Selenium supplementation protects against obesity and may extend lifespan
2021-03-30
Adding the nutrient selenium to diets protects against obesity and provides metabolic benefits to mice, according to a study published today in eLife.
The results could lead to interventions that reproduce many of the anti-aging effects associated with dietary restriction while also allowing people to eat as normal.
Several types of diet have been shown to increase healthspan - that is, the period of healthy lifespan. One of the proven methods of increasing healthspan in many organisms, including non-human mammals, is to restrict dietary intake of an amino acid ...
Factors that may predict next pandemic
2021-03-30
Humans are creating or exacerbating the environmental conditions that could lead to further pandemics, new University of Sydney research finds.
Modelling from the Sydney School of Veterinary Science suggests pressure on ecosystems, climate change and economic development are key factors associated with the diversification of pathogens (disease-causing agents, like viruses and bacteria). This has potential to lead to disease outbreaks.
The research, by Dr Balbir B Singh, Professor Michael Ward, and Associate Professor Navneet Dhand, is published in the international journal, Transboundary and Emerging Diseases.
They found a greater diversity ...
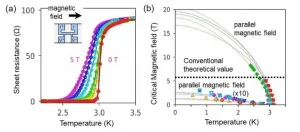
Discovery of a mechanism for making superconductors more resistant to magnetic fields
2021-03-30
Superconductivity is known to be easily destroyed by strong magnetic fields. NIMS, Osaka University and Hokkaido University have jointly discovered that a superconductor with atomic-scale thickness can retain its superconductivity even when a strong magnetic field is applied to it. The team has also identified a new mechanism behind this phenomenon. These results may facilitate the development of superconducting materials resistant to magnetic fields and topological superconductors composed of superconducting and magnetic materials.
Superconductivity has been used in various technologies, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ...
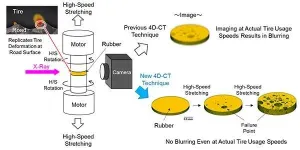
faster imaging in rubber x-ray CT imaging helps tires become smarter and more efficient
2021-03-30
Sumitomo Rubber Industries, Ltd (SRI) and Tohoku University teamed up to increase the speed of 4-Dimensional Computed Tomography (4D-CT) a thousand-fold, making it possible to observe rubber failure in tires in real-time.
This breakthrough will accelerate the development of new tire materials to provide super wear resistance, greater environmental friendliness, and longer service life. It will also aid significantly in the advancement of smart tires.
SRI initially developed 4D-CT as part of the ADVANCED 4D NANO DESIGN, a new materials development technology unveiled in 2015 that enables highly accurate analysis and simulation of the rubber's internal structure from the micro to nanoscale. This analysis ultimately ...
Mystery of photosynthetic algae evolution finally solved
2021-03-30
An evolutionary mystery that had eluded molecular biologists for decades may never have been solved if it weren't for the COVID-19 pandemic.
"Being stuck at home was a blessing in disguise, as there were no experiments that could be done. We just had our computers and lots of time," says Professor Paul Curmi, a structural biologist and molecular biophysicist with UNSW Sydney.
Prof. Curmi is referring to research published this month in Nature Communications that details the painstaking unravelling and reconstruction of a key protein in a single-celled, photosynthetic organism called a cryptophyte, a type of algae that evolved over a billion years ago.
Up until now, how cryptophytes acquired the proteins ...
Childhood adversity shapes adolescent delinquency, fatherhood
2021-03-30
About 61% of Americans have had at least one Adverse Childhood Experience (ACE), experts' formal term for a traumatic childhood event.
ACEs--which may include abuse, neglect and severe household dysfunction--often lead to psychological and social struggles that reach into adulthood, making ACEs a major public health challenge. But the long-term consequences of ACEs are just beginning to be understood in detail. To fill in the picture, two recent BYU studies analyzed how ACEs shape adolescents' delinquent behaviors as well as fathers' parenting approaches.
ACEs ...
Smokers motivated to 'quit for COVID' to ease burden on health system
2021-03-30
An international survey that included 600 smokers in the UK has found that cessation messaging focused on easing the burden on our health system is most effective in encouraging people to quit.
The research, which was conducted in April-May 2020, randomly assigned participants to view one of four quit smoking messages, two of which explicitly referenced health implications and COVID-19, one referred more vaguely to risk of chest infection, and one highlighted financial motivations for quitting.
"We wanted to explore the effectiveness of smoking cessation messaging at a time when health systems the world over are beleaguered, and all our ...
Salt substitution -- an effective way to reduce blood pressure in rural India
2021-03-30
Replacing regular common salt consumed by hypertensive patients in rural areas with a salt substitute can have a significant impact in terms of lowering their blood pressure, a new study by The George Institute for Global Health has revealed.
Researchers found that substituting a small part of the sodium in salt with potassium without altering the taste led to a substantial reduction in systolic blood pressure in these patients, supporting salt substitution as an effective, low-cost intervention for lowering blood pressure in rural India.
The study entitled "Effects of reduced-sodium added-potassium salt substitute on blood pressure in rural Indian hypertensive patients: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial" provides the first-of-its-kind evidence from ...
The third generation of siRNA delivery system makes RNAi therapy feasible
2021-03-30
In a new study published in the Cell Research, Chen-Yu Zhang's group at Nanjing University reports "In vivo self-assembled small RNA is the new generation of RNAi therapeutics".
The development of RNAi therapy has undergone two major stages, direct injection of synthetic siRNAs and delivery with artificial vehicles; both have not realized the full therapeutic potential of RNAi in clinic. In this study, Chen-Yu Zhang's group reprogram host liver with genetic circuits to direct the synthesis and self-assembly of siRNAs into secretory exosomes. In vivo assembled siRNAs are systematically distributed to multiple tissues or targeted to specific tissues (e.g., brain), inducing potent target gene silencing in these tissues. The therapeutic value of this strategy is demonstrated ...
Algorithm-based music recommendations: Low accuracy for lovers of non-mainstream music
2021-03-30
A team of researchers from Graz University of Technology, Know-Center GmbH, Johannes Kepler University Linz, University of Innsbruck, Austria and University of Utrecht, the Netherlands, compared how accurate algorithm-generated music recommendations were for mainstream and non-mainstream music listeners. They used a dataset containing the listening histories of 4,148 users of the music streaming platform Last.fm who either listened to mostly non-mainstream music or mostly mainstream music (2,074 users in each group). Based on the artists music users' listened to most frequently, the authors used a computational model to predict how likely music users were to like the music recommended ...
Urban and transport planning linked to 2,000 premature deaths per year in Barcelona and Madrid
2021-03-30
Failure to comply with international exposure recommendations for air pollution, noise, heat and access to green space is associated with more than 1,000 deaths per year in Barcelona and more than 900 in Madrid, accounting for 7% and 3% of overall premature mortality, respectively.
This is the conclusion of a new study by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation. This study is the first to estimate premature mortality impacts and the distribution by socioeconomic status of multiple environmental exposures related to urban planning and transport in the two cities.
Today, more than half of the ...
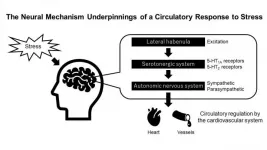
The neural mechanism of a circulatory response to stress
2021-03-30
Tsukuba, Japan - Although the heart beats autonomously, its function can be regulated by the brain in response to, for instance, stressful events. In a new study, researchers from the University of Tsukuba discovered a novel mechanism by which a specific part of the brain, the lateral habenula (LHb), regulates the cardiovascular system.
The cardiovascular system, specifically the heart and blood vessels, have a certain autonomy that allows them to function independently from the brain. In order for the individual to adapt to new, potentially threatening situations, the brain does have some regulatory power over the cardiovascular ...
Chronic inflammatory liver disease: cell stress mechanisms identified
2021-03-30
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a rare, chronic, inflammatory disease of the bile ducts and is difficult to treat, since its causes have not yet been adequately researched. Using RNA sequencing, an international research consortium led by Michael Trauner, Head of MedUni Vienna's Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology (Department of Medicine III), has now succeeded in identifying a new prognostic factor for PSC from liver biopsies. This is so-called cellular ER stress. ER stress is the name given to a complex cellular response to stress caused by the build-up of misfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
PSC is a rare disease with a poor prognosis and can lead to cirrhosis ...
New AI-based versatile software for tracking many cells in 3D microscope videos
2021-03-30
In modern basic life science research as well as in drug discovery, recording and analyzing the images of cells over time using 3D microscopy has become extremely important. Once the images have been recorded, the same cell in different images at different time points has to be accurately identified ("cell tracking") because the living cells captured in the images are in motion. However, tracking many cells automatically in 3D microscope videos has been considerably difficult.
In the Kimura laboratory at the Nagoya City University, Dr. Chentao Wen and colleagues developed the 1st AI-based software called 3DeeCellTracker that can run on a desktop PC and automatically track cells in 3D microscope videos. ...
Researchers reveal SARS-CoV-2 distribution and relation to tissue damage in patients
2021-03-30
Researchers have mapped the distribution of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, in deceased patients with the disease, and shed new light on how viral load relates to tissue damage.
Their study of 11 autopsy cases, published today in eLife, may contribute to our understanding of how COVID-19 develops in the body following infection.
More than 24 million SARS-CoV-2 infections have been reported to date, and the number of deaths attributed to COVID-19 has exceeded 828,000 worldwide. COVID-19 occurs with varying degrees of severity. While most patients have mild symptoms, some experience more severe symptoms and may need to be hospitalised. A minority of those in hospital may enter a critical condition, with respiratory failure, blood vessel complications, or multiple organ ...
Cardiorespiratory fitness improves grades at school
2021-03-30
Recent studies indicate a link between children's cardiorespiratory fitness and their school performance: the more athletic they are, the better their marks in the main subjects - French and mathematics. Similarly, cardiorespiratory fitness is known to benefit cognitive abilities, such as memory and attention. But what is the real influence of such fitness on school results? To answer this question, researchers at the University of Geneva (UNIGE), Switzerland tested pupils from eight Geneva schools. Their results, published in the journal Medicine & Science in Sport & Exercise, show that there is an indirect link with cardiorespiratory fitness influencing ...
Breaking records like baking bread
2021-03-30
Alloying, the process of mixing metals in different ratios, has been a known method for creating materials with enhanced properties for thousands of years, ever since copper and tin were combined to form the much harder bronze. Despite its age, this technology remains at the heart of modern electronics and optics industries. Semiconducting alloys, for instance, can be engineered to optimize a device's electrical, mechanical and optical properties.
Alloys of oxygen with group III elements, such as aluminum, gallium, and indium, are important semiconductor materials with vast applications ...
Beetle outbreak impacts vary across Colorado forests
2021-03-30
It's no secret. Colorado's forests have had a tough time in recent years. While natural disturbances such as insect outbreaks and wildfires occurred historically and maintained forest health over time, multiple, simultaneous insect disturbances in the greater region over the past two decades have led to rapid changes in the state's forests.
A bird's eye view can reveal much about these changes. Annual aerial surveys conducted by the Colorado State Forest Service and USDA Forest Service have provided yearly snapshots for the state. New collaborative research led by Colorado State University and the University of Wisconsin-Madison now supplements this understanding with even greater spatial detail.
The ...
Teens describe their gender and sexuality in diverse ways, but some are being left behind
2021-03-30
A growing number of young people are identifying as part of the LGBTQ+ community, and many are challenging binaries in gender and sexual identity to reflect a broader spectrum of experience beyond man or woman and gay or straight. But not everyone is participating equally in these diverse forms of expression, according to new research from the University of California, Santa Cruz.
Psychology Professor Phillip Hammack's latest paper, published in the Journal of Adolescent Research, is shedding light on the social factors that can either hinder or support expression of diversity in sexual and gender identity ...
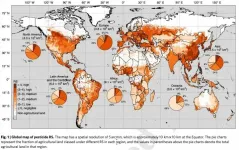
64% of global agricultural land at risk of pesticide pollution?
2021-03-30
The study, published in Nature Geoscience, produced a global model mapping pollution risk caused by 92 chemicals commonly used in agricultural pesticides in 168 countries.
The study examined risk to soil, the atmosphere, and surface and ground water.
The map also revealed Asia houses the largest land areas at high risk of pollution, with China, Japan, Malaysia, and the Philippines at highest risk. Some of these areas are considered "food bowl" nations, feeding a large portion of the world's population.
University of Sydney Research Associate and the study's lead author, Dr Fiona Tang, said the widespread use of pesticides in agriculture - while boosting productivity - could have potential implications for the environment, human and animal ...
Prime editing enables precise gene editing without collateral damage
2021-03-30
The latest gene editing technology, prime editing, expands the "genetic toolbox" for more precisely creating disease models and correcting genetic problems, scientists say.
In only the second published study of prime editing's use in a mouse model, Medical College of Georgia scientists report prime editing and traditional CRISPR both successfully shut down a gene involved in the differentiation of smooth muscle cells, which help give strength and movement to organs and blood vessels.
However, prime editing snips only a single strand of the double-stranded DNA. CRISPR makes double-strand cuts, which can be lethal to cells, and produces unintended edits at both the work site as well as randomly across the genome, ...
'Bottom-up' approach needed to study freshwater blooms
2021-03-30
HANOVER, N.H. - March 30, 2021 - Cyanobacteria living at the bottom of lakes may hold important, under-researched clues about the threat posed by these harmful organisms, according to a Dartmouth-led study.
The research, published in the Journal of Plankton Research, urges a more comprehensive approach to cyanobacteria studies in order to manage the dangerous blooms during a time of global climate change.
"Most studies of cyanobacteria focus on the times when they are visible in the water column," said Kathryn Cottingham, the Dartmouth Professor in the Arts and ...
How to talk to people about climate change
2021-03-30
As our planet warms, seas rise and catastrophic weather events become more frequent, action on climate change has never been more important. But how do you convince people who still don't believe that humans contribute to the warming climate?
New UBC research may offer some insight, examining biases towards climate information and offering tools to overcome these and communicate climate change more effectively.
Researchers examined 44 studies conducted over the past five years on the attentional and perceptual biases of climate change - the tendency to pay special attention to or perceive particular aspects of climate change. They identified a number of ...
New statistical method eases data reproducibility crisis
2021-03-30
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- A reproducibility crisis is ongoing in scientific research, where many studies may be difficult or impossible to replicate and thereby validate, especially when the study involves a very large sample size. For example, to evaluate the validity of a high-throughput genetic study's findings scientists must be able to replicate the study and achieve the same results. Now researchers at Penn State and the University of Minnesota have developed a statistical tool that can accurately estimate the replicability of a study, thus eliminating the need to duplicate the work and effectively ...
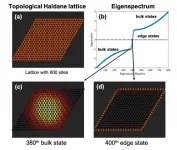
Topological protection of entangled two-photon light in photonic topological insulators
2021-03-30
In a joint effort, researchers from the Humboldt-Universität (Berlin), the Max Born Institute (Berlin) and the University of Central Florida (USA), have revealed the necessary conditions for the robust transport of entangled states of two-photon light in photonic topological insulators, paving the way the towards noise-resistant transport of quantum information. The results have appeared in Nature Communications.
Originally discovered in condensed matter systems, topological insulators are two-dimensional materials that support scattering-free (uni-directional) transport along their edges, even in the presence of defects and disorder. In ...
[1] ... [2468]
[2469]
[2470]
[2471]
[2472]
[2473]
[2474]
[2475]
2476
[2477]
[2478]
[2479]
[2480]
[2481]
[2482]
[2483]
[2484]
... [8813]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.