Even small levels of nitrate in drinking water results in smaller babies
2021-03-24
The more nitrate there is in mothers' drinking water, the smaller the babies they give birth to. But alarmingly, the declining birth weight can also be registered when the women are exposed to nitrate levels below the EU's threshold of 50 milligrams of nitrate per litre.
This is shown by a register-based study of more than 850,000 births in Denmark carried out in a Danish-American partnership led by Professor Torben Sigsgaard from the Department of Public Health at Aarhus University and Professor Leslie Stayner and Dr. Vanessa Coffman from the Division of Epidemiology and Biostatistics at the University of Illinois at Chicago, School of Public Health.
On the ...
'Mother's own milk' for premature infants: Minority mothers need effective strategies
2021-03-24
March 24, 2021 - For premature infants who can't breastfeed on their own, "mother's own milk" (MOM) is by far the best nutrition. There's an urgent need for effective ways to increase the relatively low rates of MOM feeding for preterm infants born to Black and Hispanic mothers. But so far, research has offered little or no specific guidance, concludes an evidence-based review in Advances in Neonatal Care, official journal of the National Association of Neonatal Nurses. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
Until studies of targeted, culturally appropriate interventions are performed, available evidence points to some promising approaches to overcoming obstacles and facilitating ...
Dangerous landfill pollutants ranked in order of toxicity by MU researchers
2021-03-24
COLUMBIA, Mo. - Nearly 2,000 active landfills are spread across the U.S., with the majority of garbage discarded by homes and businesses finding its way to a landfill. The resulting chemicals and toxins that build up at these sites can then leach into soil and groundwater, and this "leachate" can present serious hazards to the environment and to the people who live nearby.
To help environmental agencies battle the toxic threats posed by landfills, researchers at the University of Missouri -- in partnership with the USDA Forest Service -- have developed a system ...
A novel marker of adult human neural stem cells discovered
2021-03-24
HOUSTON - (Mar 24, 2021) -The mammalian center for learning and memory, hippocampus, has a remarkable capacity to generate new neurons throughout life. Newborn neurons are produced by neural stem cells (NSCs) and they are crucial for forming neural circuits required for learning and memory, and mood control. During aging, the number of NSCs declines, leading to decreased neurogenesis and age-associated cognitive decline, anxiety, and depression. Thus, identifying the core molecular machinery responsible for NSC preservation is of fundamental importance if we are to use neurogenesis to halt or reverse hippocampal age-related pathology.
While there are increasing number of tools available to study NSCs and neurogenesis in mouse models, one of the major ...
A better treatment for sickle cell disease
2021-03-24
Sickle cell disease is the most prevalent inherited blood disorder in the world, affecting 70,000 to 100,000 Americans. However, it is considered an orphan disease, meaning it impacts less than 200,000 people nationally, and is therefore underrepresented in therapeutic research.
A team led by Abhishek Jain from the Department of Biomedical Engineering at Texas A&M University is working to address this disease.
"I'm trying to create these new types of disease models that can impact health care, with the long-term goal of emphasizing on applying these tools ...
New research finds seating assignments on airplanes can reduce the spread of COVID-19
2021-03-24
>
CATONSVILLE, MD, March 24, 2021 - COVID-19 has been shown to spread on airplanes by infected passengers, so minimizing the risk of secondary infections aboard aircraft may save lives. New research in the INFORMS journal Service Science uses two models to help solve the airplane seating assignment problem (ASAP). The models can lower the transmission risk of COVID-19 more so than the strategy of blocking the middle seats, given the same number of passengers.
"Blocking the middle seat on an airplane may provide limited benefit in reducing the risk of transmission of COVID-19. Rather, other health protocols are better supported at preventing the transmission ...
New drug candidate against COVID-19
2021-03-24
SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic, arrived one year ago and turned our lives upside-down.
While worldwide vaccination programs are currently ongoing, we do not yet know for how long the vaccine will provide immune protection against infection, and if the currently approved vaccines can provide protection against the emerging virus variants.
In addition, it appears that vaccines cannot prevent illness for people who have already been infected. In contrast to vaccines, there are currently no effective drugs that act against the virus SARS-CoV-2.
New research by Associate Professor Jasmin Mecinovic and co-workers from the Department of Physics, Chemistry and Pharmacy, University of Southern Denmark, now presents a compound that might provide a basis for the ...
Shining light to make hydrogen
2021-03-24
Decarbonizing the economy and achieving the transition from fossil fuels to renewable energies is one of the most urgent global challenges of the 21st century. Hydrogen can play a key role in this process as a promising climate-neutral energy vehicle. Yet, the so-called green hydrogen economy requires that hydrogen production be based exclusively on renewable energy. In addition, it should ideally not use expensive and rare metal catalysts, whose production has severe environmental consequences. To address this challenge, ITQB NOVA researchers Inês Cardoso Pereira and Mónica Martins are working on an innovative technology to produce hydrogen from light using non-photosynthetic microorganisms.
Hydrogen offers exciting new possibilities as an energy vehicle, ...
Black hole shows magnetic fields surrounding it are strong enough to resist gravity
2021-03-24
The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) collaboration, a multinational team of over 300 scientists including two astrophysicists from the University of the Witwatersrand (Wits University), has revealed today a new view of the massive object at the centre of the M87 galaxy: how it looks in polarised light.
This is the first time astronomers have been able to measure polarisation, a signature of magnetic fields, this close to the edge of a black hole. The observations are key to explaining how the M87 galaxy, located 55 million light-years away, is able to launch energetic jets from its core.
"We are now seeing the next crucial piece of evidence to understand how magnetic fields behave around black holes, and how activity in this very compact region of space can drive powerful ...
Astronomers image magnetic fields at the edge of M87's black hole
2021-03-24
The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) collaboration, who produced the first ever image of a black hole, has today revealed a new view of the massive object at the centre of the Messier 87 (M87) galaxy: how it looks in polarised light. This is the first time astronomers have been able to measure polarisation, a signature of magnetic fields, this close to the edge of a black hole. The observations are key to explaining how the M87 galaxy, located 55 million light-years away, is able to launch energetic jets from its core.
"We are now seeing the next crucial piece of evidence to understand ...
Positive self-image and self-esteem protects against weight gain in adolescence
2021-03-24
A new study from the University of Bergen (UiB) shows that the way young people view their bodies have a great impact on their BMI.
In a two-year follow up study among 1225 Norwegian adolescents in their early teens, professor Eivind Meland and his team examined how body mass index, self-esteem and self-rated health were mutually impacted and influenced by body dissatisfaction.
"We revealed that positive self-image and self-esteem protected against weight gain", professor emeritus Meland says.
The girls had in general lower body confidence than boys, the study shows.
Body dissatisfaction
The eager to be thinner, dieting, and wanting to change something with the body all impaired self-rated health ...
Want a healthier home? Start with your couch
2021-03-24
A new study shows that when people replace their old couch with a new one that has no added flame retardants, levels of the harmful chemicals in household dust drop significantly. Replacing the foam inside the couch cushions is also just as effective. The findings confirm that choosing healthier furniture without flame retardants can make a big difference in people's--especially children's--everyday exposures to these toxic chemicals.
"We've long suspected that couches are a major source of toxic chemicals in dust. Now, for the first time, we have evidence demonstrating the positive impacts of replacing old furniture containing flame retardants," ...
Effective Field Theories and the nature of the universe
2021-03-24
What is the world made of? This question, which goes back millennia, was revisited by theoretical physicist Steven Weinberg from the University of Texas in Austin, TX, USA in the first of an international seminar series, 'All Things EFT'. Weinberg's seminar has now been published as an article in the journal EPJ H.
And Weinberg is well placed to discuss both Effective Field Theories (EFTs) and the nature of the Universe, as he shared the 1979 Nobel Prize for Physics for developing a theory to unify the weak and electromagnetic interactions between elementary particles. This fed into the development of the ...
Aspirin not as effective as anticoagulation
2021-03-24
Ruptures of the carotid artery (cervical artery dissection) are the most common cause of stroke in people under 50 years of age, with an annual incidence of 2-3 cases per 100,000 persons. Salicylic-acid preparations (acetylsalicylic acid: aspirin, Aspegic) and blood-thinning medication (anticoagulants) are used for treatment. The multicenter therapy study "Biomarkers and Antithrombotic Treatment in Cervical Artery Dissection (TREAT-CAD, NCT02046460)" investigated whether dissections - tears in the wall of vessels supplying blood to the brain - can be treated with aspirin or whether more complex blood thinning (anticoagulation) ...
Tiny currents may impact vital ocean food source
2021-03-24
Copepods are tiny crustaceans about the size of a grain of rice, but they are one of the most important parts of the Earth's aquatic ecosystems. Their behavior and interaction with the environment, however, remains a relative mystery. Now, a recent paper published in the Journal of Experimental Biology sheds new light on how these miniature marvels move and cluster in the ocean.
Researchers from Bigelow Laboratory of Ocean Sciences and the Georgia Institute of Technology found that the copepods gather around small vortexes in the ocean, a finding which could have significant implications for the food web.
"We're getting at a mechanism that helps us understand how the ecosystem ...
RUDN University chemists found a way to increase the efficiency of metathesis reactions
2021-03-24
Chemists from RUDN University found out that fluorine and fluoroalkyl groups increase the efficiency of catalysts in metathesis reactions that are used in the pharmaceutical industry and polymer chemistry. The team also identified fluorine-containing compounds that can simplify the purification of the catalyst from the reaction product, making it reusable. The results of the study were published in the Russian Chemical Reviews journal.
Many medicinal drugs and polymers are based on olefins, organic compounds with a double bond between carbon atoms. To obtain useful substances from them, scientists used the metathesis reaction. In the course of metathesis, ...
Shame of contracting Covid-19 can prevent individuals declaring infection to authorities
2021-03-24
New research from the University of Kent and Leeds Beckett University has found that feelings of shame and stigmatisation at the idea of contracting Covid-19 are linked to lower compliance of social distancing and the likelihood of reporting infection to authorities and potential contacts in Italy, South Korea and the USA.
In contrast, the study found that individuals who trust their Government's response to the Covid-19 pandemic and feel a mutual solidarity are more likely to report Covid-19 contraction to authorities and acquaintances.
In Italy and South Korea, individuals are also more likely to follow social distancing regulations if they trust their Government's response to the pandemic, while in the USA, trust does not lead to social distancing compliance. This could ...
Building a picture of fathers in the family justice system in England
2021-03-24
The invisibility of dads who lose access to their children because of concerns about child neglect or their ability to provide safe care comes under the spotlight in new research.
A research partnership between the University of East Anglia and Lancaster University provides new evidence ('Up Against It': Understanding Fathers' Repeat Appearance in Local Authority Care Proceedings) about fathers' involvement in care and recurrent care proceedings in England.
A national conference today (Wednesday 24th March), co-hosted online by the two universities, will share key insights from this study, funded by the Nuffield ...
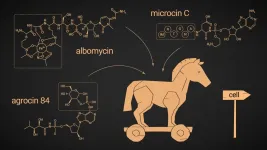
Beware of fellow bacteria bearing gifts: Skoltech research presents new potential antimicrobial agen
2021-03-24
Skoltech researchers examined the antibiotic compounds that employ a 'Trojan horse' strategy to get into a bacterial cell unrecognized and prevent the synthesis of proteins, ultimately killing the cell. They were able to identify new gene clusters that look like those of known 'Trojan horses' - these likely guide the biosynthesis of new antimicrobials that require further investigation. The review paper was published in the journal RSC Chemical Biology.
When it comes to antimicrobial attacks, the most difficult thing is breaching the formidable outer defenses: getting inside a target cell to deploy the deadly weapon can be tricky. A number of antimicrobial compounds employ the well-known 'Trojan horse' strategy: they present themselves to a cell ...
Clarity needed in classification systems for processed foods
2021-03-24
During this unique study researchers from the University of Surrey and European Food Information Council (EUFIC) reviewed over 100 scientific papers to examine if different criteria exist in developing classification systems for processed foods and, if so, what distinguishes them.
Classification systems that categorise foods according to their "level of processing" have been used to predict diet quality and health outcomes, inform guidelines and in product development.
Researchers found that most classification system's criteria are not aligned with existing scientific evidence on nutrition and food processing. It is thought that this may stem from different perspectives and intentions behind the development of some classification systems. Researchers also noted a failure ...
The world's earliest stone technologies are likely to be older than previously thought
2021-03-24
A new study from the University of Kent's School of Anthropology and Conservation has found that Oldowan and Acheulean stone tool technologies are likely to be tens of thousands of years older than current evidence suggests.
They are currently the two oldest, well-documented stone tool technologies known to archaeologists.
These findings, published by the Journal of Human Evolution, provide a new chronological foundation from which to understand the production of stone tool technologies by our early ancestors. They also widen the time frame within which to discuss the evolution of human technological capabilities and associated dietary and behavioural shifts.
For the study, a team led by Kent's Dr Alastair Key and Dr David Roberts, alongside Dr Ivan Jaric from the Biology ...
Decades of radiation-based scientific theory disproven by Ben-Gurion University US-based study
2021-03-24
BEER-SHEVA, Israel...March 24, 2021 - Surprisingly, exposure to a high background radiation might actually lead to clear beneficial health effects in humans, according to Ben-Gurion University of the Negev and Nuclear Research Center Negev (NRCN) scientists. This is the first large-scale study which examines the two major sources of background radiation (terrestrial radiation and cosmic radiation), covering the entire U.S. population.
The study's findings were recently published in Biogerontology.
Background radiation is an ionizing radiation that exists ...
Snapshot of COVID-19 vaccine intentions highlights challenges of achieving community immunity goals
2021-03-24
Ahead of the first U.S. emergency use authorization for a COVID-19 vaccine, only half of Americans said they were likely to get vaccinated as soon as possible, according to an in-depth study led by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
The researchers conducted an online survey of 2,525 Americans in a two-week period from late November to early December, asking them about their intentions regarding COVID-19 vaccination as well as other values and beliefs. About 50 percent responded that they intended to get vaccinated as soon as possible. About 10 percent said they intended not to be vaccinated at all. The remaining 40 percent replied that they probably wouldn't be vaccinated, or probably would be but not as soon as possible.
The findings ...
How grasslands respond to climate change
2021-03-24
"Based on field experiments with increased carbon dioxide concentration, artificial warming, and modified water supply, scientists understand quite well how future climate change will affect grassland vegetation. Such knowledge is largely missing for effects that already occurred in the last century," says Hans Schnyder, Professor of Grassland at the TUM.
Based on the Park Grass Experiment at Rothamsted, researchers have now shown that future predicted effects of climate change on the nutrient status of grassland vegetation have already taken hold in the last century.
Plant intrinsic mechanisms respond to CO2 increase
Since 1856, research at Rothamsted has been testing the effects of different fertilizer applications on yield performance ...
New images reveal magnetic structures near supermassive black hole
2021-03-24
A new view of the region closest to the supermassive black hole at the center of the galaxy Messier 87 (M87) has shown important details of the magnetic fields close to the black hole and hints about how powerful jets of material can originate in that region.
A worldwide team of astronomers using the Event Horizon Telescope, a collection of eight telescopes, including the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) in Chile, measured a signature of magnetic fields -- called polarization -- around the black hole. Polarization is the orientation of the electric fields in light and radio waves and it can ...
[1] ... [2491]
[2492]
[2493]
[2494]
[2495]
[2496]
[2497]
[2498]
2499
[2500]
[2501]
[2502]
[2503]
[2504]
[2505]
[2506]
[2507]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.