Size of grass blades offers better understanding of their vulnerability to climate change
2021-03-25
One-third of the Earth's surface is covered by more than 11,000 grass species -- including crops like wheat, corn, rice and sugar cane that account for the bulk of the world's agricultural food production and important biofuels. But grass is so common that few people realize how diverse and important it really is.
Research published today in the journal Nature provides insights that scientists could use not only to improve crop design but also to more accurately model the effects of climate change. It also offers new clues that could help scientists use ...
'Break a leg' not so lucky when it leads to limb deformities
2021-03-25
Orthopaedic researchers are one step closer to preventing life-long arm and leg deformities from childhood fractures that do not heal properly.
A new study led by the University of South Australia and published in the journal Bone, sheds light on the role that a protein plays in this process.
Lead author Dr Michelle Su says that because children's bones are still growing, an injury to the growth plate can lead to a limb in a shortened position, compared to the unaffected side.
"Cartilage tissue near the ends of long bones is known as the growth plate that is responsible for bone growth in children and, unfortunately, 30 per cent of childhood and teen fractures involve this growth ...
Pumice the key to solving seabird mass death mystery
2021-03-25
Researchers have used the evidence of pumice from an underwater volcanic eruption to answer a long-standing mystery about a mass death of migrating seabirds.
New research into the mass death of millions of shearwater birds in 2013 suggests seabirds are eating non-food materials including floating pumice stones, because they are starving, potentially indicating broader health issues for the marine ecosystem.
The research which was led by CSIRO, Australia's national science agency, and QUT, was published in the journal Marine Ecology Progress Series, that examined a 2013 seabird "wreck" in which up to 3 million ...
Planting trees to save the planet: The Chinese experience
2021-03-25
A coordinated global effort to reduce the production of greenhouse gas emissions from industry and other sectors may not stop climate change, but Earth has a powerful ally that humans might partner with to achieve carbon neutrality: Mother Nature. An international team of researchers called for the use of natural climate solutions to help "cancel" produced emissions and remove existing emissions as part of a comprehensive plan to keep global warming below 1.5 degrees Celsius -- the point at which damage to human life and livelihoods could become catastrophic, according to the United Nations' Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.
The researchers published their invited views on March 24 in ...
Researchers realized homogenization of surface active sites of heterogeneous catalyst
2021-03-25
Recently, the team led by Professor WU Changzheng from School of Chemistry and Materials Science from University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) in cooperation with the team led by Prof. WU Hengan from School of Engineering Science, realized the homogenization of surface active sites of heterogeneous catalyst by dissolving the electrocatalytic active metal in molten gallium. The related results have been published on the Nature Catalysis on March 11th.
Due to the existence of various defects and crystal faces, the active components on the surface of heterogeneous catalysts are often in different ...
Exercise can improve sleep quality even when you don't perceive a difference
2021-03-25
Tsukuba, Japan - Physical exercise has long been prescribed as a way to improve the quality of sleep. But now, researchers from Japan have found that even when exercise causes objectively measured changes in sleep quality, these changes may not be subjectively perceptible.
In a study published this month in Scientific Reports, researchers from the University of Tsukuba have revealed that vigorous exercise was able to modulate various sleep parameters associated with improved sleep, without affecting subjective reports regarding sleep quality.
Exercise is ...
Second drug targeting KRASG12C shows benefit in mutated non-small-cell lung cancer
2021-03-25
Lugano, Switzerland; Denver, CO, USA, 25 March 2021 - Clinical activity with a second drug inhibiting KRASG12C confirms its role as a therapeutic target in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harbouring this mutation, according to results from a study with the KRASG12C inhibitor adagrasib reported at the European Lung Cancer Virtual Congress 2021. (1)
"As we strive to identify the oncogenic driver in more and more of our patients with NSCLC, it becomes critical that we develop therapies that can target these identified oncogenic drivers," said lead author Gregory Riely, from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, ...
Study of NCOA3 yields novel findings of melanoma progression
2021-03-25
For the first time, activation of nuclear receptor coactivator 3 (NCOA3) has been shown to promote the development of melanoma through regulation of ultraviolet radiation (UVR) sensitivity, cell cycle progression and circumvention of the DNA damage response. Results of a pre-clinical study led by Mohammed Kashani-Sabet, M.D., Medical Director of the Cancer Center at Sutter's California Pacific Medical Center (CPMC) in San Francisco, CA were published online today in Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
"Our research suggests a previously unreported mechanism by which NCOA3 regulates the DNA damage response and acts as a potential therapeutic target in melanoma, whereby activation ...
Researchers show how stem cell depletion leads to recurring pregnancy loss
2021-03-25
Durham, NC - Depletion of a certain type of stem cell in the womb lining during pregnancy could be a significant factor behind miscarriage, according to a study released today in STEM CELLS. The study, by researchers at Warwick Medical School, University of Warwick, Coventry, England, reports on how recurrent pregnancy loss is a result of the loss of decidual precursor cells prior to conception.
"This raises the possibility that they can be harnessed to prevent pregnancy disorders," said corresponding author Jan J. Brosens, M.D., Ph.D., professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Warwick Medical School (WMS).
The womb lining - or endometrium - is a ...
Researchers at Stanford and Carnegie Mellon reveal cost of key climate solution
2021-03-25
Perhaps the best hope for slowing climate change - capturing and storing carbon dioxide emissions underground - has remained elusive due in part to uncertainty about its economic feasibility.
In an effort to provide clarity on this point, researchers at Stanford University and Carnegie Mellon University have estimated the energy demands involved with a critical stage of the process. (Watch video here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-ZPIwwQs9aM)
Their findings, published April 8 in Environmental Science & Technology, suggest that managing and ...
Starting smoking cessation in hospitalized patients would reduce many premature deaths
2021-03-25
Smoking cigarettes causes 480,000 premature deaths each year in the United States, due mainly to a two-fold risk of cardiovascular disease and a 20-fold risk of lung cancer. Although smoking rates have declined dramatically, there are currently 35 million smokers in the U.S.
In a commentary published in the Ochsner Medical Journal, Charles H. Hennekens, M.D., Dr.PH, senior author, the First Sir Richard Doll Professor, and senior academic advisor in the Schmidt College of Medicine at Florida Atlantic University, and colleagues, highlight how failure to institute smoking cessation in hospitalized patients is a missed opportunity to avoid many premature deaths.
Each year in the U.S., ...
Scientists find evidence that novel coronavirus invades the mouth's cells
2021-03-25
An international team led by scientists at the National Institutes of Health and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, has found evidence that SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, infects cells in the mouth.
While it's well known that the upper airways and lungs are primary sites of SARS-CoV-2 infection, there are clues the virus can infect cells in other parts of the body, such as the digestive system, blood vessels, kidneys and, as this new study shows, the mouth. The potential of the virus to infect multiple areas of the body might help explain the wide-ranging symptoms experienced by COVID-19 patients, including oral symptoms such as taste loss, dry mouth and blistering.
Moreover, the findings ...
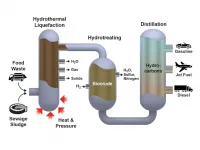
Biocrude passes the 2,000-hour catalyst stability test
2021-03-25
RICHLAND, WASH.--A large-scale demonstration converting biocrude to renewable diesel fuel has passed a significant test, operating for more than 2,000 hours continuously without losing effectiveness. Scientists and engineers led by the U.S. Department of Energy's Pacific Northwest National Laboratory conducted the research to show that the process is robust enough to handle many kinds of raw material without failing.
"The biocrude oil came from many different sources, including wastewater sludge from Detroit, and food waste collected from prison and an army base," said John Holladay, a PNNL scientist and co-director of the joint Bioproducts Institute, a collaboration between ...
New protein helps carnivorous plants sense and trap their prey
2021-03-25
LA JOLLA--(March 25, 2021) The brush of an insect's wing is enough to trigger a Venus flytrap to snap shut, but the biology of how these plants sense and respond to touch is still poorly understood, especially at the molecular level. Now, a new study by Salk and Scripps Research scientists identifies what appears to be a key protein involved in touch sensitivity for flytraps and other carnivorous plants.
The findings, published March 16, 2021, in the journal eLife, help explain a critical process that has long puzzled botanists. This could help scientists better understand how plants of all kinds sense and respond to mechanical stimulation, and could also have a potential application in medical therapies that mechanically stimulate human cells such as neurons.
"We know that plants ...
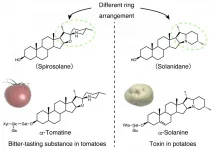
Toxin in potatoes evolved from a bitter-tasting compound in tomatoes
2021-03-25
A multi-institutional collaboration has revealed that α-solanine, a toxic compound found in potato plants, is a divergent of the bitter-tasting α-tomatine, which is found in tomato plants. The research group included Associate Professor MIZUTANI Masaharu and Researcher AKIYAMA Ryota et al. of Kobe University's Graduate School of Agricultural Science, Assistant Professor WATANABE Bunta of Kyoto University's Institute for Chemical Research, Senior Research Scientist UMEMOTO Naoyuki of the RIKEN Center for Sustainable Resource Science, and Professor MURANAKA Toshiya of Osaka University's Graduate School of Engineering.
It ...
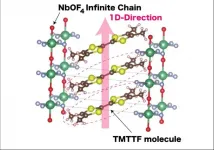
Researchers discover new organic conductor
2021-03-25
Salts are far more complicated than the food seasoning - they can even act as electrical conductors, shuttling current through systems. Extremely well studied and understood, the electrical properties of salts were first theorized in 1834. Now, nearly 200 years later, researchers based in Japan have uncovered a new kind of salt.
The results were published on March 17 in Inorganic Chemistry, a journal of the American Chemical Society.
The researchers were specifically investigating how one-dimensional versions of three-dimensional substances exhibit unique physical phenomena and functionality in a process called the ...
New insights into close encounters between albatross and fishing vessels
2021-03-25
CORVALLIS, Ore. - A novel analysis of encounters between albatross and commercial fishing vessels across the North Pacific Ocean is giving researchers important new understanding about seabird-vessel interactions that could help reduce harmful encounters.
The new research method, which combines location data from GPS-tagged albatross and commercial fishing vessels, allows researchers to accurately identify bird-vessel encounters and better understand bird behavior, environmental conditions and the characteristics that influence these encounters.
"It is hard to conceptualize how often birds ...
Arctic sponge survival in the extreme deep-sea
2021-03-25
For the first time, researchers from the SponGES project collected year-round video footage and hydrodynamic data from the mysterious world of a deep-sea sponge ground in the Arctic. Deep-sea sponge grounds are often compared to the rich ecosystems of coral reefs and form true oases. In a world where all light has disappeared and without obvious food sources, they provide a habitat for other invertebrates and a refuge for fish in the otherwise barren landscape. It is still puzzling how these biodiversity hotspots survive in this extreme environment as deep as 1500 metres below the water surface. With over 700 hundred ...
Gearing up nanoscale machines
2021-03-25
Ikoma, Japan - Gear trains have been used for centuries to translate changes in gear rotational speed into changes in rotational force. Cars, drills, and basically anything that has spinning parts use them. Molecular-scale gears are a much more recent invention that could use light or a chemical stimulus to initiate gear rotation. Researchers at Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST), Japan, in partnership with research teams at University Paul Sabatier, France, report in a new study published in Chemical Science a means to visualize snapshots of an ultrasmall ...
Better postoperative recovery for physically active
2021-03-25
People who are physically active on a regular basis recover better after surgery for colorectal cancer. However, starting to exercise only after the diagnosis is a fact had no effect on recovery, a University of Gothenburg thesis shows.
In working on his thesis, Aron Onerup, who obtained his doctorate in surgery at the University's Sahlgrenska Academy and is now a specialist doctor at Sahlgrenska University Hospital, carried out an observational study of 115 patients diagnosed with colorectal cancer.
The participants who had been physically inactive proved, three weeks after their surgery, to be at higher risk of not feeling that they ...
How tiny machines become capable of learning
2021-03-25
Microswimmers are artificial, self-propelled, microscopic particles. They are capable of directional motion in a solution. The Molecular Nanophotonics Group at Leipzig University has developed special particles that are smaller than one-thirtieth of the diameter of a hair. They can change their direction of motion by heating tiny gold particles on their surface and converting this energy into motion. "However, these miniaturised machines cannot take in and learn information like their living counterparts. To achieve this, we control the microswimmers externally so that they learn to navigate in a virtual environment through what is known as reinforcement learning," said Cichos.
With the help of virtual rewards, the microswimmers find their way through the liquid ...
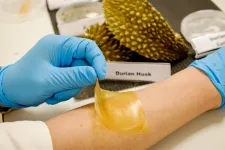
NTU Singapore scientists develop antibacterial gel bandage using durian husk
2021-03-25
Food scientists from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) have made an antibacterial gel bandage using the discarded husks of the popular tropical fruit, durian.
Known as the "King of Fruits" in Southeast Asia, the durian has a thick husk with spiky thorns which is discarded, while the sweet flesh surrounding the seeds on the inside is considered a delicacy.
By extracting high-quality cellulose from the durian husks and combining it with glycerol - a waste by-product from the biodiesel and soap industry - NTU scientists created a soft gel, similar to silicon sheets, which can be cut into bandages of various shapes and sizes.
They then added the organic molecules produced from baker's yeast known as natural yeast phenolics, making the bandage deadly ...
How improving acoustic monitoring of bats could help protecting biodiversity
2021-03-25
In order to assess the risk of bats dying at wind turbines, it is common practice to record the acoustic activity of bats within the operating range of the rotor blades. For this purpose, ultrasonic detectors are attached to the nacelles of the mast top. In a recent analysis, a team of scientists led by the Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research (Leibniz-IZW) concludes that the effectiveness of this acoustic monitoring is insufficient to reliably predict mortality risk, especially for bats at large turbines. They therefore recommend installing supplementary ultrasonic detectors at other locations on the wind turbines and developing additional techniques such as radar and thermal imaging cameras for monitoring. The results of their analysis are published in ...
Insufficient financial reporting may lead to underestimation of environmental liabilities
2021-03-25
European listed companies in the energy and mining sector provide, to say the least, sparse information on future environmental costs in their annual reports. Researchers believe that stricter guidelines are required as the lack of information may lead to underestimation of environmental liabilities, resulting in that future generations may have to bear the burden of cleanup costs.
"I believe that the future environmental liabilities such as decommissioning costs are often underestimated and few understand the burden these costs might impose on future generations. If, for example, an oil & gas company fails, it costs an incredible amount to clean up after old oil wells and the risk is great that the taxpayers will have to pay the bill. Therefore, it is important that environmental obligations ...
Relieve your stress, relieve your allergies
2021-03-25
Increased allergic reactions may be tied to the corticotropin-releasing stress hormone (CRH), suggests a study published this month in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences. These findings may help clarify the mechanism by which CRH induces proliferation of mast cells (MC) - agents involved in the development of allergies in the human nasal cavity.
"In my daily practice, I meet many patients with allergies who say their symptoms worsened due to psychological stress," states lead researcher Mika Yamanaka-Takaichi, a graduate student of the Department of Dermatology, Osaka City University, "This is what led me to do this research."
Together with Professor Daisuke Tsuruta of the same department, they hypothesized that due to its ...
[1] ... [2487]
[2488]
[2489]
[2490]
[2491]
[2492]
[2493]
[2494]
2495
[2496]
[2497]
[2498]
[2499]
[2500]
[2501]
[2502]
[2503]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.