Survey of Geisinger employees shows increasing acceptance of COVID-19 vaccines
2021-03-24
DANVILLE, Pa. - A survey of Geisinger employees conducted over two weeks in December 2020 found a steady increase in intent among healthcare workers to receive the COVID-19 vaccine.
On Dec. 4, 2020, an announcement about anticipated vaccine availability was emailed to all 23,784 Geisinger employees. Recipients were asked to indicate their intention to receive a vaccine when one was available to them and the reasons for any hesitation they might have. More than two-thirds of employees responded to the survey.
Of those who completed the survey before Dec. 10, when an independent FDA advisory committee ...
Vaccine science and side effects: How news messages affect views on vaccination
2021-03-24
News coverage of expert scientific evidence on vaccine safety is effective at increasing public acceptance of vaccines, but the positive effect is diminished when the expert message is juxtaposed with a personal narrative about real side effects, new research has found.
The study, by researchers affiliated with the Annenberg Public Policy Center (APPC) of the University of Pennsylvania and the University of Illinois, tested the effects of messages about vaccination in televised news reports. These included video clips of Dr. Anthony Fauci, director of the U.S. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, talking about evidence supporting the value and safety of the MMR (measles, mumps and rubella) vaccine, and a mother who's refusing to vaccinate ...
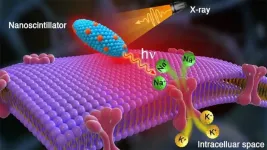
Shining a healing light on the brain
2021-03-24
Scientists make pivotal discovery of method for wireless modulation of neurons with X-rays that could improve the lives of patients with brain disorders. The X-ray source only requires a machine like that found in a dentist's office.
Many people worldwide suffer from movement-related brain disorders. Epilepsy accounts for more than 50 million; essential tremor, 40 million; and Parkinson's disease, 10 million.
Relief for some brain disorder sufferers may one day be on the way in the form of a new treatment invented by researchers from the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory and ...
Group testing method developed for COVID-19
2021-03-24
Researchers Mario Guarracino the HSE Laboratory of Algorithms and Technologies for Networks Analysis in Nizhny Novgorod and Julius ?ilinskas and Algirdas Lančinskas from Vilnius University, have proposed a new method of testing for COVID-19. This group method allows results to be obtained 13 times faster as compared to individual testing of each sample. The research paper was published in the journal Scientific Reports.
The COVID-19 pandemic has already affected millions of people from over 200 countries. The rapid virus expansion demonstrated how fast such infections can spread in today's globalized world. At the beginning of the pandemic, when little was known about the virus and vaccines had not yet ...
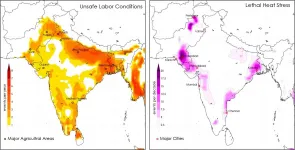
Deadly heat waves will be common in South Asia, even at 1.5 degrees of warming
2021-03-24
WASHINGTON--Residents of South Asia already periodically experience heat waves at the current level of warming. But a new study projecting the amount of heat stress residents of the region will experience in the future finds with 2 degrees Celsius of warming, the population's exposure to heat stress will nearly triple.
Limiting warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius will likely reduce that impact by half, but deadly heat stress will become commonplace across South Asia, according to the new study in Geophysical Research Letters, AGU's journal publishing high-impact, short-format reports with immediate implications spanning all Earth and space sciences.
With ...
Zooming in on muscle cells
2021-03-24
An old technique flexes its muscles
Sarcomeres are small repeating subunits of myofibrils, the long cylinders that bundle together to make the muscle fibres. Inside the sarcomeres, filaments of the proteins myosin and actin interact to generate muscle contraction and relaxation. So far, traditional experimental approaches to investigate the structure and function of muscle tissue were performed on reconstructed protein complexes or suffered from low resolution. "Electron cryo-tomography, instead, allows us to obtain detailed and artefact-free 3D images of the frozen muscle", says Raunser.
Cryo-ET was for a long time an established yet niche methodology. But recent technical advances in electron cryo-microscopy (cryo-EM) as well as the new development of ...
Decline in black cherry regeneration may herald wider forest change
2021-03-24
In the heart of black cherry's native range, including a part of the Allegheny Hardwoods that bills itself as the "Black Cherry Capital of the World," the tree's regeneration, growth and survival have all been declining for more than a decade. In a new analysis, a team of USDA Forest Service and University of Missouri scientists identify likely factors behind the tree's decline and, more significantly, conclude that black cherry may be the tip of the iceberg in terms of change in eastern deciduous forests.
Scientists used a combination of synthesis of existing research and new analyses to examine the leading hypotheses for black cherry's regeneration failure. They conclude that the two factors that are ...
Programs help shield Black youth from effects of racism
2021-03-24
Family-centered prevention programs that foster protective caregiving can buffer the negative effects of racial discrimination on young Black people, according to a study published by University of Georgia researchers.
Research shows that Black youth exposed to various levels of racial discrimination--including slurs, threats and false accusations--are at a high risk for poor mental health outcomes such as hopelessness, conduct problems, drug use and depression. After participating in family-oriented programs, high school-age adolescents who encountered high levels of racial discrimination and received supportive caregiving evinced fewer increases in conduct problems and depression/anxiety symptoms two years later.
"This research shows that ...
Reading between the diamonds
2021-03-24
The high temperatures and pressures of the Earth's mantle forge carbon-rich minerals known as carbonates into diamond. But less is known about the fate of carbonates that travel even deeper underground -- depths from which no sample has ever been recovered.
Now, Michigan State University's Susannah Dorfman and her team are unearthing an answer with lab tools that mimic these extreme conditions.
"What we were interested in is, when is carbon not diamond?" added Dorfman.
In a paper recently published in Nature Communications, scientists in Dorfman's Experimental ...
Aerosol formation in clouds
2021-03-24
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have studied for the first time how chemical reactions in clouds can influence the global climate. They found that isoprene, the dominant non-methane organic compound emitted into the atmosphere, can strongly contribute to the formation of organic aerosols in clouds. They published their results today in the journal Science Advances.
Aerosols, a mixture of solid or liquid particles suspended in the air, play an important role in Earth's climate. Aerosols originate either from natural or human sources. They influence Earth's radiation balance by interacting with sunlight and forming clouds. However, their effect remains the single most significant uncertainty ...
New cancer immunotherapy recruits help from lymphatic vessels
2021-03-24
CHICAGO -- Immunotherapy, which recruits the body's own immune system to attack cancer, has given many cancer patients a new avenue to treat the disease.
But many cancer immunotherapy treatments can be expensive, have devastating side effects, and only work in a fraction of patients.
Researchers at the Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering at the University of Chicago have developed a new therapeutic vaccine that uses a patient's own tumor cells to train their immune system to find and kill cancer.
The vaccine, which is injected into the skin just like a traditional vaccine, stopped ...
An overlooked strand of the Southern San Andreas Fault may pose a major earthquake risk
2021-03-24
Addressing uncertainties about where large earthquakes are most likely to occur along the southern San Andreas fault, which splits into multiple strands east of Los Angeles, a new study identifies a strand that has largely flown under the radar of public concern as the region's greatest earthquake threat. The study determines that the Mission Creek strand, which passes through major water and power infrastructure for the greater Los Angeles region, may account for almost the entire slip rate of this portion of the fault, suggesting it may actually be the primary Pacific-North American plate boundary fault at this latitude. The San Andreas fault threatens large future earthquakes, since its southernmost section has not ruptured in almost 300 years ...
Greenland caves: Time travel to a warm Arctic
2021-03-24
A 12-centimetre-thick sample of a deposit from a cave in the northeast of Greenland offers unique insights into the High Arctic's climate more than 500,000 years ago. The geologist and cave scientist Prof. Gina Moseley collected it during an exploratory expedition in 2015 for her palaeoclimatic research in one of the most sensitive areas of the world to climate change. The cave is located at 80° North 35 km from the coast and 60 km from the Greenland Ice Sheet margin. It was part of the Greenland Caves Project, funded by 59 different sponsors including the National Geographic Society. Moseley and her team are interested in the climate and environmental history captured by the unique cave deposit. "Mineral deposits formed ...
Approved medications preserve platelets and protect mice from bacterial blood infections
2021-03-24
A study of 49 patients reveals that toxins from the bacterial pathogen Staphylococcus aureus can destroy the body's blood-clotting platelets, raising the risk of death during bacterial blood infections. Further experiments in mice also showed that the approved drugs ticagrelor and oseltamivir protected platelets and helped treat infections, suggesting these compounds could be repurposed into badly needed therapies for blood infections. Bacterial blood infections have mortality rates as high as 20% to 30% even with supportive care, and these rates have remained high for decades. Blood infections can also cause complications such as sepsis and endocarditis, and the rise of multidrug resistance has only compounded what was already a serious ...
Exploiting cancer cells to aid in their own destruction
2021-03-24
Immunotherapy, which recruits the body's own immune system to attack cancer, has given many cancer patients a new avenue to treat the disease.
But many cancer immunotherapy treatments can be expensive, have devastating side effects, and only work in a fraction of patients.
Researchers at the Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering at the University of Chicago have developed a new therapeutic vaccine that uses a patient's own tumor cells to train their immune system to find and kill cancer.
The vaccine, which is injected into the skin just like a traditional vaccine, stopped melanoma tumor growth in mouse models. It even worked long-term, destroying new tumors long after the therapy was given.
The results were published ...
Green leafy vegetables essential for muscle strength
2021-03-24
Eating just one cup of leafy green vegetables every day could boost muscle function, according to new Edith Cowan University (ECU) research.
The study, published today in the Journal of Nutrition, found that people who consumed a nitrate-rich diet, predominantly from vegetables, had significantly better muscle function of their lower limb.
Poor muscle function is linked to greater risk of falls and fractures and is considered a key indicator of general health and wellbeing.
Researchers examined data from 3,759 Australians taking part in Melbourne's Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute AusDiab study over a 12-year ...
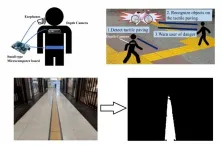
Stay on track! Support system to help the visually impaired navigate tactile paving
2021-03-24
Sight is by far the sense that we humans use the most when navigating an environment. When those who are blind or visually impaired walk alone, they put themselves at great risk of falling or colliding with obstacles, especially when traversing new places. Unfortunately, the number of visually impaired people throughout the world is likely to increase in the near future because of the rapidly aging population. Thus, there is an urgent need for innovative and cost-effective solutions to help visually impaired people navigate safely.
A promising strategy that was first implemented in Japan and then replicated throughout the world is called tactile paving. Inspired by Braille, the reading system of the blind, tactile paving essentially consists of ...
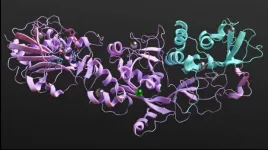
'Silencing' protein to weaken COVID-19
2021-03-24
When invaded by a virus, our body cells launch an alert to neighboring cells to increase their antiviral defenses to prevent the infection from spreading. Some viruses, however, manage to bypass this system by mimicking the host's RNA, preventing them from being detected by the infected cell and avoiding this alert. In the case of SARS-CoV-2, this mimicking uses a protein known as nsp14. This protein is also very important for virus multiplication, a task which is facilitated by its binding to the nsp10 protein, resulting in a protein complex. Interfering with nsp14 binding and with the nsp10-nsp14 protein complex is the aim of the most recent ITQB NOVA research in COVID-19, led by researchers Margarida Saramago, Rute Matos and Cecília Arraiano.
The researchers ...
Photosynthesis could be as old as life itself
2021-03-24
Researchers find that the earliest bacteria had the tools to perform a crucial step in photosynthesis, changing how we think life evolved on Earth.
The finding also challenges expectations for how life might have evolved on other planets. The evolution of photosynthesis that produces oxygen is thought to be the key factor in the eventual emergence of complex life. This was thought to take several billion years to evolve, but if in fact the earliest life could do it, then other planets may have evolved complex life much earlier than previously thought.
The ...
New machine learning tool diagnoses electron beams in an efficient, non-invasive way
2021-03-24
Beams of accelerated electrons power electron microscopes, X-ray lasers, medical accelerators and other devices. To optimize the performance of these applications, operators must be able to analyze the quality of the beams and adjust them as needed.
For the past few years, researchers at the Department of Energy's SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory have been developing "virtual diagnostics" that use machine learning to obtain crucial information about beam quality in an efficient, non-invasive way. Now, a new virtual diagnostic approach, published in Scientific Reports, incorporates additional information about the beam that allows the method to work in situations where conventional ...
Stanford economist and others assess aquaculture's promise and peril
2021-03-24
Despite aquaculture's potential to feed a growing world population while relieving pressure on badly depleted oceans, the industry has been plagued by questions about its environmental impacts. (Watch related video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DG_nl7-naYo)
But over the years, the diverse industry - which ranges from massive open-ocean salmon cages to family farm freshwater tilapia ponds - has made significant strides toward sustainability, according to a new Stanford-led analysis.
The study notes, however, that in order for the global aquaculture sector to deliver on its full promise, more effective oversight measures are ...
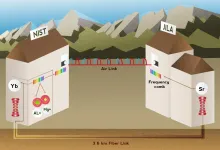
NIST team compares 3 top atomic clocks with record accuracy over both fiber and air
2021-03-24
In a significant advance toward the future redefinition of the international unit of time, the second, a research team led by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has compared three of the world's leading atomic clocks with record accuracy over both air and optical fiber links.
Described in the March 25 issue of Nature, the NIST-led work is the first to compare three clocks, based on different atoms, and the first to link the most advanced atomic clocks in different locations over the air. These atomic clock comparisons place the scientific community one step closer to meeting the guidelines for redefinition of the second.
"These comparisons are really defining ...
Soils or plants will absorb more CO2 as carbon levels rise - but not both
2021-03-24
Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere fuels plant growth. As carbon levels rise, it's appealing to think of supercharged plant growth and massive tree-planting campaigns drawing down the CO2 produced by fossil fuel burning, agriculture and other human activities.
New research published March 24 in Nature, however, suggests that when elevated carbon dioxide levels drive increased plant growth, it takes a surprisingly steep toll on another big carbon sink: the soil.
One likely explanation, the authors say, is that plants effectively mine the soil for nutrients they need to keep up with carbon-fueled growth. Extracting the extra nutrients requires revving up microbial activity, which then releases CO2 into the atmosphere that might otherwise remain locked in soil.
The findings contradict ...
Optical fiber could boost power of superconducting quantum computers
2021-03-24
The secret to building superconducting quantum computers with massive processing power may be an ordinary telecommunications technology - optical fiber.
Physicists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have measured and controlled a superconducting quantum bit (qubit) using light-conducting fiber instead of metal electrical wires, paving the way to packing a million qubits into a quantum computer rather than just a few thousand. The demonstration is described in the March 25 issue of Nature.
Superconducting circuits are a leading technology for making quantum computers because they are reliable and easily mass produced. But these circuits must operate at cryogenic temperatures, and schemes for wiring them to room-temperature electronics are complex and prone to ...
Towards a better understanding of societal responses to climate change
2021-03-24
As the signs of today's human-caused climate change become ever more alarming, research into the ways past societies responded to natural climate changes is growing increasingly urgent. Scholars have often argued that climatic changes plunge communities into crisis and provide the conditions that lead societies to collapse, but a growing body of research shows that the impacts of climate change on past populations are rarely so straightforward.
In a new paper published in Nature, scholars in archaeology, geography, history and paleoclimatology present a framework for research into what they term 'the History of Climate and Society' (HCS). The framework uses a series of ...
[1] ... [2489]
[2490]
[2491]
[2492]
[2493]
[2494]
[2495]
[2496]
2497
[2498]
[2499]
[2500]
[2501]
[2502]
[2503]
[2504]
[2505]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.