Covid-19 mask study finds layering, material choice matter
2021-04-02
Wearing a face mask can protect yourself and others from Covid-19, but the type of material and how many fabric layers used can significantly affect exposure risk, finds a study from the Georgia Institute of Technology.
The study measured the filtration efficiency of submicron particles passing through a variety of different materials. For comparison, a human hair is about 50 microns in diameter while 1 millimeter is 1,000 microns in size.
"A submicron particle can stay in the air for hours and days, depending on the ventilation, so if you have a room that is not ventilated or poorly ventilated then these small particles can stay there for a very long period of time," said Nga Lee (Sally) Ng, associate professor and Tanner Faculty Fellow in the School of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering ...
Significant decline in subarachnoid hemorrhage hospitalizations due to COVID-19
2021-04-02
New research led by investigators from Boston Medical Center and Grady Memorial Hospital demonstrates the significant decline in hospitalizations for neurological emergencies during the COVID-19 pandemic. The rate of Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) - bleeding in the space between the brain and the tissue covering the brain - hospitalizations declined 22.5 percent during the study period, which is consistent with the other reported decreases in emergencies such as stroke or heart attacks.
Published in Stroke & Vascular Neurology, the study compares subarachnoid hemorrhage hospital admissions for the months following throughout the initial COVID surge, in hospitals that bore ...
COVID-19 patients can be categorized into three groups
2021-04-02
In a new study, researchers identify three clinical COVID-19 phenotypes, reflecting patient populations with different comorbidities, complications and clinical outcomes. The three phenotypes are described in a paper published this week in the open-access journal PLOS ONE 1st authors Elizabeth Lusczek and Nicholas Ingraham of University of Minnesota Medical School, US, and colleagues.
COVID-19 has infected more than 18 million people and led to more than 700,000 deaths around the world. Emergency department presentation varies widely, suggesting that distinct clinical phenotypes exist and, importantly, that these distinct phenotypic presentations may respond differently ...
Serving size, satisfaction influence food waste on campus
2021-04-02
HOUSTON - (April 2, 2021) - Understanding what drives food choices can help high-volume food service operations like universities reduce waste, according to a new study.
Researchers have concluded that food waste in places like university cafeterias is driven by how much people put on their plates, how familiar they are with what's on the menu and how much they like - or don't like - what they're served.
Food waste has been studied often in households, but not so often in institutional settings like university dining commons. What drives food choices in these "all-you-care-to-eat" facilities is different because diners don't perceive personal financial penalty if they leave food on their plates.
Published in the journal Foods, "Food Choice and Waste in University Dining Commons ...
Novel cancer vaccine targets oncogenes known to evade immunity in melanoma and neuroblastoma models
2021-04-02
A personalized tumor cell vaccine strategy targeting Myc oncogenes combined with checkpoint therapy creates an effective immune response that bypasses antigen selection and immune privilege, according to a pre-clinical study for neuroblastoma and melanoma. The neuroblastoma model showed a 75% cure with long-term survival, researchers at Children's National Hospital found.
Myc is a family of regulator genes and proto-oncogenes that help manage cell growth and differentiation in the body. When Myc mutates to an oncogene, it can promote cancer cell growth. The Myc oncogenes are ...
Experimental therapy for parasitic heart disease may also help stop COVID-19
2021-04-02
James McKerrow, MD, PhD, dean of the Skaggs School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences at University of California San Diego, has long studied neglected tropical diseases -- chronic and disabling parasitic infections that primarily affect poor and underserved communities in developing nations. They're called "neglected" because there is little financial incentive for pharmaceutical companies to develop therapies for them.
One of these neglected diseases is Chagas disease, the leading cause of heart failure in Latin America, which is spread by "kissing bugs" carrying the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi. These parasites produce an enzyme called cruzain that helps ...
Unusual mechanism in rare mutation associated with Alzheimer's uncovered
2021-04-02
A novel mechanism has been identified that might explain why a rare mutation is associated with familial Alzheimer's disease in a new study by investigators at the University of Chicago. The paper, published on April 2 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine, characterizes a mutation located in a genetic region that was not previously thought be pathogenic, upending assumptions about what kinds of mutations can be associated with Alzheimer's Disease.
Alzheimer's, a neurodegenerative disease that currently affects more than 6 million Americans, has ...
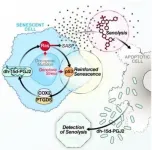
The first non-invasive biomarker to track and verify efficacy of senolytic drugs
2021-04-02
Buck Institute researchers have discovered and are developing a novel, non-invasive biomarker test that can be used to measure and track performance of senolytics: a class of drugs that selectively eliminate senescent cells. The discovery is expected to play a major role in efforts to develop treatments that would battle a myriad of chronic age-related conditions that range from arthritis to lung disease to Alzheimer's disease and glaucoma. This biomarker is a unique signaling lipid metabolite, normally exclusively intracellular, but is released when senescent cells are forced to die. This metabolite is detectible in blood and urine, making non-invasive ...
Dual-bed catalyst enables high conversion of syngas to gasoline-range liquid hydrocarbons
2021-04-02
Gasoline, the primary transportation fuel, contains hydrocarbons with 5-11 carbons (C5-11) and is almost derived from petroleum at present.
Gasoline can also be produced from non-petroleum syngas. Nonetheless, achieving high conversions of syngas to C5-11 with excellent selectivity and stability remains a challenge.
A research group led by Prof. LIU Zhongmin and Prof. ZHU Wenliang from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences realized highly efficient and selective conversion of syngas to gasoline-range liquid hydrocarbons over a dual-bed catalyst.
The study was published in Chem Catalysis on April 2.
This dual-bed catalyst, (CZA +Al2O3)/N-ZSM-5(97), consists ...
Health and academic professionals with dependents at high risk of quitting after COVID-19
2021-04-02
Up to one in five employees at an academic medical institution are considering leaving their professions due to the strains of coping with the pandemic in their own lives, according to a new University of Utah Health study. Individuals who had caregiving responsibilities were among those most likely to contemplate leaving or reducing hours.
The findings suggest that retaining highly trained doctors, nurses, and scientists in the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic could be the next great health care challenge.
"It's sobering to learn that, during a time of economic recession, at least one-fifth of our workforce were considering leaving their jobs because of the severe levels of stress they were experiencing," says Angela Fagerlin, Ph.D., the study's senior author and professor ...
Hidden diversity of coral more important for conservation than previously thought
2021-04-02
SAN FRANCISCO, CA (April 2, 2021) -- In recent years, advancements in DNA sequencing have exposed a large amount of hidden diversity in reef-building corals: species that appear identical to one another but are genetically distinct. Typically ignored as they are invisible to the naked eye, a team of researchers at the California Academy of Sciences and The University of Queensland, along with over a dozen international collaborators, is taking a more holistic approach to understand these hidden species by investigating overlooked ecological differences that have wide-ranging implications for the vulnerability and resilience of reef-building corals. The team hopes that their findings, ...
Experiences of a health system's employees during COVID-19
2021-04-02
What The Study Did: This survey study examined the career development, productivity, childcare needs and likelihood of leaving the workforce among employees at an academic medical center during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Authors: Angela Fagerlin, Ph.D., of the University of Utah in Salt Lake City, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.3997)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding ...
Racial, ethnic differences among children enrolled in HMOs
2021-04-02
What The Study Did: Researchers compared rates of health maintenance organization (HMO) enrollment, by race and ethnicity, for children with commercial and public coverage with the use of national survey data.
Authors: Alon Peltz, M.D., M.B.A., M.H.S., of Harvard Medical School in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.4162)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional ...
US deaths normally change less than 2% each year; in 2020, they rose nearly 23%
2021-04-02
Extended surges in the South and West in the summer and early winter of 2020 resulted in regional increases in excess death rates, both from COVID-19 and from other causes, a 50-state analysis of excess death trends has found. Virginia Commonwealth University researchers' latest study notes that Black Americans had the highest excess death rates per capita of any racial or ethnic group in 2020.
The research, publishing Friday in the Journal of the American Medical Association, offers new data from the last 10 months of 2020 on how many Americans died during 2020 as a result of the effects of the pandemic -- beyond the number of COVID-19 deaths alone -- and which states and racial groups were hit hardest.
The rate of excess deaths -- or deaths above the number that ...
Most US adults who vape want to quit, study finds
2021-04-02
More than 60% of U.S. adults who vape are interested in quitting, according to a study published today in JAMA Network Open by MUSC Hollings Cancer Center researchers. And among those who vape to help them to quit smoking, some are successful while others continue smoking and using electronic cigarettes.
The study, which analyzed longitudinal survey data from more than 30,000 adults across the country, aimed to provide the most up-to-date estimate of how many Americans are interested in stopping their use of e-cigarettes or have made past attempts to quit.
According to the findings, former cigarette smokers had the highest intentions and interest in quitting. This is likely due to an increasing number of smokers using e-cigarettes to transition away from cigarettes, said the study's authors.
While ...
Excess deaths from COVID-19 and other causes in US
2021-04-02
What The Study Did: This study updates an analysis of deaths in the United States in 2020, including deaths due to COVID-19 as well as all other causes.
Authors: Steven H. Woolf, M.D., M.P.H., of the Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine in Richmond, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2021.5199)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other ...
Radicalization to extremist ideologies is often triggered by negative life events
2021-04-02
People who radicalize to extremist ideologies often are triggered by negative life events or exposure to propaganda, and those who escape from extreme groups frequently are aided by an individual or group that intervenes to help them reject the philosophy, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
Expanding access to mental health care, creating opportunities for exposure to diverse cultural groups and media literacy education all are important strategies that may aid the battle against extremism, according to researchers. However, harsh law enforcement actions often are unproductive in changing people's extremist beliefs.
The RAND study describes personal accounts based on interviews ...
Fungi could manipulate bacteria to enrich soil with nutrients
2021-04-02
ITHACA, NY, April 2, 2021 - A team of researchers from the Boyce Thompson Institute (BTI) has discovered a distinct group of bacteria that may help fungi and plants acquire soil nutrients. The findings could point the way to cost-effective and eco-friendly methods of enriching soil and improving crop yields, reducing farmers' reliance on conventional fertilizers.
Researchers know that arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi establish symbiotic relationships with the roots of 70% of all land plants. In this relationship, plants trade fatty acids for the fungi's nitrogen and phosphorus. However, AM fungi lack the ...
How pathogenic bacteria weather the slings and arrows of infection
2021-04-02
Infectious diseases are a leading cause of global mortality. During an infection, bacteria experience many different stresses -- some from the host itself, some from co-colonizing microbes and others from therapies employed to treat the infection. In this arms race to outwit their competition, bacteria have evolved mechanisms to stay alive in the face of adversities. One such mechanism is the stringent response pathway. Understanding how the activation of the stringent response pathway is controlled can provide clues to treat infection.
In new research published this week online in the journal END ...
Lanternfly's attraction to vertical silhouettes could help monitor, trap it
2021-04-02
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Like moths to a flame, spotted lanternflies are visually drawn toward and seemingly captivated by vertical objects such as utility poles, a behavior that could be valuable in predicting where the pests might be heading, according to entomologists in Penn State's College of Agricultural Sciences.
Research from the laboratory of Tom Baker, recently published in the Journal of Insect Behavior, is laying the foundation for future strategies to monitor and possibly trap the invasive insect from Asia, which first was found in North America in Berks County, Pennsylvania, in 2014. The planthopper now is confirmed in 34 Pennsylvania counties and several surrounding states.
These findings show that telephone poles attract flight-dispersing ...
Toddler TV time not to blame for attention problems
2021-04-02
Acomprehensive review published in the journal Psychological Science re-examines previous work that claimed to show a direct link between early screen time and attention problems in children. Although other studies do not reflect these findings, the earlier research continues to be widely reported by the media.
"The findings from the original study, upon further scrutiny, are not borne out. We found that there is still no evidence that TV, by itself, causes ADHD or any kind of attention problems in young children," said Wallace E. Dixon, Jr., a professor of psychology ...
Baby aspirin linked to lower risk of colorectal cancer death
2021-04-02
Long-term, regular use of baby aspirin--at least 15 times per month--prior to a diagnosis of colorectal cancer (CRC) may reduce the risk of death from the disease by limiting the spread of cancerous tumors pre-diagnosis, according to a study led by Cedars-Sinai Cancer researchers.
While previous research has offered consistent evidence that low-dose aspirin use reduces colorectal cancer risk, key findings from the study, published in the peer-reviewed Journal of the National Cancer Institute, revealed that the use of baby aspirin prior to the diagnosis of non-metastatic CRC was associated with a lower rate of metastasis, or tumor spread. Starting ...
COVID-19 survivors might need just one dose of two-part vaccine
2021-04-02
LOS ANGELES (April 1, 2021) -- A single dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine for individuals who previously had COVID-19 generates an immunologic response similar to that of individuals receiving the two-dose recommended sequence, according to a Cedars-Sinai study published today by the journal Nature Medicine.
"Our findings extend those from smaller studies reported elsewhere and support a potential strategy of providing a single dose of vaccine to persons with a confirmed prior history of coronavirus infection, along with two doses for people not previously infected," said Susan Cheng, MD, MPH, MMSc, associate professor of Cardiology and director of Public Health Research at ...
A PTV-based polymer enabled organic solar cells with over 16% efficiency
2021-04-02
Organic solar cell (OSC) is one of the most important green energy technologies. The photovoltaic efficiencies of OSCs are closely related to the photoactive layers, which are prepared by blending electron donor and acceptor materials. With the emergence of a large number of new organic photovoltaic materials and effective molecular modification methods, the photovoltaic efficiency of OSCs has been greatly improved. Accordingly, the molecular structure of the materials is becoming much more complex with high costs, which is difficult to meet the requirements of the industrialization of OSCs. Thus, it is of great importance to develop novel photovoltaic ...
Probiotics keep calves healthy, too!
2021-04-02
Scientists in Japan have developed and tested a novel probiotic formulation to control severe diarrhea in calves, ensuring their health and reducing mortality, and in turn reducing economic loss.
The health of calves is a crucial component in animal husbandry; diseases that affect calves cause economic losses to livestock farms either directly, due to death of the calves, or indirectly, due to weight loss that reduces productivity over the animals' lifespans. In Japan, bovine rotavirus (BRV) and bovine cryptosporidiosis infections are major diseases that cause severe diarrhea in calves.
A team of scientists from Hokkaido, including Associate Professor Satoru Konnai of the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine at Hokkaido University, have ...
[1] ... [2476]
[2477]
[2478]
[2479]
[2480]
[2481]
[2482]
[2483]
2484
[2485]
[2486]
[2487]
[2488]
[2489]
[2490]
[2491]
[2492]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.