Urban 'escalator' means disadvantaged rural students miss out on top universities
2021-03-25
Bright but disadvantaged students from urban areas are more likely to enter elite UK universities than similar peers from rural communities due to an urban 'escalator effect', according to a new study.
Researchers from the University of Bath analysed data from 800,000 English students commencing university in the years 2008, 2010, 2012, 2014 and 2016.
They found that while in general rural areas had higher overall progression to university than city centres and surrounding areas, when controlling for factors including socio-economic status, age, ethnicity and sex, disadvantaged pupils from rural areas were less likely to progress to one of 27 'top' UK universities.
The authors suggest the difference ...
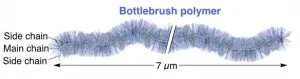
The world's longest bottlebrush polymer ever synthesized
2021-03-25
NIMS and RIKEN have succeeded in synthesizing the longest ever bottlebrush polymer. This polymer--resembling a green foxtail--is composed of a main chain and numerous side chains grafting from it. The team also succeeded in giving various chemical properties to the ultralong bottlebrush polymer. These achievements are expected to substantially advance the current synthetic methods of bottlebrush polymers. This technique may be applicable to the development of flexible and low-friction polymeric materials.
In the development of polymeric materials, it is necessary to link molecular units with desired chemical properties, called monomers, to ...
Scientists first realized real-time GW-BSE investigations on Spin-Valley exciton dynamics
2021-03-25
Prof. ZHAO Jin's research team from University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) has made important progress in the development of Spin-Valley exciton dynamics. The research developed an ab initio nonadiabatic molecular dynamics (NAMD) method based on for the spin-resolved exciton dynamics. The team gained the first clear and complete physical picture of valley exciton dynamics in MoS2 from the perspective of first-principles calculations based on GW plus real-time Bethe-Salpeter equation (GW + rtBSE-NAMD).
It can accurately include many-body effects at the level of first principles and break through the bottleneck of GW+BSE method in ...
Revealing nano big bang -- Scientists observe the first milliseconds of crystal formation
2021-03-25
When we grow crystals, atoms first group together into small clusters - a process called nucleation. But understanding exactly how such atomic ordering emerges from the chaos of randomly moving atoms has long eluded scientists.
Classical nucleation theory suggests that crystals form one atom at a time, steadily increasing the level of order. Modern studies have also observed a two-step nucleation process, where a temporary, high-energy structure forms first, which then changes into a stable crystal. But according to an international research team co-led by the ...
More protein doesn't mean more strength in resistance-trained middle-aged adults
2021-03-25
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- A 10-week muscle-building and dietary program involving 50 middle-aged adults found no evidence that eating a high-protein diet increased strength or muscle mass more than consuming a moderate amount of protein while training. The intervention involved a standard strength-training protocol with sessions three times per week. None of the participants had previous weightlifting experience.
Published in the American Journal of Physiology: Endocrinology and Metabolism, the study is one of the most comprehensive investigations of the health effects of diet and resistance training in middle-aged adults, the researchers say. Participants were 40-64 years ...
Fossil fuel companies benefit from inefficient pricing on climate and health consequences
2021-03-25
Fossil fuel producers in the U.S. are directly benefiting from implicit subsidies on the order of $62 billion a year because of inefficient pricing that doesn't properly account for the costs of damages to the environment, climate, and human health.
That's the finding of a newly published study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) by Yale School of the Environment Economics Professor Matthew Kotchen that analyzed gasoline, natural gas, diesel, and coal.
The total annual implicit subsidy is equivalent to an average of 3% of the U.S. gross domestic product, according to the study which examined data from 2010-2018. ...
Want a longer, healthier life? Resolve your arguments by day's end, OSU study says
2021-03-25
A recent Oregon State University study found that when people feel they have resolved an argument, the emotional response associated with that disagreement is significantly reduced and, in some situations, almost entirely erased.
That reduction in stress may have a major impact on overall health, researchers say.
"Everyone experiences stress in their daily lives. You aren't going to stop stressful things from happening. But the extent to which you can tie them off, bring them to an end and resolve them is definitely going to pay dividends in terms of your well-being," said Robert Stawski, senior author on the study and an associate professor ...
GSA's journals add new research articles on COVID-19 and aging
2021-03-25
The Gerontological Society of America's highly cited, peer-reviewed journals are continuing to publish scientific articles on COVID-19. The following were published between January 8 and March 15; all are free to access:
Comment on: "Beyond chronological age: Frailty and multimorbidity predict in-hospital mortality in patients with coronavirus disease 2019": Letter to the editor in The Journals of Gerontology, Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences by Noémie Girard, MS, Geoffrey Odille, MS, Stéphane Sanchez, MD, Sarah Lelarge, ...
Distinctively Black names found long before Civil War
2021-03-25
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Long before Tyrone, Jermaine and Darnell came along, there were Isaac, Abe and Prince.
A new study reveals the earliest evidence of distinctively Black first names in the United States, finding them arising in the early 1700s and then becoming increasingly common in the late 1700s and early 1800s.
The results confirm previous work that shows the use of Black names didn't start during the civil rights movement of the 1960s, as some scholars have argued, said Trevon Logan, co-author of the study and professor of economics at The Ohio State University.
"Even ...
Two new species of already-endangered screech owls discovered in Amazon rainforest
2021-03-25
The Amazon rainforest is teeming with creatures unknown to science--and that's just in broad daylight. After dark, the forest is a whole new place, alive with nocturnal animals that have remained even more elusive to scientists than their day-shift counterparts. In a new paper in Zootaxa, researchers described two new species of screech owls that live in the Amazon and Atlantic forests, both of which are already critically endangered.
"Screech owls are considered a well-understood group compared to some other types of organisms in these areas," says John Bates, curator of birds at the Field Museum in Chicago and one of the study's authors. "But when you start listening to them and comparing ...
New light on baryonic matter and gravity on cosmic scales
2021-03-25
Scientists estimate that dark matter and dark energy together are some 95% of the gravitational material in the universe while the remaining 5% is baryonic matter, which is the "normal" matter composing stars, planets, and living beings. However for decades almost one half of this matter has not been found either. Now, using a new technique, a team in which the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) has participated, has shown that this "missing" baryonic matter is found filling the space between the galaxies as hot, low density gas. The same technique also gives a new tool that shows that the gravitational attraction experienced by ...
Researchers use machine learning to rank cancer drugs in order of efficacy
2021-03-25
Researchers from Queen Mary University of London have developed a machine learning algorithm that ranks drugs based on their efficacy in reducing cancer cell growth. The approach may have the potential to advance personalised therapies in the future by allowing oncologists to select the best drugs to treat individual cancer patients.
The method, named Drug Ranking Using Machine Learning (DRUML), was published today in Nature Communications and is based on machine learning analysis of data derived from the study of proteins expressed in cancer cells. Having been trained on ...
MIT engineers make filters from tree branches to purify drinking water
2021-03-25
The interiors of nonflowering trees such as pine and ginkgo contain sapwood lined with straw-like conduits known as xylem, which draw water up through a tree's trunk and branches. Xylem conduits are interconnected via thin membranes that act as natural sieves, filtering out bubbles from water and sap.
MIT engineers have been investigating sapwood's natural filtering ability, and have previously fabricated simple filters from peeled cross-sections of sapwood branches, demonstrating that the low-tech design effectively filters bacteria.
Now, the same team has advanced the technology and shown that it works in real-world situations. They have fabricated new xylem filters that can filter out pathogens ...
Scientists find evidence that novel coronavirus infects the mouth's cells
2021-03-25
An international team of scientists has found evidence that SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, infects cells in the mouth. While it's well known that the upper airways and lungs are primary sites of SARS-CoV-2 infection, there are clues the virus can infect cells in other parts of the body, such as the digestive system, blood vessels, kidneys and, as this new study shows, the mouth. The potential of the virus to infect multiple areas of the body might help explain the wide-ranging symptoms experienced by COVID-19 patients, including oral symptoms such as taste loss, ...
Frequent consumption of meals prepared away from home associated with an increased risk of death
2021-03-25
Philadelphia, March 25, 2021 - Dining out is a popular activity worldwide, but there has been little research into its association with health outcomes. Investigators looked at the association between eating out and risk of death and concluded that eating out very frequently is significantly associated with an increased risk of all-cause death, which warrants further investigation. Their results appear in the Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, published by Elsevier.
Eating out is a popular activity. The US Department of Agriculture recently estimated that Americans' daily energy intake from food away from home increased from 17 percent in 1977-1978 to 34 percent in 2011-2012. At the same time, the number of restaurants has ...
Preservative used in hundreds of popular foods may harm the immune system
2021-03-25
WASHINGTON - A food preservative used to prolong the shelf life of Pop-Tarts, Rice Krispies Treats, Cheez-Its and almost 1,250 other popular processed foods may harm the immune system, according to a new peer-reviewed study by Environmental Working Group.
For the study, published this week in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, EWG researchers used data from the Environmental Protection Agency's Toxicity Forecaster, or ToxCast, to assess the health hazards of the most common chemicals added to food, as well as the "forever chemicals" known as PFAS, which can migrate to food from packaging.
EWG's analysis of ToxCast data showed that the preservative tert-butylhydroquinone, ...
Failed your New Year resolution again? Join the club
2021-03-25
New Edith Cowan University (ECU) research has found that despite having the best intentions, most people give up on their New Year resolutions within the first month.
The study also revealed that approximately half the people surveyed had the same, or nearly the same, resolution as in the previous year, and more than half of the resolutions listed focused on either diet or exercise.
The research, led by ECU Associate Professor Joanne Dickson, investigated personal goal factors that predicted greater wellbeing and sticking with one's most important New Year resolution over time. Around 180 Australian and UK participants took part in an online survey over a two-month period. ...
Inhibiting impact of dust aerosols on eastern Pacific tropical cyclones from the perspective of energy transmission
2021-03-25
The thermodynamic state of the tropical atmosphere plays an important role in the development of tropical cyclone (TC) intensity. A TC imports thermodynamic energy from ocean-air heat and moisture fluxes and exports heat aloft at the much colder upper troposphere, through a radially and vertically directed overturning circulation in a TC. The work done through this cycle drives the TC's winds.
A negative response of cloud water in the lower troposphere to dust aerosol optical depth (AOD) has recently been reported in Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aosl.2020.100028) by Dr. Zhenxi Zhang from the Inner Mongolia University of Technology, Hohhot, China, by analyzing MERRA-2 reanalysis data and GCM simulations from CMIP6.
"The ...
Anabolic androgenic steroids accelerate brain aging
2021-03-25
Philadelphia, March 25, 2021 - Anabolic androgenic steroids (AAS), a synthetic version of the male sex hormone testosterone, are sometimes used as a medical treatment for hormone imbalance. But the vast majority of AAS is used to enhance athletic performance or build muscle because when paired with strength training. AAS use increases muscle mass and strength, and its use is known to have many side effects, ranging from acne to heart problems to increased aggression. A new study now suggests that AAS can also have deleterious effects on the brain, causing it to age prematurely.
The report appears in Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and ...
Technology uses 'single' approach to develop electronics, acoustics
2021-03-25
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - A Purdue University innovator has developed a new approach to creating popular thin films used for devices across a broad range of fields, including optics, acoustics and electronics.
Epitaxial lithium niobate (LNO) thin films are an attractive material for electronics and other devices. These films offer flexibility and other properties that are important to manufacturers.
The challenge is that these devices demand high-quality thin films that can be difficult to grow and produce. Haiyan Wang, a Purdue materials engineer, developed a new approach to creating these films. The work is published in Advanced Photonics Research.
"We created an approach ...
NCCN 2021 Virtual Annual Conference addresses cancer care in a year of crisis and innovation
2021-03-25
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [March 25, 2021] -- New recommendations to advance racial equity, ways to mitigate the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on cancer care, and ongoing strategies for preventing and controlling HPV-associated cancers led the conversation at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®) 2021 Virtual Annual Conference March 18-20. More than 1,300 attendees from across the United States and more than 40 countries met online to learn about updates to the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) and new research in the field. Sessions explored supportive care and ways to help survivors return to work, updates on best ...
Revealing complex behavior of a turbulent plume at the calving front of a Greenlandic glacier
2021-03-25
For the first time, scientists have succeeded in continuous monitoring of a subglacial discharge plume, providing a deeper understanding of the glacier-fjord environment.
As marine-terminating glaciers melt, the fresh water from the glacier interacts with the seawater to form subglacial discharge plumes, or convective water flows. These turbulent plumes are known to accelerate the melting and breakup (calving) of glaciers, drive fjord-scale circulation and mixing, and create foraging hotspots for birds. Currently, the scientific understanding of the dynamics of subglacial plumes based on direct measurements is limited to isolated instances.
A team of scientists consisting of Hokkaido University's Assistant Professor Evgeny A. Podolskiy and Professor Shin Sugiyama, and the ...
Genome sequenced for pesky pumpkin pathogen
2021-03-24
URBANA, Ill. - Pumpkin growers dread the tiny tan scabs that form on their fruit, each lesion a telltale sign of bacterial spot disease. The specks don't just mar the fruit's flesh, they provide entry points for rot-inducing fungus and other pathogens that can destroy pumpkins and other cucurbits from the inside out. Either way, farmers pay the price, with marketable yields reduced by as much as 90%.
Despite the disease's severity, scientists don't know much about the genetics of the pathogen that causes it; nearly all the molecular information required for accurate diagnostic testing and targeted treatments is lacking for the disease.
In a new study, University of Illinois scientists, with the help of two undergraduate students, have assembled the first complete ...
Harvard, Smithsonian astronomers help capture first image of black hole's magnetic fields
2021-03-24
Cambridge, MA - Astronomers have now obtained a new view of the supermassive black hole at the center of galaxy M87. Images released today by the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) collaboration reveal how the black hole, some 55 million light-years away, appears in polarized light.
The image marks the first time astronomers have captured and mapped polarization, a sign of magnetic fields, so close to the edge of a black hole.
Scientists still don't understand how magnetic fields -- areas where magnetism affects how matter moves -- influence black hole activity. Do they help direct matter into the hungry mouths of black holes? Can ...
COVID-19 vaccines may not produce sufficient antibody response in transplant recipients
2021-03-24
When clinical trials were conducted to determine the immunogenicity -- the ability to elicit an immune response -- for the first two vaccines marshaled against SARS-CoV-2the virus that causes COVID-19, one group was not among those included: people who have received solid organ transplants and others (such as those with autoimmune disorders) who are immunocompromised.
Now, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers have tried to rectify that inequity, taking one of the first looks at how people who are immunocompromised respond to their first dose of one of the two mRNA vaccines -- Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech -- currently being administered worldwide. Their findings, as published March 15, 2021, in a research letter in the END ...
[1] ... [2488]
[2489]
[2490]
[2491]
[2492]
[2493]
[2494]
[2495]
2496
[2497]
[2498]
[2499]
[2500]
[2501]
[2502]
[2503]
[2504]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.