How blockchain and machine learning can deliver the promise of omnichannel marketing
2021-03-24
Researchers from University of Minnesota, New York University, University of Pennsylvania, BI Norwegian Business School, University of Michigan, National Bureau of Economic Research, and University of North Carolina published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that examines how advances in machine learning (ML) and blockchain can address inherent frictions in omnichannel marketing and raises many questions for practice and research.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Informational Challenges in Omnichannel Marketing Remedies and ...
Extreme temperatures, heat stress and forced migration
2021-03-24
The study, building on cooperation between climate scientists from the MENA region, aimed at assessing emerging heatwave characteristics. The research team used a first-of-its-kind multi-model ensemble of climate projections designed exclusively for the geographic area. Such detailed downscaling studies had been lacking for this region. The researchers then projected future hot spells and characterised them with the Heat Wave Magnitude Index. The good match among the model results and with observations indicates a high level of confidence in the heat wave projections.
"Our results for a business-as-usual ...
Recharge your batteries
2021-03-24
March 24, 2021 -- Perhaps the most frustrating limitation of owning an all-electric car is how long it takes to fully charge the battery. For a Tesla, for example, it takes about 40 minutes to charge it to 80% capacity using the most powerful charging station.
Scientists have long thought the laws of physics limited how fast you could safely recharge a battery, but new research by University of Utah chemical engineering assistant professor Tao Gao has opened the door to creating a battery that can be recharged in just a fraction of the time.
Gao's research was detailed in a new paper published in the scientific journal Joule. The study was conducted while Gao was a postdoctoral researcher at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology under ...
Study finds foster youth lack critical financial skills
2021-03-24
VANCOUVER, Wash. - Most people rely on family members to help them learn how to open a bank account, find a job or create a budget, but that's often not an option for youth in foster care, according to a recent study in Child & Family Social Work.
"Foster kids have distinctive challenges," said Amy Salazar, lead author on the study and an assistant professor at Washington State University Vancouver. "They need more support in several areas, and financial capability is one of them, especially when they're transitioning out of the foster care system and into adulthood."
For the study, Salazar and her co-authors surveyed 97 foster care youths aged 14 to 20. They found that those who were age 18 and over had more ...
Light pollution drives increased risk of West Nile virus
2021-03-24
Florida has experienced a relatively mild winter, which typically translates to more mosquitoes in the summer and more birds on which they can feast. If history repeats itself, it's likely there will be an uptick in West Nile virus cases this year, especially in the outer fringes of the suburbs where much of the nighttime illumination emanates from the skyglow of nearby cities.
A new study from the University of South Florida (USF) is the first to provide direct evidence that light pollution is driving infectious disease patterns in nature. The research team previously determined mosquitoes and birds are attracted to light, greatly enhancing the likelihood ...
How to prevent and treat high blood pressure with exercise
2021-03-24
The first personalised advice on the most effective exercise to lower blood pressure is published today in the European Journal of Preventive Cardiology, a journal of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1 The ESC consensus document recommends specific activities according to an individual's current blood pressure level.
One in four heart attacks are caused by high blood pressure. It is estimated that by 2025, around 60% of the world's population will have hypertension. While it is widely accepted that exercise lowers blood pressure, until now recommendations have focused on the amount of exercise per week, without considering an individual's starting blood ...
Snappy evolution was behind the success of ancient crocodiles
2021-03-24
New research led by the University of Bristol has revealed that crocodiles once flourished on land and in the oceans as a result of fast evolution.
Modern crocodiles are predators living in rivers, lakes and wetlands, grabbing fish, reptiles, birds and mammals with their conspicuous snouts and powerful jaws.
However, new research published today in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, shows that ancient crocodiles were once much more varied because of rapid evolution.
In the time of the dinosaurs, some crocodiles experimented with dolphin-like adaptations to living in the oceans, and others lived on land as fast-moving plant-eaters.
The researchers studied over 200 skulls and jaws, including ...
Individual SARS-CoV-2 neutralising antibody immunity lasts from days to decades
2021-03-24
SINGAPORE, 23 March 2021 - Scientists from Duke-NUS Medical School, the National Centre for Infectious Diseases (NCID) and the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) Infectious Diseases Labs found that antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 wane at different rates, lasting for mere days in some individuals, while remaining present in others for decades. The study, published in The Lancet Microbe, shows that the severity of the infection could be a deciding factor in having longer-lasting antibodies. Individuals with low levels of neutralising ...
Rugby study identifies new method to diagnose concussion using saliva
2021-03-24
A University of Birmingham-led study of top-flight UK rugby players - carried out in collaboration with the Rugby Football Union (RFU), Premiership Rugby, and Marker Diagnostics - has identified a method of accurately diagnosing concussion using saliva, paving the way for the first non-invasive clinical test for concussion for use in sport and other settings.
Following the team's previous research, which identified that the concentration of specific molecules in saliva changes rapidly after a traumatic brain injury, the researchers embarked on a three-year study in elite rugby to establish if these 'biomarkers' could be used as a diagnostic test ...
Distinct chemical 'signatures' for concussion identified in spit of elite rugby players
2021-03-24
Potentially paves way for non-invasive diagnostic test at all levels of participation
On a par with the assessment currently provided in professional sports
Could work alongside 'gold standard' head injury protocol used in elite sports
Distinct chemical 'signatures' for concussion have been identified in the spit of elite male rugby players, reveals research published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
This potentially paves the way for a non-invasive and rapid diagnostic test for the condition that could be used pitch side and after the game at all levels of participation, suggest the researchers.
This is especially important because ...
Scientists observe complex tunable magnetism in a topological material
2021-03-23
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Ames Laboratory have observed novel helical magnetic ordering in the topological compound EuIn2As2 which supports exotic electrical conduction tunable by a magnetic field. The discovery has significant implications for basic research into functional topological properties and may one day find use in a number of advanced technology applications.
Topological materials burst onto the scene in the physical sciences about fifteen years ago, decades after their existence had been theorized. Called 'topological' because their bulk electronic bands are "knotted" together, the surfaces of topological insulators "untie the knot" and become metallic. Researchers ...
Flu shot associated with fewer, less severe COVID cases
2021-03-23
People who received a flu shot last flu season were significantly less likely to test positive for a COVID-19 infection when the pandemic hit, according to a new study. And those who did test positive for COVID-19 had fewer complications if they received their flu shot.
These new findings mean senior author Marion Hofmann Bowman, M.D., is continuing to recommend the flu shot to her patients even as the flu season may be winding down.
"It's particularly relevant for vaccine hesitance, and maybe taking the flu shot this year can ease some angst about the new COVID-19 vaccine," says Hofmann, an associate professor of internal medicine and a cardiologist at the Michigan ...
Curbing COVID-19 on campuses nationwide
2021-03-23
While COVID-19 cases may be on the decline, the virus is still prevalent nationwide, and higher education institutions need to prepare for a successful 2021 academic year. New research from Clemson University in The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health, one of the world's premier peer-reviewed general medical journals, indicates how surveillance-based informative testing (SBIT) mitigates the spread of COVID-19 on campus, paving the way for other institutions, even those without the infrastructure or funding for mass-scale testing.
SBIT was implemented during the first two weeks of the Fall semester at Clemson. According to the study, ...
BMI1, a promising gene to protect against Alzheimer's disease
2021-03-23
Another step towards understanding Alzheimer's disease has been taken at the Maisonneuve-Rosemont Hospital Research Centre. Molecular biologist Gilbert Bernier, and professor of neurosciences at Université de Montréal, has discovered a new function for the BMI1 gene, which is known to inhibit brain aging. The results of his work have just been published in Nature Communications.
In his laboratory, Bernier was able to establish that BMI1 was required to prevent the DNA of neurons from disorganizing in a particular way called G4 structures. This phenomenon occurs in the brains of people with Alzheimer's disease, but not in healthy elderly ...
Neutrons reveal unpredicted binding between SARS-CoV-2, hepatitis C antiviral drug
2021-03-23
Scientists have found new, unexpected behaviors when SARS-CoV-2 - the virus that causes COVID-19 - encounters drugs known as inhibitors, which bind to certain components of the virus and block its ability to reproduce.
Published in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, the research provides key insights for advancing drug design and drug repurposing efforts to treat COVID-19.
Researchers at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory used neutron scattering to investigate interactions between telaprevir, a drug used to treat hepatitis C viral infection, and the SARS-CoV-2 main protease, the enzyme responsible for enabling the virus to reproduce.
They ...
Researchers hunt for drugs that keep HIV latent
2021-03-23
When the human immunodeficiency virus infects cells, it can either exploit the cells to start making more copies of itself or remain dormant--a phenomenon called latency. Keeping these reservoirs latent is a challenge. A new paper, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, has found a way to look for chemicals that can keep the virus suppressed into its dormant state.
"The current drug treatments block healthy cells from becoming infected by the virus," said Yiyang Lu, a PhD student in the Dar lab at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign. "The latent reservoir poses a bigger problem because it can start producing the virus at any time. Consequently, patients have to remain on antiretroviral therapy all their lives to prevent ...
study: Precautions used to prevent COVID-19 decreased common respiratory illness rates
2021-03-23
Boston - Wearing masks and physical distancing - two key infection prevention strategies implemented to stop the spread of COVID-19 - may have led to the dramatic decrease in rates of common respiratory viral infections, such as influenza. A study led by researchers at Boston Medical Center (BMC) showed an approximately 80 percent reduction in cases of influenza and other common viral respiratory infections when compared to similar time periods in previous years, before wearing masks, physical distancing, and school closures were implemented to help stop the spread of COVID-19. Published online in Open Forum Infectious ...
Global health care worker burnout is high and 'unsustainable'
2021-03-23
SAN ANTONIO (March 23, 2021) -- More than half of all health care workers worldwide are experiencing burnout that, if not addressed, could cause many to leave their fields in favor of less-stressful occupations or choose early retirement. And the COVID-19 pandemic has only made it worse.
That's the warning of a surgeon from The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio in a letter and a call for global action published March 22 in the Lancet journal EClinicalMedicine.
"A recent survey done in Medscape of nearly 7,500 physicians globally showed that burnout has reached a very high rate," said END ...
Deactivating cancer cell gene boosts immunotherapy for head and neck cancers
2021-03-23
By targeting an enzyme that plays a key role in head and neck cancer cells, researchers from the UCLA School of Dentistry were able to significantly slow the growth and spread of tumors in mice and enhance the effectiveness of an immunotherapy to which these types of cancers often become resistant.
Their findings, END ...
Arsenal used by parasite to affect cellular defense and enhance leishmaniasis is revealed
2021-03-23
Researchers have succeeded in revealing the arsenal used by protozoans of the genus Leishmania in human cells to make leishmaniasis more severe, especially in cases of the mucocutaneous variety of the disease, which can cause deformations in patients. The discovery points the way to a search for novel treatments for the disease as well as casting light on a key mechanism involved in other diseases.
The mechanism involves Leishmania, macrophages and a virus that lives endosymbiotically in the parasite and is known as the Leishmania RNA virus (LRV). According to a study published in the journal iScience, the parasite inhibits activation of caspase-11 via LRV-induced autophagy. Caspases are a family of enzymes that ...
Pilot study finds evidence of bartonella infection in schizophrenia patients
2021-03-23
A pilot study from North Carolina State University and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill has found evidence of Bartonella infection in the blood of people with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder.
"Researchers have been looking at the connection between bacterial infection and neuropsychiatric disease for some time," says Dr. Erin Lashnits, a former veterinary internist at NC State, current faculty member at the University of Wisconsin and first author of the study.
"Specifically, there has been research suggesting that cat ownership is associated with schizophrenia ...
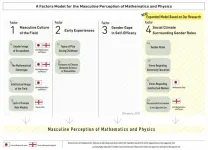
Social context affects gendered views of STEM subjects in England and Japan
2021-03-23
Concern over attractiveness to the opposite sex affects the masculine image of physics and mathematics only in England, while having a negative view of intellectual women is correlated with a masculine image of mathematics as a field only in Japan, according to a survey conducted in the two countries by a Japanese research group. This comparative study shows that programs to increase women's representation in these fields must take into account each country's social context surrounding gender roles.
Why do so few women choose to study and work in STEM (science, technology, ...
OCD among new mothers more prevalent than previously thought
2021-03-23
Obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) among those who have recently given birth is more common than previously thought, and much of this can be attributed to thoughts of harm related to the baby, new UBC research has found.
The researchers also learned that OCD can go undetected when new parents aren't asked specifically about infant-related harm.
OCD is an anxiety-related condition characterized by the recurrence of unwanted, intrusive and distressing thoughts. If left untreated, it can interfere with parenting, relationships and daily living.
The study estimates that eight per cent of postpartum women report symptoms ...
Nine potentially harmful stimulants found in supplements listing deterenol as ingredient
2021-03-23
ANN ARBOR, Mich., (March 23, 2021) Researchers are urging consumers to avoid using weight loss or sports supplements that list deterenol as an ingredient. Scientists at NSF International (NSF), Harvard Medical School and Cambridge Health Alliance recently tested 17 brands of supplements listing deterenol as an ingredient and found nine potentially harmful, experimental stimulants in the products.
Researchers at the Netherlands' National Institute for Public Health and the Environment (RIVM) and Belgium's Sciensano also participated in the study.
Supplements containing deterenol have not been approved for use in humans in the United States and have been linked to reports of adverse events, including nausea, vomiting, sweating, agitation, ...
How human cells coordinate the start of DNA replication
2021-03-23
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) President and CEO Bruce Stillman has been dissecting DNA replication, a critical step in cell division, since the 1980s. His lab studies how Origin Recognition Complexes--ORCs--coordinate DNA duplication. They discovered how our cells assemble and disassemble ORCs during the cell division cycle. One ORC protein is sequestered into small liquid droplets, keeping it apart until the right time to recruit other proteins and initiate DNA replication.
The ORC recognizes where to initiate replication at numerous locations along the long, linear stretches of DNA ...
[1] ... [2494]
[2495]
[2496]
[2497]
[2498]
[2499]
[2500]
[2501]
2502
[2503]
[2504]
[2505]
[2506]
[2507]
[2508]
[2509]
[2510]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.