The persistent danger after landscape fires
2021-03-26
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) cause oxidative stress at the cellular level. Research shows that this way, amongst others, they inhibit the germination capacity of plants, produce cytotoxins or exert toxic effects on aquatic invertebrates. Environmentally persistent free radicals (EPFR) are potential precursors of ROS because they can react with water to form these radical species. "Therefore, EPFR are associated with harmful effects on the ecosystem and human health," explains Gabriel Sigmund, the lead investigator of the study.
"Our study shows that these environmentally persistent free radicals ...
No increase in colorectal cancer after obesity surgery
2021-03-26
Colorectal cancer risk does not rise after bariatric surgery, a study from the University of Gothenburg shows. This finding is important for patients with obesity, and their healthcare professionals, when deciding upon such an operation.
Obesity is a known risk factor for several types of cancer, including colorectal cancer (affecting the colon or rectum). It is already established that bariatric surgery leads to a decrease in overall cancer risk in patients with obesity.
However, some studies on colorectal cancer have shown an elevated cancer risk after bariatric surgery, while others have reported a risk reduction. ...
Discovery of a third T cell lineage
2021-03-26
The immune systems of all vertebrates contain specialized cells, called T cells, that play a fundamental role in protecting against fungal, bacterial, parasitic and viral infections. T cells use 'molecular sensors' called T cell receptors (TCRs) on their surface that can detect and eliminate the invading pathogens. For most of the past four decades, it was considered that there were only two T cell lineages, αβ and γδ T cells, characterized by their cell surface expressed αβ and γδ TCRs, respectively.
In a paper published today in Science, an international team of scientists at the University of New Mexico (US), Monash University (Australia), and the US National Institutes of Health, has defined a novel T cell lineage, called γμ ...
Shrub willow as a bioenergy crop
2021-03-26
Renewable energy demand and consumption is at an all-time high in the United States.
Shrub willow - a quick-growing woody crop - can be an excellent source of renewable bioenergy. The crop is harvested and turned into wood chips, which can be used for heat, mulch, animal bedding, biochar, and biofuel.
In a new study, researchers grew shrub willow on a semi-commercial scale to better understand the nuances of this bioenergy crop. The research was published in Agronomy Journal, a publication of the American Society of Agronomy.
"We learned and developed key know-hows that we can transfer to industry partners interested in this crop," says Armen Kemanian. Kemanian is a member of the American Society of Agronomy and is the ...
Leap forward' in risk management of rectal cancer
2021-03-26
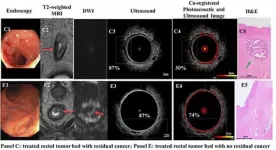
Rectal cancer, along with colon cancer, is the third-most common type of cancer in the United States, and treatment and surgery greatly affect the quality of life of patients. A multi-disciplinary team at Washington University in St. Louis has developed and tested an innovative imaging technique that is able to differentiate between rectal tissues with residual cancers and those without tumors after chemotherapy and radiation, which could one day help to avoid unnecessary surgeries in some patients who have achieved complete tumor destruction after chemoradiation.
Quing Zhu, PhD, professor of biomedical engineering at the McKelvey School of Engineering, and members of her lab developed ...
IQWiG publishes new version of its General Methods - English translation now available
2021-03-26
The Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) revised its methods paper and published the German original version "Allgemeine Methoden 6.0" (General Methods 6.0) on http://www.iqwig.de in November 2020. This document is the basis for the scientific work of the Institute and its external experts as well as for the collaboration with its contracting agencies, the Federal Joint Committee (G-BA) and Federal Ministry of Health (BMG). The English translation is now available on http://www.iqwig.de/en/about-us/methods/methods-paper/.
New features include statements on the investigation of the relationship between volume of services and quality, a section on different treatment periods in studies, and a more concrete approach to the assessment of clinical relevance.
In ...
Sorting out nanodiamonds with fluorescent centers
2021-03-26
Scientists have developed a method to use lasers to control the movement of nanodiamonds with fluorescent centers.
Scientists have long been working on improving their ability to use lasers to move small objects without actually touching them. This method of 'optical trapping and manipulation' is already utilized in optics, biological sciences and chemistry. But objects become much more difficult to control once they grow to nanoscale size.
Now, a team of scientists including Hokkaido University's Keiji Sasaki and Osaka Prefecture University ...
Risk prediction to reduce minority disparities in USPSTF lung cancer screening guidelines
2021-03-26
Leesburg, VA, March 26, 2021--According to ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), updated United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) lung cancer screening (LCS) guidelines based solely on age, pack-years, and quit-years perpetuate eligibility disparities among racial and ethnic minorities, although incorporating certain risk prediction models may help reduce such inequalities.
By pulling data from the 2015 National Health Interview Survey (NHIS), Journal of the National Cancer Institute researchers (Landy et al.) were able to "estimate the effects of USPSTF-2020 guidelines on disparities in LCS eligibility for the non-institutionalized civilian US population," wrote Massachusetts ...
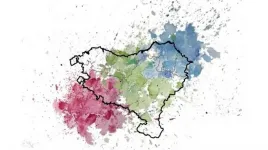
The origin and uniqueness of Basque genetics revealed
2021-03-26
The Basques are a unique population in Western Europe; their language is not related to any Indo-European language. Furthermore, genetically speaking, they have been considered to have distinct features. However, until now there was no conclusive study to explain the origin of their singularity.
Now, an international research team led by UPF has confirmed that the Basques' genetic uniqueness is the result of genetic continuity since the Iron Age, characterized by periods of isolation and scarce gene flow, and not its external origin in respect of other Iberian populations.
The study, led by David Comas, principal investigator at UPF and at the Institute of Evolutionary Biology (IBE: CSIC-UPF), has involved ...
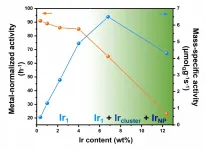
High-loading atomically dispersed Ir/MoC catalyst for hydrogenation reaction
2021-03-26
Atomically dispersed catalysts have received extensive research attention, because they exhibit excellent activity and unique selectivity for many important catalytic reactions. The atomically dispersed nature of these metal catalysts confers their unique electronic structures as well as designated coordination-unsaturated environments for the optimized adsorption/activation of the reactants. One grand challenge faced by these atomically dispersed catalysts is that the supported isolated metal \atoms are usually thermally unstable and tend to aggregate into large clusters/particles at evaluated reaction temperatures. As a result, most reported atomically dispersed catalysts have an extremely low metal loading below ...
Climate change significantly increases population displacement risk
2021-03-26
Every year, millions of people around the world are displaced from their homes due to severe weather caused by climate change. According to the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement, 10.3 million people were displaced as a result of climate-?related events in the last six months alone - four times the number displaced by war and conflict in the same period. One of the main causes of displacement is flooding. A recent example is the situation in eastern Australia, where tens of thousands of people are having to flee their homes to seek safety from this hundred-?year flood.
An international research team led by the Weather ...
Robust cell junctions are critical for maintaining stem cell function
2021-03-26
The skin is the largest organ in the human body, and its outermost part, called the epidermis, is replenished every three weeks. The cells fueling this renewal of the epidermal stem cells, found in specialized areas or niche, within a region of the hair follicle (or root) is known as the 'bulge compartment'. The bulge compartment resident stem cells are multipotent meaning that they can contribute to the repair of skin when it's injured, and also regenerate the hair follicles during normal development. While several groups have focused attention on the stem cells themselves, less is known about niche or extrinsic factors that influence the state of these stem cells.
In the recent paper published in the Developmental Cell, ...
Incurable Leigh Syndrome: German scientists create first human model for rare disease
2021-03-26
Leigh syndrome is the most severe mitochondrial disease in children. It causes severe muscle weakness, movement defects, and intellectual disabilities. It usually leads to death within the first years of life. No causative treatment is currently available. One of the genes frequently mutated in patients is SURF1, which encodes for a protein involved in the process of energy generation in the cells. Animal models did not recapitulate the defects seen in the patients carrying mutations in SURF1. Therefore, the scientists did not have the tool to start understanding the disease mechanisms and to identify possible targets for treatment. They report about the first ...
Scent of a species
2021-03-26
Apple flies have fascinated scientists right from the mid-19th century, as they are a captivating example of speciation, the beginning of a new species. Correspondence between Charles Darwin and Benjamin Walsh, who observed the apple flies and hawthorn flies in North America, began the rich history of this scientific question in evolutionary biology. When settlers in North America introduced apple trees to the region, what happened within the hawthorn flies to make them shift to this new host plant in the last 300 years?
Continuing the 160-year-old inquiry into the origins of the apple fly, a team of scientists from around the world has just published their research in the Proceedings of the Royal Society B. The researchers span three continents, from the National Centre for Biological ...
Slc20a1b is essential for hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell expansion in zebrafish
2021-03-26
Hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells (HSPCs) include hematopoietic stem cells and several lineage-biased hematopoietic progenitor cells, which can provide all blood cell types in an adult organism. Among them, hematopoietic stem cells have the ability of self-renewal and multi-lineage differentiation, and can rapidly respond under acute hematopoietic conditions. Meanwhile, the hematopoietic progenitor cells can maintain the supply of blood cells in homeostatic hematopoiesis. In a word, HSPCs are the core of the blood system, once their homeostasis is destroyed, it will lead to serious blood diseases and even death. Therefore, the researches associated with the HSPCs can provide a strong support for relevant ...
Dogs (not) gone wild: DNA tests show most 'wild dogs' in Australia are pure dingoes
2021-03-26
Almost all wild canines in Australia are genetically more than half dingo, a new study led by UNSW Sydney shows - suggesting that lethal measures to control 'wild dog' populations are primarily targeting dingoes.
The study, published today in Australian Mammalogy, collates the results from over 5000 DNA samples of wild canines across the country, making it the largest and most comprehensive dingo data set to date.
The team found that 99 per cent of wild canines tested were pure dingoes or dingo-dominant hybrids (that is, a hybrid canine with more than 50 per cent dingo genes).
Of the remaining ...
UCI study finds high-fiber diet brings significant changes to human gut microbiome
2021-03-26
Irvine, Calif., March 25, 2021 -- A short-term intervention in daily fiber consumption can significantly alter the gut microbiome and nutrient intake, according to a study led by University of California, Irvine researchers. The research was recently published by the American Society for Microbiology.
Dietary fiber consists of resistant carbohydrates found in fruits, vegetables and whole grains. Fiber persists in our digestion system, and while not digestible by humans, our gut bacteria can metabolize fiber into short-chain fatty acids and other byproducts critical to human health.
Currently, the average person in North America consumes less than 50 percent of the recommended dietary ...
Study exposes global ripple effects of regional water scarcity
2021-03-26
Water scarcity is often understood as a problem for regions experiencing drought, but a new study led by Tufts University researchers finds that not only can localized water shortages impact the global economy, but changes in global demand can have positive and negative ripple effects in river basins across the globe.
In addition to Tufts engineers, the team included experts from the Joint Global Change Research Institute at the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, and Cornell University.
"We're finding that water scarcity dynamics are more complicated than traditionally acknowledged," said Flannery Dolan, a graduate student ...
AI used in battle against asbestos-linked cancer
2021-03-26
International genomics research led by the University of Leicester has used artificial intelligence (AI) to study an aggressive form of cancer, which could improve patient outcomes.
Mesothelioma is caused by breathing asbestos particles and most commonly occurs in the linings of the lungs or abdomen. Currently, only seven per cent of people survive five years after diagnosis, with a prognosis averaging 12 to 18 months.
New research undertaken by the Leicester Mesothelioma Research Programme has now revealed, using AI analysis of DNA-sequenced mesotheliomas, that they evolve along similar or repeated paths between individuals. These paths predict the aggressiveness and possible therapy of this otherwise incurable cancer.
Professor ...
CTC mutations may predict outcomes in some castrate-resistant prostate cancer patients
2021-03-26
Bottom Line: Various genetic alterations in circulating tumor cells (CTCs) were associated with clinical outcomes and resistance to hormone therapy in patients with metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC).
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Molecular Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research
Author: Andrew Armstrong, MD, MSc, a medical oncologist at the Duke Cancer Institute Center for Prostate and Urologic Cancers at Duke University
Background: While only a minority of men with mCRPC have primary resistance to the androgen receptor (AR) inhibitors enzalutamide (Xtandi) or abiraterone acetate (Yonsa or Zytiga), most men will ...
Measurable changes in brain activity during first few months of studying a new language
2021-03-26
A study with first-time learners of Japanese has measured how brain activity changes after just a few months of studying a new language. The results show that acquiring a new language initially boosts brain activity, which then reduces as language skills improve.
"In the first few months, you can quantitatively measure language-skill improvement by tracking brain activations," said Professor Kuniyoshi L. Sakai, a neuroscientist at the University of Tokyo and first author of the research recently published in Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience.
Researchers followed 15 volunteers as they moved to Tokyo and completed introductory Japanese classes for at least three hours each day. All volunteers ...
Physicians' financial conflicts of interest may play a role in black lung diagnoses
2021-03-26
March 23, 2021-- A new study published online in the Annals of the American Thoracic Society examines if the source of physician payment for a medical opinion influences whether the physician finds that a coal miner has black lung disease. The study is the first to look at this relationship in the workers' compensation process.
In "Association Between Financial Conflicts of Interest and ILO Classifications for Black Lung Disease," Lee S. Friedman, PhD, associate professor, School of Public Health, Division of Environmental and Occupational Health Sciences, University of Illinois Chicago and colleagues looked at which party reimbursed B-readers--physicians trained and licensed by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) and approved by the U.S. ...
Study reveals bias among doctors who classify X-rays for coal miner's black lung claims
2021-03-26
University of Illinois Chicago researchers are the first to report on the financial conflicts of interest that exist among doctors who review the chest X-rays of coal miners who file workers' compensation claims of totally disabling disease with the U.S. Department of Labor's Federal Black Lung Program.
The UIC researchers found that the determinations of these doctors - who are known as B-readers and who are certified by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, or NIOSH - were strongly associated with the party that hired them.
By analyzing ...
X-rays combined with AI offer fast diagnostic tool in detecting COVID-19
2021-03-26
X-rays, first used clinically in the late 1890s, could be a leading-edge diagnostic tool for COVID-19 patients with the help of artificial intelligence, according to a team of researchers in Brazil who taught a computer program, through various machine learning methods, to detect COVID-19 in chest X-rays with 95.6 to 98.5% accuracy.
They published their results in IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, a joint publication of the IEEE and the Chinese Association of Automation.
The researchers have previously focused on detecting and classifying ...
School closures disproportionately hit disadvantaged students in the US
2021-03-26
The uneven distribution of school closures in the US since September 2020 threatens to exacerbate regional, racial and class-based divides in educational performance, according to research by Zachary Parolin, of Bocconi University's Department of Social and Political Science, recently published in Nature Human Behavior. For example, in October, only 35% of White students were on distance learning, compared with 52% of Black students, 60% of Hispanic students and 65% of Asian students. And schools recording the lowest math scores were 15% more likely to be closed.
Professor Parolin and Emma Lee (Columbia University) found in fact that exposure ...
[1] ... [2482]
[2483]
[2484]
[2485]
[2486]
[2487]
[2488]
[2489]
2490
[2491]
[2492]
[2493]
[2494]
[2495]
[2496]
[2497]
[2498]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.