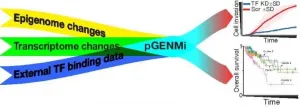
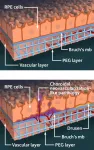
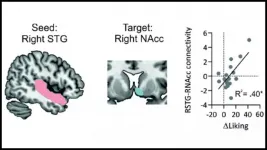
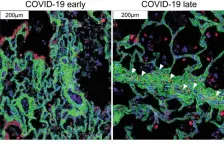
New computational models to understand colon cancer
2021-03-29
Although the development of secondary cancerous growths, called metastasis, is the primary cause of death in most cancers, the cellular changes that drive it are poorly understood. In a new study, published in Genome Biology, researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have developed a new modeling approach to better understand how tumors become aggressive.
"Researchers have identified several cellular pathways that change when a tumor becomes aggressive. However, it is difficult to understand how they affect the tumor," said Steven Offer, an assistant professor of molecular pharmacology and experimental therapeutics at Mayo Clinic, Minnesota. "We wanted to develop a simple system that can model how cancer cells form ...
Percutaneous image guided thermal ablation safe, effective therapy for metastatic gynecologic cancers
2021-03-29
FINDINGS
A new study by researchers at the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center found using percutaneous image guided needle based thermal ablation -- the precise application of extreme heat or cold to a tumor using sophisticated ultrasound, CT or MRI in a single outpatient session -- is a safe and effective adjunctive therapy for the local control of metastatic gynecologic cancers throughout lungs, liver, soft tissues in the abdomen and pelvis and bones in patients with advanced localized cancers unresponsive to systemic therapy.
Nearly 96% of the patients in the study achieved a complete tumor response over a median follow up period of 10 months. The overall survival rate was 37.5 months and the progression-free ...
Racial disparities in chronic disease death rates persist despite efforts to close gap
2021-03-29
BOSTON - In the last 20 years, Black adults living in rural areas of the United States have experienced high mortality rates due to diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease and stroke compared to white adults. In a research letter written by colleagues at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) and published in the END ...
Lab model offers hope for macular degeneration patients
2021-03-29
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD), which leads to a loss of central vision, is the most frequent cause of blindness in adults 50 years of age or older, affecting an estimated 196 million people worldwide. There is no cure, though treatment can slow the onset and preserve some vision.
Recently, however, researchers at the University of Rochester have made an important breakthrough in the quest for an AMD cure. Their first three-dimensional (3D) lab model mimics the part of the human retina affected in macular degeneration.
Their model combines stem cell-derived ...
Why the brain enjoys music
2021-03-29
Communication between the brain's auditory and reward circuits is the reason why humans find music rewarding, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
Despite no obvious biological benefits, humans love music. Neuroimaging studies highlight similarities between how the brain's reward circuits process music and other rewards like food, money, and alcohol. Yet neuroimaging studies are correlational by nature. In a new study, Mas-Herrero et al. sought to nail down the causal role of this circuitry by using non-invasive brain stimulation.
A group of pop music fans listened ...
New technique provides detailed map of lung pathology in COVID-19
2021-03-29
A team led by investigators at Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian has used advanced technology and analytics to map, at single-cell resolution, the cellular landscape of diseased lung tissue in severe COVID-19 and other infectious lung diseases.
In the study, published online March 29 in Nature, the researchers imaged autopsied lung tissue in a way that simultaneously highlighted dozens of molecular markers on cells. Analyzing these data using novel analytical tools revealed new insights into the causes of damage in these lung illnesses and a rich data resource for further research.
"COVID-19 is a complex disease, and we still don't understand exactly what it does to a lot of organs, but with this study we were able to develop ...
Brazilian researchers obtain more efficient red bioluminescence
2021-03-29
Researchers at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar) in the state of São Paulo, Brazil, have developed a novel far red light-emitting luciferin-luciferase system that is more efficient than those available commercially. An article on the subject is published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences.
The study was supported by São Paulo Research Foundation - FAPESP via the Thematic Project "Arthropod bioluminescence: biological diversity in Brazilian biomes, biochemical origin, structural/functional evolution of luciferases, molecular differentiation of lanterns, biotechnological, environmental and educational applications", for which the principal ...
Remote-friendly student project presentations enable creativity and risk-taking
2021-03-29
ANN ARBOR--In a two-year study that could help guide educators developing the post-pandemic new normal, student groups at the University of Michigan assigned to make video presentations showed more creativity and risk-taking than groups making conventional in-person presentations.
"Given the importance of project-based learning, our study provides a way to turn virtual limitations into an advantage," said Fei Wen, U-M associate professor of chemical engineering. "We can enhance the student experience and learning outcomes."
Higher education, along with society at large, anticipates a shift in the balance between ...
Common medications contain animal byproducts, study finds
2021-03-29
More physicians and pharmacists are advocating for patients to be made aware of animal byproducts contained in common medications, according to new research in the Journal of Osteopathic Medicine. Common medications, including widely used blood thinners and hormones, are often derived from animal byproducts and prescribed without consulting the patient about their beliefs.
"Patients deserve to know what their medications are made of, yet this information is rarely shared," said Sara Reed, student doctor at Lincoln Memorial University (LMU) DeBusk ...
Coastal lupine faces specific extinction threat from climate change
2021-03-29
Climate change is altering the world we share with all living things. But it's surprisingly difficult to single out climate change as an extinction threat for any one particular species protected under the Endangered Species Act.
To date, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service has only formally considered impacts from climate change in listing actions for four animal species and one alpine tree.
But the effects of climate change extend to temperate climates as well. A new analysis of population data published in the journal Ecosphere shows that climate change represents a specific extinction threat for an endangered coastal lupine plant.
Biologists including Eleanor Pardini at Washington University in St. Louis have tracked all of the known stands ...
Tires turned into graphene that makes stronger concrete
2021-03-29
HOUSTON - (March 29, 2021) - This could be where the rubber truly hits the road.
Rice University scientists have optimized a process to convert waste from rubber tires into graphene that can, in turn, be used to strengthen concrete.
The environmental benefits of adding graphene to concrete are clear, chemist James Tour said.
"Concrete is the most-produced material in the world, and simply making it produces as much as 9% of the world's carbon dioxide emissions," Tour said. "If we can use less concrete in our roads, buildings and bridges, we can eliminate some of the emissions at the very start."
Recycled tire waste is already used as a component of Portland cement, but graphene has been proven to strengthen cementitious materials, ...
Study looks at impacts of COVID-19 and Cyclone Harold on fishers in Fiji
2021-03-29
SUVA, Fiji (March 29, 2021) - A new study published in the journal Environmental Science and Policy addresses the impacts of COVID-19 and Cyclone Harold on Indo-Fijians engaged in small scale fisheries.
The paper says that countries, including Fiji, need to address ethical and social justice considerations and the politics of recovery efforts by putting vulnerable and marginalized groups front and center in the aftermath of pandemics and natural disasters.
What countries cannot afford is for economic recovery efforts to put additional burdens and risk on those invested in the SSF sector, and cause further widening of inequities, and increase ...
Apes show dramatically different early immune responses compared to monkeys
2021-03-29
A new study out of the University of Chicago and the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign in humans, chimpanzees, rhesus macaques and baboons has found key differences in early gene expression in response to pathogen exposure, highlighting the importance of choosing the right animal model for the right questions. The study was published on March 26 in END ...
Parents often don't use child car seats in ride-share
2021-03-29
A national survey of parents revealed that most parents who used ride-share services did so with their children, but only half of the respondents reported that children who were 8 years or younger traveled in the recommended child car seats or booster seats when in ride-share vehicles. Among parents of children in this age group, over 40 percent used only a seat belt for their child, while 10 percent allowed their child to travel on a lap or unrestrained. Overall, parents reported lower rates of child car seat use in ride-share compared with how their child usually travels. Findings were published in the journal Academic Pediatrics.
"Our results are concerning, as ...
Prognostic value of molecular classification in metastatic breast cancer confirmed
2021-03-29
Barcelona researchers at the Hospital Clínic-IDIBAPS Research Institute, the University of Barcelona and the SOLTI academic cancer research group have shown that the molecular classification of breast cancer, which divides it into four subtypes (Luminal A, Luminal B, HER2-enriched and Basal-like) is useful for predicting the benefits of treatment in patients with advanced hormone-sensitive breast cancer. This is the largest study to have shown the value of the biomarker, and the first to do so in the context of a CDK4/6 inhibitor like ribociclib.
The study, published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), was coordinated by Professor Aleix Prat, head of the Medical Oncology ...
Diabetes drug may be a new weapon against HIV
2021-03-29
CHAPEL HILL, NC - A team led by scientists at the UNC School of Medicine discovered an important vulnerability of the AIDS-causing retrovirus HIV, and has shown in preclinical experiments that a widely used diabetes drug, metformin, seems able to exploit this vulnerability.
The scientists, whose study is published in Nature Immunology, found that HIV, when it infects immune cells called CD4 T cells, helps fuel its own replication by boosting a key process in the cells' production of chemical energy. They also found that the diabetes drug metformin inhibits the same process and thereby suppresses HIV replication in these cells, in both cell-culture and mouse experiments.
"These findings suggest that metformin and other drugs that reduce T cell metabolism ...
TGen-ASU review suggests added sugars are contributing to liver disease among children
2021-03-29
PHOENIX, Ariz. -- March 29, 2021 -- A review of more than 20 studies by researchers at Arizona State University and the Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen), an affiliate of City of Hope, suggests that nonalcoholic fatty-liver disease (NAFLD) is a growing dietary problem for children across the globe.
"The prevalence of fatty-liver disease is escalating not only in adults, but also in children," said Johanna DiStefano, Ph.D., a Professor and head of TGen's Diabetes and Fibrotic Disease Unit, and the review's senior author. "Like type 2 diabetes, NAFLD used to be considered a disease that developed only in adulthood, ...
How coastal forests are managed can impact water cycle
2021-03-29
Younger trees take up and release less water than mature trees 10 years or older, researchers from North Carolina State University found in a new study that tracked how water moves through wetland pine forests near the North Carolina coast.
Their findings, published in Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, suggest managers should time timber harvests to leave older trees alongside new growth to mitigate runoff.
"The water balance, especially in coastal sites, is very important," said the study's lead author Maricar Aguilos, postdoctoral research associate in forestry and environmental resources at NC State. "We have so much water there. We wanted to understand how land-use changes impact water use and drainage in the forests, ...
Scientists create simple synthetic cell that grows and divides normally
2021-03-29
Five years ago, scientists created a single-celled synthetic organism that, with only 473 genes, was the simplest living cell ever known. However, this bacteria-like organism behaved strangely when growing and dividing, producing cells with wildly different shapes and sizes.
Now, scientists have identified seven genes that can be added to tame the cells' unruly nature, causing them to neatly divide into uniform orbs. This achievement, a collaboration between the J. Craig Venter Institute (JCVI), the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Center for Bits and Atoms, was described in the journal Cell.
Identifying these genes is an important step toward engineering synthetic cells that do useful things. Such ...
Low parental socioeconomic status during pregnancy alters early fetal brain development
2021-03-29
Maternal socioeconomic status impacts babies even before birth, emphasizing the need for policy interventions to support the wellbeing of pregnant women, according to newly published END ...
WIC Nutrition Program increased enrollment shifting from paper vouchers to electronic
2021-03-29
PHILADELPHIA -- The U.S. government's Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children, usually abbreviated as WIC, saw a jump in enrollment of nearly 8 percent in states that implemented a federally mandated switch from paper vouchers to electronic benefit cards (EBTs), according to a study led by researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
The finding, published in JAMA Pediatrics, supports the rationale for the switch, which was to increase participation by making it easier and less stigmatizing to obtain and redeem WIC benefits.
"The broad takeaway ...
Autism rates have increased and show differences in ethnic minorities
2021-03-29
Around one in 57 (1.76%) children in the UK is on the autistic spectrum, significantly higher than previously reported, according to a study of more than 7 million children carried out by researchers from the University of Cambridge's Department of Psychiatry in collaboration with researchers from Newcastle University and Maastricht University.
Black and Chinese pupils were 26% and 38% more likely to be autistic respectively and autistic children were much more likely to face significant social disadvantage. The results are published today in JAMA Pediatrics.
The team drew on data from the School Census from the National Pupil Database, collected by the Department for Education from individuals aged 2-21 years old in state-funded schools in England. Of more than 7 million ...
Assessment of simulated SARS-CoV-2 infection, mortality risk associated with radiation therapy among patients in 8 RCTs
2021-03-29
What The Study Did: This comparative effectiveness study investigates how the COVID-19 pandemic is associated with the benefits and risks of standard radiation therapy in simulated patients.
Authors: Rifaquat Rahman, M.D., of the Dana-Farber/Brigham and Women's Cancer Center in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.3304)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, ...
A visit to 'Dr. Google' makes patients better at diagnosis
2021-03-29
BOSTON --Medical professionals often advise patients not to search the Internet for their symptoms before coming into the clinic, yet many people turn to "Dr. Google" when feeling sick. Concerns about "cyberchondria" -- or increased anxiety induced by the Internet -- have made the value of using Internet searches controversial. In a new study that used case vignettes, researchers from Brigham and Women's Hospital and Harvard Medical School Department of Health Care Policy explored the impact Internet searches have on patients' abilities to reach a correct diagnosis. They found that study outcomes suggest the Internet may not be so harmful after all. Participants ...
Younger age of first drug use associated with faster development of substance use disorder
2021-03-29
Younger age of first cannabis use or prescription drug misuse is associated with faster development of substance use disorders
NIH analysis measures the prevalence of nine substance use disorders after first substance use or misuse in young people
A new study shows that in the time after first trying cannabis or first misusing prescription drugs, the percentages of young people who develop the corresponding substance use disorder are higher among adolescents (ages 12-17) than young adults (ages 18-25). In addition, 30% of young adults develop a heroin use disorder and 25% develop a methamphetamine use disorder a year after first using heroin or methamphetamine. These findings, published in JAMA Pediatrics, emphasize the vulnerability ...
[1] ... [2470]
[2471]
[2472]
[2473]
[2474]
[2475]
[2476]
[2477]
2478
[2479]
[2480]
[2481]
[2482]
[2483]
[2484]
[2485]
[2486]
... [8813]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.