Lessons from computer science can make medical devices fair for all
2021-04-01
Technology can be biased, and its design can disadvantage certain demographic groups. While efforts to address bias and promote fairness in technologies are rapidly growing in a variety of technical disciplines, Achuta Kadambi argues that similar growth is not occurring fast enough for medical engineering. "Although computer science companies terminate lucrative but biased facial recognition systems, biased medical devices continue to be sold as commercial products," writes Kadambi in a Perspective. Bias in medical devices results in undesirable performance variation across demographic groups and can greatly influence health inequality. For example, optical biosensors that use light to monitor vital signs like blood oxygenation ...
Origin of modern rainforests traced to end-Cretaceous asteroid impact
2021-04-01
In an analysis of thousands of fossil pollen and leaves spanning the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K/Pg) boundary, researchers found that the cataclysmic asteroid impact that resulted in the destruction of nearly 75% of all terrestrial life on Earth drastically restructured tropical forests, setting the stage for the evolution of what has become one of the planet's most diverse ecosystems - the neotropical rainforest. While the end-Cretaceous impact nearly 66 million years ago was catastrophic for terrestrial ecosystems worldwide, its long-term effects on tropical forests have remained a mystery. This is largely due to the lack of palaeobotanical exploration in the region, which has only just begun to provide ...
How dopamine drives hallucination-like perception in mice
2021-04-01
An increase of dopamine in the brain's striatum triggers auditory hallucination-like experiences in mice, revealing a possible causal role for dopamine-dependent neurological circuits in symptoms of psychosis. These findings from a new study could inform novel targeted approaches to treating those with psychotic disorders, like schizophrenia. Auditory and visual hallucinations - perceptions of hearing or seeing something without observing external sensory stimuli - are central symptoms of psychotic disorders and are thought by some to be caused by excessive dopamine ...
A new state of light
2021-04-01
A single "super photon" made up of many thousands of individual light particles: About ten years ago, researchers at the University of Bonn produced such an extreme aggregate state for the first time and presented a completely new light source. The state is called optical Bose-Einstein condensate and has captivated many physicists ever since, because this exotic world of light particles is home to its very own physical phenomena. Researchers led by Prof. Dr. Martin Weitz, who discovered the super photon, and theoretical physicist Prof. Dr. Johann Kroha have returned from their latest "expedition" into the quantum world with a very special observation. They report of a new, previously ...
Capturing the complex
2021-04-01
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) -- Despite the fact that our planet is mostly ocean and human maritime activity is more intense than it has ever been, we know remarkably little about the state of the ocean's biodiversity -- the variety and balance of species that support healthy and productive ecosystems. And it's no surprise -- marine biodiversity is complex, human impacts are uneven, and species respond differently to different stressors.
"It is really hard to know how a species is doing by just looking out from your local coast, or dipping underwater on SCUBA," said Ben Halpern, a marine ecologist at the Bren School of Environmental Science & Management at UC Santa ...
Mice with hallucination-like behaviors reveal insight into psychotic illness
2021-04-01
The humble lab mouse has provided invaluable clues to understanding diseases ranging from cancer to diabetes to COVID-19. But when it comes to psychiatric conditions, the lab mouse has been sidelined, its rodent mind considered too different from that of humans to provide much insight into mental illness.
A new study, however, shows there are important links between human and mouse minds in how they function -- and malfunction. Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis devised a rigorous approach to study how hallucinations are produced in the brain, providing a promising entry point to the development of much-needed new therapies for schizophrenia.
The study, published April 2 in ...
Flowers!
2021-04-01
Tropical rainforests today are biodiversity hotspots and play an important role in the world's climate systems. A new study published today in Science sheds light on the origins of modern rainforests and may help scientists understand how rainforests will respond to a rapidly changing climate in the future.
The study led by researchers at the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute (STRI) shows that the asteroid impact that ended the reign of dinosaurs 66 million years ago also caused 45% of plants in what is now Colombia to go extinct, and it made way for the reign of flowering plants in modern tropical rainforests.
"We wondered how tropical rainforests changed after a drastic ecological perturbation such as the Chicxulub impact, so we looked for tropical plant fossils," said Mónica ...
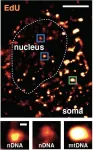
How brain cells repair their DNA reveals "hot spots" of aging and disease
2021-04-01
LA JOLLA--(April 1, 2021) Neurons lack the ability to replicate their DNA, so they're constantly working to repair damage to their genome. Now, a new study by Salk scientists finds that these repairs are not random, but instead focus on protecting certain genetic "hot spots" that appear to play a critical role in neural identity and function.
The findings, published in the April 2, 2021, issue of Science, give novel insights into the genetic structures involved in aging and neurodegeneration, and could point to the development of potential new therapies for diseases such Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and other age-related dementia disorders.
"This research shows for the first time that ...
NOAA study shows promise of forecasting meteotsunamis
2021-04-01
On the afternoon of April 13, 2018, a large wave of water surged across Lake Michigan and flooded the shores of the picturesque beach town of Ludington, Michigan, damaging homes and boat docks, and flooding intake pipes. Thanks to a local citizen's photos and other data, NOAA scientists reconstructed the event in models and determined this was the first ever documented meteotsunami in the Great Lakes caused by an atmospheric inertia-gravity wave.
An atmospheric inertia-gravity wave is a wave of air that can run from 6 to 60 miles long that is created when a mass of stable air is displaced by an air mass with significantly ...
A robot that senses hidden objects
2021-04-01
In recent years, robots have gained artificial vision, touch, and even smell. "Researchers have been giving robots human-like perception," says MIT Associate Professor Fadel Adib. In a new paper, Adib's team is pushing the technology a step further. "We're trying to give robots superhuman perception," he says.
The researchers have developed a robot that uses radio waves, which can pass through walls, to sense occluded objects. The robot, called RF-Grasp, combines this powerful sensing with more traditional computer vision to locate and grasp items that might otherwise be blocked from view. The advance could one day streamline e-commerce fulfillment in warehouses or help a machine pluck a screwdriver from a jumbled toolkit.
The research will be presented in May at the IEEE International ...
Two plant immune branches more intimately connected than previously believed
2021-04-01
Plant inducible defense starts with the recognition of microbes, which leads to the activation of a complex set of cellular responses. There are many ways to recognize a microbe, and recognition of microbial features by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) outside the cell was long thought to activate the first line of defense: Pattern Triggered Immunity, or PTI. To avoid these defense responses, microbes of all kinds evolved the ability to deliver effector molecules to the plant cell, either directly into the cytoplasm or into the area just outside the cell, where they are taken up into the cytoplasm. ...
Diet and exercise may increase efficacy of chemotherapy for children with cancer
2021-04-01
New research published today in the journal Blood Advances is the first to show that restricting calories, reducing fat and sugar intake, and increasing physical activity may boost the effectiveness of chemotherapy for older children and adolescents with leukemia. This intervention, which improved chemotherapy outcomes for children being treated at two institutions, will be further studied through a national trial later this year.
B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), a cancer affecting the white blood cells in the bone marrow, is the most common type of cancer in children. In the study, researchers assessed the effects of diet and exercise on 40 individuals aged 10-21 undergoing chemotherapy at ...
Low-calorie diet and mild exercise improve survival for young people with leukemia
2021-04-01
In some cancers, including leukemia in children and adolescents, obesity can negatively affect survival outcomes. Obese young people with leukemia are 50% more likely to relapse after treatment than their lean counterparts.
Now, a study led by researchers at UCLA and Children's Hospital Los Angeles has shown that a combination of modest dietary changes and exercise can dramatically improve survival outcomes for those with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, the most common childhood cancer.
The researchers found that patients who reduced their calorie intake by 10% or more and adopted a moderate exercise program immediately after their diagnosis had, on average, 70% less ...
New research on Alzheimer's Disease shows 'lifestyle origin at least in some degree'
2021-04-01
For years, research to pin down the underlying cause of Alzheimer's Disease has been focused on plaque found to be building up in the brain in AD patients. But treatments targeted at breaking down that buildup have been ineffective in restoring cognitive function, suggesting that the buildup may be a side effect of AD and not the cause itself.
A new study led by a team of Brigham Young University researchers finds novel cellular-level support for an alternate theory that is growing in strength: Alzheimer's could actually be a result of metabolic dysfunction in the brain. In other words, there is growing evidence that diet and lifestyle are at the ...
Diet + exercise + chemo = increased survival in youth with leukemia
2021-04-01
Los Angeles (April 1, 2021) -- Overweight children and adolescents receiving chemotherapy for treatment of leukemia are less successful battling the disease compared to their lean peers. Now, research conducted at the END ...
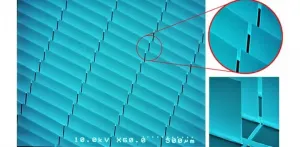
Smart glass has a bright future
2021-04-01
Buildings are responsible for 40 percent of primary energy consumption and 36 percent of total CO2 emissions. And, as we know, CO2 emissions trigger global warming, sea level rise, and profound changes in ocean ecosystems. Substituting the inefficient glazing areas of buildings with energy efficient smart glazing windows has great potential to decrease energy consumption for lighting and temperature control.
Harmut Hillmer et al. of the University of Kassel in Germany demonstrate that potential in "MOEMS micromirror arrays in smart windows for daylight steering," a paper published recently in the inaugural issue of the Journal of Optical Microsystems.
"Our smart glazing ...
Undetected coronavirus variant was in at least 15 countries before its discovery
2021-04-01
A highly contagious SARS-CoV-2 variant was unknowingly spreading for months in the United States by October 2020, according to a new study from researchers with The University of Texas at Austin COVID-19 Modeling Consortium. Scientists first discovered it in early December in the United Kingdom, where the highly contagious and more lethal variant is thought to have originated. The journal Emerging Infectious Diseases, which has published an early-release version of the study, provides evidence that the coronavirus variant B117 (501Y) had spread across the globe undetected for months when scientists discovered it.
"By the time we learned about the U.K. variant ...
Study finds why some cancer drugs may be ineffective
2021-04-01
A possible explanation for why many cancer drugs that kill tumor cells in mouse models won't work in human trials has been found by researchers with The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth) School of Biomedical Informatics and McGovern Medical School.
The research was published today in Nature Communications.
In the study, investigators reported the extensive presence of mouse viruses in patient-derived xenografts (PDX). PDX models are developed by implanting human tumor tissues in immune-deficient mice, and are commonly ...
New GSA Bulletin articles published ahead of print in March
2021-04-01
Boulder, Colo., USA: The Geological Society of America regularly publishes
articles online ahead of print. For March, GSA Bulletin topics
include multiple articles about the dynamics of China and Tibet; the ups
and downs of the Missouri River; the Los Rastros Formation, Argentina; the
Olympic Mountains of Washington State; methane seep deposits; meandering
rivers; and the northwest Hawaiian Ridge. You can find these articles at
https://bulletin.geoscienceworld.org/content/early/recent
.
Transition from a passive to active continental ...
Connecting the dots between engagement and learning
2021-04-01
We've all heard the adage, "If at first you don't succeed, try, try again," but new research from Carnegie Mellon University and the University of Pittsburgh finds that it isn't all about repetition. Rather, internal states like engagement can also have an impact on learning.
The collaborative research, published in Nature Neuroscience, examined how changes in internal states, such as arousal, attention, motivation, and engagement can affect the learning process using brain-computer interface (BCI) technology. Findings suggest that changes in internal states can systematically influence how behavior improves with learning, thus paving the way ...
African elephants' range is just 17% of what it could be, study finds
2021-04-01
A study reported in the journal Current Biology on April 1 has both good news and bad news for the future of African elephants. While about 18 million square kilometers of Africa--an area bigger than the whole of Russia--still has suitable habitat for elephants, the actual range of African elephants has shrunk to just 17%of what it could be due to human pressure and the killing of elephants for ivory.
"We looked at every square kilometer of the continent," says lead author Jake Wall of the Mara Elephant Project in Kenya. "We found that 62% of those 29.2 million ...
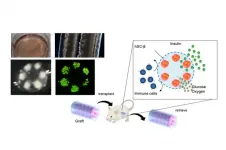
Replacing what was lost: A novel cell therapy for type I diabetes mellitus
2021-04-01
Tokyo, Japan - Type I Diabetes Mellitus (T1D) is an autoimmune disorder leading to permanent loss of insulin-producing beta-cells in the pancreas. In a new study, researchers from The University of Tokyo developed a novel device for the long-term transplantation of iPSC-derived human pancreatic beta-cells.
T1D develops when autoimmune antibodies destroy pancreatic beta-cells that are responsible for the production of insulin. Insulin regulates blood glucose levels, and in the absence of it high levels of blood glucose slowly damage the kidneys, eyes and peripheral ...
Skin deep: Aquatic skin adaptations of whales and hippos evolved independently
2021-04-01
A new study shows that the similarly smooth, nearly hairless skin of whales and hippopotamuses evolved independently. The work suggests that their last common ancestor was likely a land-dwelling mammal, uprooting current thinking that the skin came fine-tuned for life in the water from a shared amphibious ancestor. The study is published today in the journal Current Biology and was led by researchers at the American Museum of Natural History; University of California, Irvine; University of California, Riverside; Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics; and the LOEWE-Centre for Translational Biodiversity Genomics (Germany).
"How mammals left terra firma and became fully aquatic is one of the most fascinating evolutionary ...
New mechanism by which senescent cells turn on genes encoding for tumor-regulating factors
2021-04-01
PHILADELPHIA -- (April 1, 2021 -- Scientists at The Wistar Institute identified a new mechanism of transcriptional control of cellular senescence that drives the release of inflammatory molecules that influence tumor development through altering the surrounding microenvironment. The study, published in Nature Cell Biology, reports that methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) and 14 (METTL14) proteins moonlight as transcriptional regulators that allow for establishment of the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP).
Cellular senescence is a stable state of growth arrest in which cells stop dividing but remain viable and produce an array of inflammatory and growth-promoting molecules collectively defined as SASP. These molecules account ...
UMD helps quantify how climate change has slowed global agricultural productivity growth
2021-04-01
The University of Maryland (UMD) has collaborated with Cornell University and Stanford University to quantify the man-made effects of climate change on global agricultural productivity growth for the first time. In a new study published in Nature Climate Change, researchers developed a robust model of weather effects on productivity, looking at productivity in both the presence and absence of climate change. Results indicate a 21% reduction in global agricultural productivity since 1961, which according to researchers is equivalent to completely losing the last 7 years ...
[1] ... [2479]
[2480]
[2481]
[2482]
[2483]
[2484]
[2485]
[2486]
2487
[2488]
[2489]
[2490]
[2491]
[2492]
[2493]
[2494]
[2495]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.