Tree fungus reduces fertilizer requirement for ketchup tomatoes
2021-03-31
Tomatoes are an important and popular crop, but the tasty ketchup, salsa and pasta sauce they yield comes at a price: overuse of chemical fertilizers. Now, researchers report in ACS' Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry they have recruited a fungus to bolster fertilizer efficiency, meaning tastier tomatoes can be grown with less fertilizer.
Tomato plants have a long growth period and need more nutrients -- particularly nitrogen and phosphorus-- than many other crops. Supplying these nutrients through a chemical fertilizer is inefficient, because the nutrients can leach away, evaporate or get trapped in insoluble compounds in the soil, among other problems. Some farmers react by overusing ...
Processed meat linked to higher risk of mortality and cardiovascular disease
2021-03-31
Key Points
The PURE study is the first multinational study exploring the association between unprocessed and processed meat intakes with health outcomes in low-, middle-, and high-income countries.
The consumption of unprocessed red meat and poultry was not found to be associated with mortality nor major cardiovascular disease events.
In contrast, higher processed meat intake was associated with higher risks of both total mortality and major cardiovascular disease.
Rockville, MD - Red meat is a major source of medium- and long-chain saturated fatty acids, which may lead to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Processed meat, which has been modified to improve taste or extend its shelf-life, has also been associated with an increased ...
Study ratifies link of processed meat to cardiovascular disease and death
2021-03-31
Hamilton, ON (March 31, 2021) - A global study led by Hamilton scientists has found a link between eating processed meat and a higher risk of cardiovascular disease. The same study did not find the same link with unprocessed red meat or poultry.
The information comes from the diets and health outcomes of 134,297 people from 21 countries spanning five continents, who were tracked by researchers for data on meat consumption and cardiovascular illnesses.
After following the participants for almost a decade, the researchers found consumption of 150 grams or more of processed meat a week was associated with a 46 per cent higher risk of cardiovascular disease and a 51 per cent ...
Tilapias are not precocious, they are just resilient
2021-03-31
Tilapias living in crowded aquaculture ponds or small freshwater reservoirs adapt so well to these stressful environments that they stop growing and reproduce at a smaller size than their stress-free counterparts.
A new study by researchers at the University of Kelaniya in Sri Lanka and the University of British Columbia, explains that while most fishes die when stressed, tilapias survive in rough environments by stunting and carrying on with their lives in dwarf form.
"Tilapia and other fish in the Cichlidae family do not spawn 'earlier' than other fishes, as it is commonly believed," Upali S. Amarasinghe, lead author of the study and professor at the University of Kelaniya, said. "Rather, they are uncommonly tolerant of stressful ...
Exercise, healthy diet in midlife may prevent serious health conditions in senior years
2021-03-31
DALLAS, March 31, 2021 -- Following a routine of regular physical activity combined with a diet including fruits, vegetables and other healthy foods may be key to middle-aged adults achieving optimal cardiometabolic health later in life, according to new research using data from the Framingham Heart Study published today in the Journal of the American Heart Association, an open access journal of the American Heart Association.
Cardiometabolic health risk factors include the metabolic syndrome, a cluster of disorders such as excess fat around the waist, insulin resistance and high blood pressure. Presence of the metabolic syndrome may increase the risk of developing heart disease, stroke and Type 2 diabetes.
Researchers noted it has been unclear ...
Impacts of sunscreen on coral reefs needs urgent attention, say scientists
2021-03-31
More research is needed on the environmental impact of sunscreen on the world's coral reefs, scientists at the University of York say.
The concerns over the number of cases of cancer as a result of overexposure to UV solar radiation, has led to extensive production and use of skin protection products. The chemical compounds used in these products, however, can enter the environment at the points of manufacture as well as through use by the consumer.
It is already understood that UV-filter compounds have toxic effects on marine organisms, but research in this area ...
1 in 5 Americans did not seek needed medical treatment during the pandemic due to cost
2021-03-31
WASHINGTON, DC - March 31, 2021 -- Nearly 20% of Americans, or more than 46 million adults, say they did not seek treatment for a health problem in the last year due to cost, and an equal number say that if they needed some form of healthcare today they would not be able to afford it, according to a new West Health-Gallup survey. The findings come as Americans struggle through a year-plus long pandemic that has claimed over 550,000 lives and put millions of people out of work.
Americans who found themselves unemployed were about twice as likely ...
Building a culture of high-quality data
2021-03-31
The era of big data has inundated nearly all scientific fields with torrents of newly available data with the power to stimulate new research and enable inquiry at scales not previously possible. This is particularly true for ecology, where rapid growth in remote sensing, monitoring, and community science initiatives has contributed to a massive surge in the quantity and kinds of environmental data that are available to researchers.
Writing in BioScience, a team led by US Department of Agriculture ecologist Sarah McCord states that the volume of the data is only part of the story. Just as important, they say, is the quality of the data. According to the newly published article, "Big data has magnified both the burden and the complexity of ensuring ...
Study contributes to our understanding of how cocaine withdrawal affects brain circuits
2021-03-31
GENEVA, LAUSANNE, 31 March 2021: Cocaine is a highly addictive substance that, in the long term, can have adverse effects on health and wellbeing. There are around 18 million cocaine users globally, according to a UN report. Understanding how cocaine modifies brain networks could reveal potential targets for therapies to treat addiction and other neuropsychological disorders.
A new study published today in the journal Frontiers in Synaptic Neuroscience by a team of researchers from the University of Lausanne and the Wyss Center for Bio and Neuroengineering reveals that during cocaine withdrawal, neurons in a brain area associated with depression connect ...
Experimental treatment offers hope of fertility for early menopausal women
2021-03-31
CLEVELAND, Ohio (March 31, 2021)--Menopause typically signals the end of a woman's ability to become pregnant. However, in a small new study, a novel approach of administering platelet-rich plasma and gonadotropins near the ovarian follicles is showing promise in restoring ovarian function. Study results are published online today in Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS).
As more women look to build their careers before pursuing motherhood, the average age of conceiving a child continues to be pushed back. For some of these women, however, their hope of becoming pregnant is cut short by the onset of early menopause, which is described as the cessation of ovarian function ...
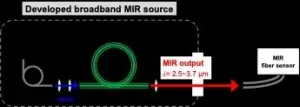
Development of a broadband mid-infrared source for remote sensing
2021-03-31
A research team of the National Institutes of Natural Sciences, National Institute for Fusion Science and Akita Prefectural University have successfully demonstrated a broadband mid-infrared (MIR) source with a simple configuration. This light source generates highly-stable broadband MIR beam at 2.5-3.7 μm wavelength range maintaining the brightness owing to its high-beam quality. Such a broadband MIR source facilitates a simplified environmental monitoring system by constructing a MIR fiber-optic sensor, which has the potential for industrial and medical applications.
In the MIR wavelength region, there are many strong absorption lines of molecules ...
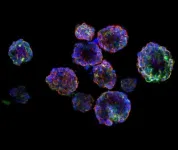
Creation of 3D organoid models to fine-tune radiation dose for nasopharyngeal cancer
2021-03-31
A*STAR's Institute of Bioengineering and Nanotechnology (IBN) has teamed up with Singapore Institute of Advanced Medicine Holdings Pte Ltd (SIAMH) to establish the first of its kind in-vitro patient-derived 3D organoid models of Nasopharyngeal Cancer (NPC).
The study was published in Frontiers in Oncology on 23 February 2021. It is the first direct experimental evidence to predict optimal Radiation Treatment (RT) boost dose required to cause sufficient damage to recurrent hypoxic (low oxygen level) NPC tumour cells, which can be further used to develop dose-painting algorithms in clinical practice.
Two patient-derived xenograft (PDX) ...
Why subsistence consumers need marketplace literacy
2021-03-31
Researchers from Loyola Marymount University, San Diego State University, Indian Institute of Management, and Iowa State University published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that examines how effective marketplace participation by subsistence consumers requires knowledge and skills that relate to what, how, and why to participate.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Marketplace Literacy as a Pathway to a Better World: Evidence from Field Experiments in Low-Access Subsistence Marketplaces" and is authored by Madhu Viswanathan, Nita Umashankar, Arun Sreekumar, and Ashley Goreczny.
Success for marketers looking to emerging markets for growth is inextricably ...
Floating gardens as a way to keep farming despite climate change
2021-03-31
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Bangladesh's floating gardens, built to grow food during flood seasons, could offer a sustainable solution for parts of the world prone to flooding because of climate change, a new study has found.
The study, published recently in the Journal of Agriculture, Food and Environment, suggests that floating gardens might not only help reduce food insecurity, but could also provide income for rural households in flood-prone parts of Bangladesh.
"We are focused here on adaptive change for people who are victims of climate change, but who did not cause climate ...
Lab-made hexagonal diamonds stiffer than natural diamonds
2021-03-31
PULLMAN, Wash. -- Nature's strongest material now has some stiff competition. For the first time, researchers have hard evidence that human-made hexagonal diamonds are stiffer than the common cubic diamonds found in nature and often used in jewelry.
Named for their six-sided crystal structure, hexagonal diamonds have been found at some meteorite impact sites, and others have been made briefly in labs, but these were either too small or had too short of an existence to be measured.
Now scientists at Washington State University's Institute for Shock Physics created hexagonal diamonds large enough to measure ...
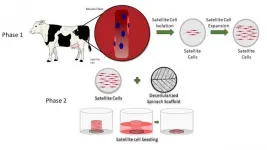
Decellularized spinach serves as an edible platform for laboratory-grown meat
2021-03-31
Chestnut Hill, Mass. (3/31/21) -- Spinach, a cost-efficient and environmentally friendly scaffold, provided an edible platform upon which a team of researchers led by a Boston College engineer has grown meat cells, an advance that may accelerate the development of cultured meat, according to a new report in the advance online edition of the journal Food BioScience.
Stripped of all but its veiny skeleton, the circulatory network of a spinach leaf successfully served as an edible substrate upon which the researchers grew bovine animal protein, said Boston College Professor of Engineering Glenn Gaudette, the lead author of the new study. The results may help increase the production of cellular agriculture ...
The 'one who causes fear' - new meat-eating predator discovered
2021-03-31
Research published today in the peer-reviewed Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology describes a newly discovered species of dinosaur - named the 'one who causes fear', or Llukalkan aliocranianus.
Around 80 million years ago as tyrannosaurs ruled the Northern Hemisphere, this lookalike was one of 10 currently known species of abelisaurids flourishing in the southern continents.
A fearsome killer, Llukalkan was "likely among the top predators" throughout Patagonia, now in Argentina, during the Late Cretaceous due to its formidable size (up to five meters long), extremely powerful ...
Preventive treatment reduces diabetic retinopathy complications
2021-03-31
Early treatment with anti-VEGF injections slowed diabetic retinopathy in a clinical study from the DRCR Retina Network (DRCR.net). However, two years into the four-year study its effect on vision was similar to standard treatment, which usually begins at the onset of late disease. The intermediate findings published today in the JAMA Ophthalmology. The study was supported by the National Eye Institute (NEI), a part of the National Institutes of Health.
"While it is possible that preventive injections of anti-VEGF drugs may help protect vision in the longer-term, ...
Widespread facemask use is vital to suppress the pandemic as lockdown lifts, say scientists
2021-03-31
A new mathematical model suggests that the easing of lockdown must be accompanied by wider and more effective use of control measures such as facemasks even with vaccination, in order to suppress COVID-19 more quickly and reduce the likelihood of another lockdown.
The model, developed by scientists at the Universities of Cambridge and Liverpool, is published today in the Journal of the Royal Society Interface. It uses mathematical equations to provide general insights about how COVID-19 will spread under different potential control scenarios.
Control measures involving facemasks, handwashing and short-scale (1-2 metre) social distancing can all limit the number of virus particles being spread between people. These are termed ...
Scientists show technology can save people from shark bites
2021-03-31
With shark bites increasing in countries like Australia - scientists say the use of personal electronic deterrents is an effective way to prevent future deaths and injuries which could save the lives of up to 1063 Australians along the coastline over the next 50 years.
The research, published in scientific journal Royal Society Open Science, shows that while shark bites are rare events, strategies to reduce shark-bite risk are also valuable because they can severely affect victims and their support groups - with one third of victims experiencing post-traumatic stress ...
Heart attacks in young adults more deadly in those with systemic inflammatory disease
2021-03-31
Heart attacks in young adults are twice as likely to be fatal in those with inflammatory conditions like psoriasis, lupus or rheumatoid arthritis. That's the finding of a study published today in the European Journal of Preventive Cardiology, a journal of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
At least 2% of people in Europe and worldwide have systemic inflammatory diseases, which often affect multiple organ systems. Many of these systemic inflammatory diseases are driven by autoimmunity, meaning the body's immune system attacks itself. Psoriasis is the most common and causes red, itchy, scaly patches on the skin, and can also cause inflammation in the joints. Rheumatoid arthritis leads to inflammation in joints of the hands and feet and in other organ systems. In systemic ...
Scientists discover unique Cornish 'falgae'
2021-03-31
Red algae that grow in Cornwall's Fal Estuary are genetically unique, new research shows.
University of Exeter scientists studied the population genetics of Phymatolithon calcareum, a coralline red algal species that forms maerl beds in shallow coastal seas from Portugal to Norway.
Large maerl beds fulfil a similar role to tropical coral reefs, providing habitats and vital shelter for hundreds or even thousands of fish and invertebrates. These algae also play an important role in storing carbon.
The findings reveal genetic differences are "structured geographically", with slight variations between populations sampled from across this large geographic area.
However, maerl ...
Urban squirrels, how much are we disturbing you?
2021-03-31
Human disturbance in urban environments makes some squirrels fail, but others perform better in novel problem-solving.
Unlike natural environments, urban areas have artificial buildings, traffics, less greenery and, most prominently, more humans. Despite these seemingly 'harsh' or stressful characteristics, some wildlife like the Eurasian red squirrel have chosen to settle down in urban environments, and they thrive. Urban wildlife often show higher behavioral flexibility and increased ability to solve novel problems, and thus can exploit new resources. However, which characteristics of urban environments influence animals' performance, and their relative importance, have remained ...
Scientists discover new genetic disease that delays brain development in children
2021-03-31
Scientists have discovered a new genetic disease, which causes some children's brains to develop abnormally, resulting in delayed intellectual development and often early onset cataracts.
The majority of patients with the condition, which is so new it doesn't have a name yet, were also microcephalic, a birth defect where a baby's head is smaller than expected when compared to babies of the same sex and age.
Researchers from the universities of Portsmouth and Southampton found that changes in a gene called coat protein complex 1 (COPB1) caused this rare genetic disease.
Now the variant has been identified, it will help clinicians come up with targeted interventions to help patients and their families, also opening the door to screening and prenatal ...
Study investigates non-verbal signs of resistance
2021-03-31
A new study examining how people with severe and profound intellectual disabilities resist activities while in care recommends that institutions improve training to help carers better understand non-verbal cues, as well as offer greater flexibility to allow individual preferences to take priority over institutional schedules.
The research, published in the journal Sociology of Health and Illness, investigated how people with limited language ability expressed their wishes and preferences, and how their support workers responded. It was carried out at a residential home and a day care centre in the UK.
The study, by Dr Clare Nicholson of St Mary's University, Twickenham, and Dr Mick ...
[1] ... [2464]
[2465]
[2466]
[2467]
[2468]
[2469]
[2470]
[2471]
2472
[2473]
[2474]
[2475]
[2476]
[2477]
[2478]
[2479]
[2480]
... [8813]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.