A divided cell is a doubled cell
2021-03-25
One big challenge for the production of synthetic cells is that they must be able to divide to have offspring. In the journal Angewandte Chemie, a team from Heidelberg has now introduced a reproducible division mechanism for synthetic vesicles. It is based on osmosis and can be controlled by an enzymatic reaction or light.
Organisms cannot simply emerge from inanimate material ("abiogenesis"), cells always come from pre-existing cells. The prospect of synthetic cells newly built from the ground up is shifting this paradigm. However, one obstacle on this path is the question of controlled division--a requirement for having "progeny".
A team from the Max Planck Institute for Medical Research in Heidelberg, Heidelberg ...
Automated embryo selection system might rise likelihood of success in treating infertility
2021-03-25
The team of researchers at Kaunas University of Technology (KTU), Lithuania applied artificial intelligence (AI) methods to evaluate data of human embryo development. The AI-based system photographs the embryos every five minutes, processes the data of their development and notifies any anomalies observed. This increases the likelihood of choosing the most viable and healthy early-stage embryo for IVF procedures. The innovation was developed in collaboration with Esco Medical Technologies, a manufacturer of medical equipment.
Almost one in six couples face infertility; about 48.5 million couples, 186 million individuals worldwide are inflicted. Europe has one of the lowest birth rates in the world, with an average of just 1.55 children per woman.
The most effective form of ...
Researchers dig deeper into how migrating cells interact in the body
2021-03-25
By offering a microscopic "tightrope" to cells, Virginia Tech and Johns Hopkins University researchers have brought new insights to the way migrating cells interact in the body. The researchers changed their testing environment for observing cell-cell interaction to more closely mirror the body, resulting in new observations of cells interacting like cars on a highway -- pairing up, speeding up, and passing one another.
Understanding the ways migrating cells react to one another is essential to predicting how cells change and evolve and how they react in applications, such as wound healing and drug delivery. In a study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, a team formed by Mechanical Engineering Associate ...
TPU scientists develop sensor with nanopores for definition doping in blood
2021-03-25
Scientists of Tomsk Polytechnic University jointly with colleagues from different countries have developed a new sensor with two layers of nanopores. In the conducted experiments, this sensor showed its efficiency as a sensor for one of the doping substances from chiral molecules. The research findings are published in Biosensors and Bioelectronics (IF: 10,257; Q1) academic journal.
The material is a thick wafer with pores of 20-30 nm in diameter. The scientists grew a layer of metal-organic frameworks (MOF) from Zn ions and organic molecules on these thick wafers. The MOF has about 3 nm nanopores only. It plays the role of a trap for molecules, which must be detected.
"This sensor can operate with chiral molecules. Such substances consisting of chiral molecules are a lot among medical ...
Renewable energy, new perspectives for photovoltaic cells
2021-03-25
In the future, photovoltaic cells could be "worn" over clothes, placed on cars or even on beach umbrellas. These are just some of the possible developments from a study published in Nature Communications by researchers at the Physics Department of the Politecnico di Milano, working with colleagues at the University of Erlangen-Nuremberg and Imperial College London.
The research includes among its authors the Institute of Photonics and Nanotechnology (IFN-CNR) researcher Franco V. A. Camargo and Professor Giulio Cerullo. It focused on photovoltaic cells made using flexible organic technology. Today's most popular photovoltaic cells, based on silicone technology, are rigid and ...
'Keep off the grass': the biofuel that could help us achieve net zero
2021-03-25
The Miscanthus genus of grasses, commonly used to add movement and texture to gardens, could quickly become the first choice for biofuel production. A new study shows these grasses can be grown in lower agricultural grade conditions - such as marginal land - due to their remarkable resilience and photosynthetic capacity at low temperatures.
Miscanthus is a promising biofuel thanks to its high biomass yield and low input requirements, which means it can adapt to a wide range of climate zones and land types. It is seen as a viable commercial option for farmers but yields ...
Headline: How energy modelling influences policymaking and vice versa
2021-03-25
Energy models are used to explore different options for the development of energy systems in virtual "laboratories". Scientists have been using energy models to provide policy advice for years. As a new study shows, energy models influence policymaking around the energy transition. Similarly, policymakers influence the work of modellers. Greater transparency is needed to ensure that political considerations do not set the agenda for future research or determine its findings, the researchers demand.
Renewable energies bring many changes, including fluctuations in the energy supply and a more geographically distributed generation system. ...
Natural Sciences students' research published in prestigious journal
2021-03-25
A collaborative research project by team of undergraduate students from the University of Exeter's Natural Sciences department has been published in a prestigious academic journal.
Lewis Howell, Eleanor Osborne and Alice Franklin have had their second-year research published in The Journal of Physical Chemistry B.
Their paper, Pattern Recognition of Chemical Waves: Finding the Activation Energy of the Autocatalytic Step in the Belousov-Zhabotinsky Reaction, was a result of their extended experiment work in the Stage 2 module "Frontiers in Science 2".
Their project involved the Belousov-Zhabotinsky chemical reaction - an ...
ArtEmis: Affective language for visual art
2021-03-25
March 7, 2021, KAUST, Saudi Arabia - KAUST Assistant Professor of Computer Science Mohamed Elhoseiny has developed, in collaboration with Stanford University, CA, and École Polytechnique (LIX), France, a large-scale dataset to train AI to reproduce human emotions when presented with artwork.
The resulting paper, "ArtEmis: Affective Language for Visual Art," will be presented at the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), the premier annual computer science conference, which will be held June 19-25, 2021.
Described as the "Affective Language for Visual Art," ArtEmis's user interface has seven emotional descriptions on average for each image, bringing the total count to over 439K emotional-explained attributions from humans on ...
Urban agriculture can help, but not solve, city food security problems
2021-03-25
While urban agriculture can play a role in supporting food supply chains for many major American cities -- contributing to food diversity, sustainability and localizing food systems -- it is unrealistic to expect rooftop gardens, community plots and the like to provide the majority of nutrition for the population of a metropolis.
That's the conclusion of a team of researchers who analyzed the nutritional needs of the population of Chicago and calculated how much food could be produced in the city by maximizing urban agriculture, and how much crop land would be needed adjacent to the city to grow the rest. The study was the first to evaluate land required to meet ...
Salivary gland cells revealed as sites of COVID-19 infection
2021-03-25
Scientists have shown that SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, can infect specific cells in the salivary gland in the mouth. The study by researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, National Institutes of Health and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and their collaborators within the Human Cell Atlas Oral & Craniofacial Network, also discovered that live cells from the mouth were found in saliva, and that the virus was able to reproduce within these infected cells.
The study revealed that salivary gland cells could play a role in transmission ...
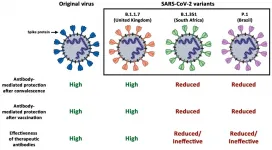
Evidence for reduced antibody protection against SARS-CoV-2 variants
2021-03-25
Göttingen, March 25, 2021. Testing and vaccination - these are the pillars on which humanity is trying to get a grip on the Coronavirus pandemic. Although it is taking longer than many had expected, it is believed that it is only a matter of time before we are all vaccinated and thus protected. However, time is also working for the virus, which has now mutated several times, with variants B.1.1.7 from the United Kingdom, B.1.351 from South Africa and P.1 from Brazil spreading rapidly. These viruses have mutations in the so-called spike protein, the structure on the surface of the virus that is responsible for attachment to host cells. At the same time, the spike protein is also the major target of the immune response. Antibodies generated in response to SARS-CoV-2 infection or vaccination ...
Nearly half of poison control calls for supersized alcopops involve underage drinkers
2021-03-25
Supersized alcopops are ready-to-drink flavored alcoholic beverages with high alcohol content that are disproportionately consumed by underage drinkers. There can be up to 5.5 standard alcoholic drinks in a single 24 ounce can, so consuming only one can of supersized alcopop is considered binge drinking, and consuming two cans can cause alcohol poisoning. Still, these products remain under-regulated and are available inexpensively at gas stations and convenience stores, where they are more readily accessible by underage youth.
New research led by George Mason University's College of Health and Human Services found that nearly ...
Warriors' down bedding could ease journey to realm of the dead
2021-03-25
The burial field in Valsgärde outside Uppsala in central Sweden contains more than 90 graves from the Iron Age.
"On a light note, we could say that Valsgärde is Scandinavia's answer to Sutton Hoo in England as portrayed in the film The Dig on Netflix," says Birgitta Berglund, professor emeritus of archaeology at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology's NTNU University Museum.
Valsgärde is especially known for its spectacular boat graves from the 600s and 700s CE. This timeframe is in the middle of what Norway calls the Merovingian period, the era just before the Viking Age.
Two of these spectacular boat graves are at the centre of this story -- or more specifically, the story is really about the down bedding that was found ...
Oncotarget: Phase 1 study of Z-Endoxifen in patients with solid tumors
2021-03-25
Oncotarget published "Phase 1 study of Z-Endoxifen in patients with advanced gynecologic, desmoid, and hormone receptor-positive solid tumors" which reported that Z-endoxifen administration was anticipated to bypass these variations, increasing active drug levels, and potentially benefiting patients responding sub-optimally to tamoxifen.
Patients with treatment-refractory gynecologic malignancies, desmoid tumors, or hormone receptor-positive solid tumors took oral Z-endoxifen daily with a 3 3 phase 1 dose escalation format over 8 dose levels.
Three patients had partial responses and 8 had prolonged stable disease; 44.4% of patients at dose levels 6–8 achieved one of these ...
Game on: Science edition
2021-03-25
UPTON, NY — Inspired by the mastery of artificial intelligence (AI) over games like Go and Super Mario, scientists at the National Synchrotron Light Source II (NSLS-II) trained an AI agent – an autonomous computational program that observes and acts – how to conduct research experiments at superhuman levels by using the same approach. The Brookhaven team published their findings in the journal Machine Learning: Science and Technology and implemented the AI agent as part of the research capabilities at NSLS-II.
As a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science User Facility located at DOE’s Brookhaven National Laboratory, NSLS-II enables scientific studies by more than 2000 researchers each year, ...
Study introduces 13 new, threatened species of sparkly moths from Hawaii
2021-03-25
Akito Kawahara was snapping pictures at a scenic outlook in Hawaii when he spotted the moth equivalent of a dodo.
An entomologist, Kawahara recognized the squiggly patterns on nearby plants as trails carved by leaf-mining caterpillars and lowered his camera to take a closer look. To his astonishment, he saw a tiny moth most experts assumed was extinct. It belonged to a genus known as Philodoria, a type of moth found only in Hawaii and one that hadn’t been documented in the wild since 1976.
“I thought, ‘Oh my God, there’s a Philodoria ...
Consumers will dub activist brands as 'woke-washers' if they cannot prove moral competency
2021-03-25
New research shows that consumers judge 'activist brands' based on how morally competent they are perceived to be when challenging free speech.
The report, co-authored by experts at the Business School (formerly Cass), Birkbeck, University of London and the University of Sussex Business School explains that stakeholders draw their conclusions on the biggest brands by measuring three moral skills: sensitivity, vision, and integration.
Lacking these traits, a brand raising controversy is judged as transgressing, reproducing and manipulating the boundaries of free speech. Displaying these traits proves the brand is not merely 'woke-washing' ...
Study reveals how long-term infection and inflammation impairs immune response as we age
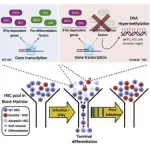
2021-03-25
HOUSTON, TX - March 25, 2021 - Humans are born with tens of thousands of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) that collectively ensure lifelong production of blood and immune cells that protect us from infections. HSCs can either duplicate to produce more stem cell progeny or differentiate to produce distinct immune cell lineages, an extremely critical decision that ensures that the body achieves the fine balance between having enough immune cells to fight invaders while still retaining enough HSCs to maintain future blood production. As we age, HSCs accumulate mutations that lead to the ...
The case of the cloudy filters: Solving the mystery of the degrading sunlight detectors
2021-03-25
More than 150 years ago, the Sun blasted Earth with a massive cloud of hot charged particles. This plasma blob generated a magnetic storm on Earth that caused sparks to leap out of telegraph equipment and even started a few fires. Now called the Carrington Event, after one of the astronomers who observed it, a magnetic storm like this could happen again anytime, only now it would affect more than telegraphs: It could damage or cause outages in wireless phone networks, GPS systems, electrical grids powering life-saving medical equipment and more.
Sun-facing satellites monitor the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) light to give us advance warning of solar storms, both big ones that could cause a Carrington-like ...
Gene discovery confirms role of serine deficiency in rare eye disease
2021-03-25
NEW YORK, NY--Treatments for a rare retinal disease may be on the horizon after a new study has identified gene variants that cause a metabolic deficiency in the eye.
The disease, macular telangiectasia type 2 (MacTel), has been a research focus of Rando Allikmets, PhD, a pioneer in the genetics of eye diseases, for nearly 15 years. MacTel occurs in approximately 1 in 5,000 adults over age 40 and slowly causes a significant loss of central vision, which can impair driving, reading, and other activities.
"MacTel is clearly a genetic disease because it tends to run in families, but it's been a tough nut to crack," says Allikmets, the William and Donna Acquavella Professor of Ophthalmic Sciences ...
Moffitt researchers use mathematical modeling to analyze dynamics of CAR T-cell therapy
2021-03-25
TAMPA, Fla. -- Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy, or CAR T, is a relatively new type of therapy approved to treat several types of aggressive B cell leukemias and lymphomas. Many patients have strong responses to CAR T; however, some have only a short response and develop disease progression quickly. Unfortunately, it is not completely understood why these patients have progression. In an article published in Proceedings of the Royal Society B, Moffitt Cancer Center researchers use mathematical modeling to help explain why CAR T cells work in some patients and not in others.
CAR T is a type of personalized immunotherapy that uses a patient's own T ...
New UCF nanotech gives boost to detection of cancer and disease
2021-03-25
ORLANDO, March 25, 2021 - Early screening can mean the difference between life and death in a cancer and disease diagnosis. That's why University of Central Florida researchers are working to develop a new screening technique that's more than 300 times as effective at detecting a biomarker for diseases like cancer than current methods.
The technique, which was detailed recently in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, uses nanoparticles with nickel-rich cores and platinum-rich shells to increase the sensitivity of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
ELISA is a test ...
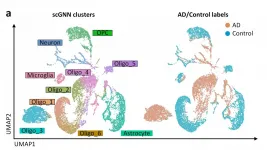
A new way to visualize mountains of biological data
2021-03-25
Studying genetic material on a cellular level, such as single-cell RNA-sequencing, can provide scientists with a detailed, high-resolution view of biological processes at work. This level of detail helps scientists determine the health of tissues and organs, and better understand the development of diseases such as Alzheimer's that impacts millions of people. However, a lot of data is also generated, and leads to the need for an efficient, easy-to-use way to analyze it.
Now, a team of engineers and scientists from the University of Missouri and the Ohio State University have created a new way to analyze data from single-cell RNA-sequencing ...
The very first structures in the Universe
2021-03-25
The very first moments of the Universe can be reconstructed mathematically even though they cannot be observed directly. Physicists from the Universities of Göttingen and Auckland (New Zealand) have greatly improved the ability of complex computer simulations to describe this early epoch. They discovered that a complex network of structures can form in the first trillionth of a second after the Big Bang. The behaviour of these objects mimics the distribution of galaxies in today's Universe. In contrast to today, however, these primordial structures are microscopically small. Typical clumps have masses of only a few grams and fit into volumes much smaller than present-day elementary particles. The results of the study have been published ...
[1] ... [2486]
[2487]
[2488]
[2489]
[2490]
[2491]
[2492]
[2493]
2494
[2495]
[2496]
[2497]
[2498]
[2499]
[2500]
[2501]
[2502]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.