic information a ribosome reads to make a protein. Depending on how a particular antisense oligonucleotide works, the target mRNA can either be destroyed or undergo subtle changes in how it's spliced, i.e. how exons, the ...
Scientists discover new type of quasiparticle
2021-06-29
Russian scientists have experimentally proved the existence of a new type of quasiparticle - previously unknown excitations of coupled pairs of photons in qubit chains. This discovery could be a step towards disorder-robust quantum metamaterials. The study was published in Physical Review B.
Superconducting qubits are a leading qubit modality today that is currently being pursued by industry and academia for quantum computing applications. However, the performance of quantum computers is largely affected by decoherence that contributes to a qubits extremely short lifespan and causes computational errors. Another ...
Microbes feast on crushed rock in subglacial lakes beneath Antarctica
2021-06-29
Pioneering research has revealed the erosion of ancient sediments found deep beneath Antarctic ice could be a vital and previously unknown source of nutrients and energy for abundant microbial life.
The study, led by the University of Bristol and published today in Nature's Communications Earth & Environment journal, sheds new light on the many compounds supporting various microbes which form part of a huge subglacial ecosystem.
Lead author Dr Beatriz Gill Olivas, a Post-Doctoral Research Associate at the University of Bristol, said: "Although the study focused on samples obtained from a single ...
Scientists observe the dynamics behind the exceptional summer 2020 Yangtze River rainfall seasonal projections
2021-06-29
During summer 2020, the Yangtze River basin experienced persistent, record-breaking meiyu rainfall. Likewise, the region suffered from severe flooding and water damage as accumulated rainfall broke records dating back to 1954. Regions outside the meiyu rain belt received significant summer rainfall as well, including Beijing, located in northeastern China.
Typically, an above average meiyu rainfall season follows a strong El Niño during the previous winter. However, summer 2020 followed a neutral El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) event. Therefore, scientists are working ...
How environmental factors could provide for a young brain
2021-06-29
A stimulating environment keeps the "hippocampus" - which is the brain's memory control center - young, so to speak. Causes of this are molecular mechanisms that affect gene regulation. These current findings from studies in mice provide clues as to why an active, varied life can help preserve mental fitness in old age. Researchers from the DZNE and the Center for Regenerative Therapies Dresden (CRTD) at the Technische Universität Dresden report on this in the journal Nature Communications.
Human DNA - and this also applies to mice - contains thousands of genes. However, it is not only the genetic blueprint that is decisive for the function of a cell and whether it is healthy or not, but above all which genes can be switched on or off. ...
83% of the Spanish population trusts in vaccination against COVID, 25 points more than in January
2021-06-29
FECYT - Spanish Foundation for Science and Technology - presented today at the headquarters of the National Museum of Science and Technology, MUNCYT, IN Alcobendas, the results of the third Social Perception Survey of scientific aspects of the COVID-19 in a debate moderated by Pampa García Molina, Editor-in-Chief of the SINC Agency, in which Raquel Yotti, Director of the Carlos III Health Institute of Madrid, Josep Lobera, Professor of Sociology at the Universidad Autónoma de Madrid (UAM) and scientific director of the Social Perception Survey on the scientific aspects of COVID-19 and ...
Through the nano hole: lego technique reveals the physics of DNA transport through nanopores
2021-06-29
Polymers are long, chain-like molecules which are everywhere in biology. DNA and RNA are polymers formed by many consecutive copies of nucleotides coupled together. When being transported within or between cells, these biological polymers must pass through nanometre-sized holes called "nanopores".
This process also underlies a rapidly developing method for analysing and sequencing DNA called nanopore sensing.
The study, published in the journal END ...
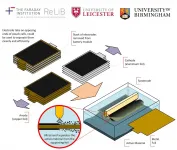
Leicester expert leads ground breaking invention on battery recycling
2021-06-29
Researchers at the University of Leicester have developed a new method to recycle electric vehicle batteries using a ground-breaking new approach that many will have experienced in the dentist's chair.
The Faraday Institution project on the recycling of lithium-ion batteries (ReLiB) led by Professor Andy Abbott at the University of Leicester used a new method, involving ultrasonic waves, to solve a critical challenge: how to separate out valuable materials from electrodes so that the materials can be fully recovered from batteries at the end of their life.
Current recycling ...
New corona mass test up to 100 times more sensitive than rapid antigen tests
2021-06-29
A new corona test developed at the University Hospital Bonn can analyze a large number of swabs simultaneously using sequencing technology and has a similarly high sensitivity as the common qPCR test. The innovative method offers great potential, especially for systematic testing in daycare centers, schools or companies. Today, the results of the study on the new Corona test have been published in the renowned journal "Nature Biotechnology".
Bonn, 6/29/2021 - In addition to vaccination, systematic testing of the population remains of central importance in order to effectively monitor and contain the spread of infections during the Coronavirus pandemic. Only in this way can the spread of the virus be effectively monitored and ...
This crystal impurity is sheer perfection
2021-06-29
Crystallization is one of the most fundamental processes found in nature - and it's what gives minerals, gems, metals, and even proteins their structure.
In the past couple of decades, scientists have tried to uncover how natural crystals self-assemble and grow - and their pioneering work has led to some exciting new technologies - from the quantum dots behind colorful QLED TV displays, to peptoids, a protein-mimic that has inspired dozens of biotech breakthroughs.
Now, a research team led by scientists at the Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and UC Berkeley has developed a nanoparticle composite that grows ...
Stretching changes the electronic properties of graphene
2021-06-29
The electronic properties of graphene can be specifically modified by stretching the material evenly, say researchers at the University of Basel. These results open the door to the development of new types of electronic components.
Graphene consists of a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice. The material is very flexible and has excellent electronic properties, making it attractive for numerous applications - electronic components in particular.
Researchers led by Professor Christian Schönenberger at the Swiss Nanoscience Institute and the Department of Physics at the University of Basel have now studied how the material's ...
Sustainable mining of raw materials from thermal springs in Chile
2021-06-29
Mineral resources from Chile are of great importance to Germany. According to statistics from the World Bank, thousands of tons of valuable minerals are imported from the South American country every year, including raw materials for lithium-ion batteries. But their extraction causes ecological and social problems: "The use of the limited freshwater resources in northern Chile for mining regularly fuels conflicts with the local population," says Professor Thomas Kohl from KIT's Institute of Applied Geosciences (AGW). "Northern Chile is one of the driest regions on earth, but has extensive geothermal resources. With a novel type of plant, it is not only possible to generate electricity in a climate-friendly way, but also to extract ...
Scientists mine the rich seam of body wearable motion sensors
2021-06-29
When positioned strategically, garment seams sewn with conductive yarn can be used to accurately track body motion, according to computer scientists at the University of Bath in the UK. Best of all, these charged seams are able to respond to subtle movements that aren't picked up by popular fitness trackers, such as watches and wristbands.
In a new study, the Bath researchers found that clothing made with conductive seams can be analysed to identify the wearer's movements.
PhD student Olivia Ruston, who presented the work at the ACM Designing Interactive Systems conference this month, said: "There are lots of potential applications for conductive yarn in any activity where you want to identify and improve ...
'The focea': A region of improved vision in mice.
2021-06-29
Mice are an important animal model of human vision due to the powerful genetic tools available in this species. However, mouse vision was thought to be different to that of humans because humans have a region of the retina specialized for fine details called the 'fovea' whereas mice do not. Researchers from the Netherlands Institute of Neuroscience (NIN) have shown that the visual cortex of mice does contain a region of enhanced visual sensitivity dubbed the 'focea', making the mouse a better model of human vision than previously expected. The findings were published ...
Clinic mandates surgical simulation training after research indicates improved performance
2021-06-29
Lithia, Florida -- June 29, 2021 -- Surgical resident training has traditionally occurred in a master-apprentice-type relationship, with graduated responsibilities until trainees are expected to perform procedures on their own. Given recent changes in the health care system, including reduced operating room time, increased difficulty of procedures and working hour restrictions, there is less time for residents to learn using traditional methods.
Researchers from the University of Manitoba and the Pan Am Clinic recently published a paper in the journal Arthroscopy, Sports Medicine, ...
Playing wind instruments generates less aerosol than vocalization, COVID-19 study finds
2021-06-29
Aerosol generated by playing woodwind and brass instruments is less than that produced when vocalising (speaking and singing) and is no different than a person breathing, new research has found. The findings, published online in the journal Aerosol Science and Technology, could be crucial to developing a roadmap for lifting COVID-19 restrictions in the performing arts, which have been significantly restricted since the start of the pandemic.
The research project, known as PERFORM (ParticulatE Respiratory Matter to InForm Guidance for the Safe Distancing of PerfOrmeRs in a COVID-19 PandeMic), was supported by Public Health England, the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport (DCMS), and UKRI and was carried out by a collaborative team from ...
[1] ... [2180]
[2181]
[2182]
[2183]
[2184]
[2185]
[2186]
[2187]
2188
[2189]
[2190]
[2191]
[2192]
[2193]
[2194]
[2195]
[2196]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.