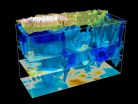
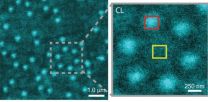
Translating thought to print
2015-05-15
Spider silk has long been noted for its graceful structure, as well as its advanced material properties: Ounce for ounce, it is stronger than steel.
MIT research has explained some of the material's mysteries, which could help design synthetic resources that mimic the extraordinary properties of natural silk. Now, scientists at MIT have developed a systematic approach to research its structure, blending computational modeling and mechanical analysis to 3D-print synthetic spider webs. These models offer insight into how spiders optimize their own webs.
"This is the ...
Epilepsy has been found to reduce the generation of new neurons
2015-05-15
This news release is available in Spanish. The mission of neural stem cells located in the hippocampus, one of the main regions of the brain, is to generate new neurons during the adult life of mammals, including human beings, of course, and their function is to participate in certain types of learning and responses to anxiety and stress. Using an epilepsy model in genetically modified mice, the researchers have discovered that hippocampal neural stem cells stop generating new neurons and are turned into reactive astrocytes, a cell type that promotes inflammation and ...
Researchers discover new ways to shut down signals involved in brain diseases
2015-05-15
A research team based at the University of Eastern Finland and the Turku Centre for Biotechnology have found new ways to block a pathway that may be responsible for several brain disorders, which could open the door to developing better treatments.
The protein NOS-1 generates nitric oxide, a chemical signal that is linked to neurological disorders from neurodegeneration, stroke and chronic pain sensitivity to anxiety and depressive disorders. These are now among the most common causes of disability and mortality, but decades of efforts have not led to a safe drug that ...
New study finds that many probiotics are contaminated with traces of gluten
2015-05-15
WASHINGTON, DC (May 15, 2015) -- More than half of popular probiotics contain traces of gluten, according to an analysis performed by investigators at the Celiac Disease Center at Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC). Tests on 22 top-selling probiotics revealed that 12 of them (or 55%) had detectable gluten.
Probiotics are commonly taken by patients for their theoretical effect in promoting gut health, though evidence of benefits is limited to a few clinical situations. "Many patients with celiac disease take dietary supplements, and probiotics are particularly popular," ...
Myriad validates active surveillance threshold with Prolaris® for men with prostate cancer
2015-05-15
SALT LAKE CITY, Utah, May 15, 2015 -- Myriad Genetics, Inc. (NASDAQ: MYGN) today presented clinical data for its Prolaris test at the 2015 American Urological Association (AUA) Annual Meeting being held May 15 to 19 in New Orleans, La. The results highlighted and underscored the significant ability of the Prolaris test to help physicians improve care for men diagnosed with prostate cancer.
In this pioneering study, Myriad presented important new clinical validation data that establishes an active surveillance (AS) threshold for men with localized prostate cancer. Specifically, ...
New test detects drug use from a single fingerprint
2015-05-15
Research published today in the journal Analyst has demonstrated a new, noninvasive test that can detect cocaine use through a simple fingerprint. For the first time, this new fingerprint method can determine whether cocaine has been ingested, rather than just touched.
Led by the University of Surrey, a team of researchers from the Netherlands Forensic Institute (NL), the National Physical Laboratory (UK), King's College London (UK) and Sheffield Hallam University (UK), used different types of an analytical chemistry technique known as mass spectrometry to analyse the ...
Men far less likely to prevent, screen for osteoporosis
2015-05-15
Great Neck, NY - While the consequences of osteoporosis are worse in men than women - including death - older males are far less likely to take preventive measures against the potentially devastating bone-thinning disease or accept recommendations for screening, according to startling new research by North Shore-LIJ Health System geriatricians.
Geriatric fellow Irina Dashkova, MD, designed and led a cross-sectional survey of 146 older adults in New York and Florida that showed stunning gender differences in perspectives, beliefs and behaviors surrounding osteoporosis, ...
Aging baby boomers, childless and unmarried, at risk of becoming 'elder orphans'
2015-05-15
Great Neck, NY - With an aging Baby Boomer population and increasing numbers of childless and unmarried seniors, nearly one-quarter of Americans over age 65 are currently or at risk to become "elder orphans," a vulnerable group requiring greater awareness and advocacy efforts, according to new research by a North Shore-LIJ geriatrician and palliative care physician.
A case study and literature review by Maria Torroella Carney, MD, chief of geriatric and palliative medicine at the North Shore-LIJ Health System, zeroes in on staggering data on the prevalence and risks ...
Perspective-taking difficulties diminished when autistic and psychosis tendencies balance
2015-05-14
Researchers at the University of Birmingham have shed new light on the relationship between autistic tendencies and psychosis proneness in neurotypical adults.
If a similar pattern were found in people diagnosed with these conditions, their findings would suggest that a co-occurrence of both conditions might balance, and diminish problems associated with perspective-taking difficulties.
The study, published in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, indicates that while increased tendencies for either condition are associated with perspective-taking difficulties, ...
Deep-water fish has a warm heart
2015-05-14
This news release is available in Japanese.
Though some large predatory fish, like tuna, have been shown to temporarily warm muscles or organs during pursuit, at least one fish may have done that one better by being able to internally generate heat that warms its heart and brain, a new study reports. This ability increases the fish's metabolic function in cold deep waters, and it shows that birds and mammals are not the only vertebrates with warm hearts. One thing that sets mammals and birds apart from vertebrates like fish is the ability to internally warm ...
Why modern hunter-gatherers live with so few kin
2015-05-14
This news release is available in Japanese.
Allowing both males and females in hunter-gatherer groups to choose their living companions reduces the number of family members in individual hunter-gatherer camps, a new study shows. The results answer a longstanding mystery about why hunter-gatherer populations have evolved to comprise large numbers of unrelated individuals, especially since hunter-gatherers have shown a strong preference to live with kin. Previously, studies have pointed to pair-bonding, or lifelong monogamous relationships in which couples go ...
Bees follow separate but similar paths in social evolution
2015-05-14
This news release is available in Japanese. There's more than one explanation for how colony-living animals like bees evolve their unique social structure, according to a detailed genome analysis conducted by Karen Kapheim and colleagues. Bees are eusocial, meaning that some of their workers forego reproduction to care for their siblings. In some cases, this can lead to an elaborate and sophisticated "superorganism" of thousands of individuals. Kapheim and colleagues took a detailed look at the genomes of ten bee species to determine if the evolution of eusociality always ...
New in the Hastings Center Report
2015-05-14
New in the Hastings Center Report
Patient-satisfaction surveys: improving health care, or leading it astray? The downside of courage, right-to-try laws, and more in the May-June 2015 issue.
Patient-Satisfaction Surveys on a Scale of 0 to 10: Improving Health Care, or Leading It Astray?
Alexandra Junewicz and Stuart J. Youngner
It is increasingly common for patient-satisfaction surveys to be used as indicators of health care quality, as well as to influence the reimbursement paid to providers. But the authors argue that the surveys could eventually compromise the ...
Study in INFORMS journal: Offline TV ads prompt online purchases by multitaskers
2015-05-14
Many television advertisers voice fears that distracted viewers -- those increasingly frenetic multitaskers using smartphones, laptops and tablets while viewing TV - are becoming less receptive to advertisers' messages. A new study published in the online Articles in Advance section of Marketing Science, a journal of the Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences (INFORMS), refutes this conventional wisdom and concludes that the "second screen" puts a virtual store in every consumer's pocket. Multitasking viewers now visit, browse, and even buy advertised ...
A 'graduation' from poverty
2015-05-14
An anti-poverty program tested extensively on three continents has produced sustained gains in individuals' income, wealth, and well-being, according to a study published today in the journal Science.
The program provides very poor people with productive assets, such as livestock, as well as job training, life-skills coaching, and health information. Known as the "Graduation" program, its intention was to examine whether helping the poor in multiple ways simultaneously could be especially effective in fighting poverty.
Overall, with more than 20,000 people enrolled ...
Love your Mother Earth
2015-05-14
A new paper, co-authored by Woods Hole Research Center Senior Scientist Richard A. Houghton, entitled, "Audit of the global carbon budget: estimate errors and their impact on uptake uncertainty", was published in the journal Biogeosciences. The paper confirms that as carbon emissions continue to climb, so too has the Earth's capacity to absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. About half of the emissions of CO2 each year remain in the atmosphere; the other half is taken up by the ecosystems on land and the oceans.
For Dr. Houghton, "There is no question that land ...
Earthquakes reveal deep secrets beneath East Asia
2015-05-14
A new work based on 3-D supercomputer simulations of earthquake data has found hidden rock structures deep under East Asia. Researchers from China, Canada, and the U.S. worked together to publish their results in March 2015 in the American Geophysical Union Journal of Geophysical Research, Solid Earth.
The scientists used seismic data from 227 East Asia earthquakes during 2007-2011, which they used to image depths to about 900 kilometers, or about 560 miles below ground.
Notable structures include a high velocity colossus beneath the Tibetan plateau, and a deep mantle ...
Campaign increases mouth and throat cancer screenings among low-income rural Floridians
2015-05-14
GAINESVILLE, Fla. -- Raising awareness of the dangers of mouth and throat cancer increased the number of black men in some of Florida's poorest counties who sought screening for the first time, opening the door to improved survival rates through early detection and treatment, UF Health researchers report.
Black men have the lowest survival rates of mouth and throat cancer in the United States, and these rates have decreased even more in recent years. To combat this problem, UF Health researchers launched a five-month media campaign targeted at black men in some of Florida's ...
Study implicates new gene in multiple sclerosis disease activity
2015-05-14
A new study led by investigators at Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) reports the discovery of a genetic variant that is associated with a patient's likelihood of responding to interferon-beta, one of the medications used in treating multiple sclerosis (MS). Published in the Annals of Neurology on May 14, the study also presents evidence that the affected gene, SLC9A9, may have a broader role in regulating the development and activity of certain immune cells that play important roles in inflammatory diseases like MS.
A proportion of MS patients experience disease activity ...
Genome-wide DNA study shows lasting impact of malnutrition in early pregnancy
2015-05-14
May 14, 2015 -- Researchers at Columbia University's Mailman School of Public Health and Leiden University in the Netherlands found that children whose mothers were malnourished at famine levels during the first 10 weeks of pregnancy had changes in DNA methylation known to suppress genes involved in growth, development, and metabolism documented at age 59. This is the first study to look at prenatal nutrition and genome-wide DNA patterns in adults exposed to severe under-nutrition at different periods of gestation. Findings are published in the International Journal of ...
Genomics laboratory capability in Liberia supports ebola virus outbreak response
2015-05-14
Army scientists working to support the Ebola virus outbreak response in West Africa have established the first genomic surveillance capability in Liberia, enabling them to monitor genetic changes in the virus within one week of sample collection. An article describing their work was recently published ahead of print in the online edition of Emerging Infectious Diseases.
In the paper, the team offers a concise evaluation of the potential impact of the evolution of Ebola virus Makona, the strain responsible for the current outbreak, based on genome reconstruction of 25 ...
Researchers hone technique for finding signs of life on the Red Planet
2015-05-14
LAWRENCE -- For centuries, people have imagined the possibility of life on Mars. But long-held dreams that Martians could be invaders of Earth, or little green men, or civilized superbeings, all have been undercut by missions to our neighboring planet that have, so far, uncovered no life at all.
Yet visits to the Red Planet by unmanned probes from NASA and the European Space Agency have found evidence that a prime condition for life once may have existed: water.
"There has been a tremendous amount of very exciting findings this year that Mars once contained actively ...
Real and false-color images of Siberia
2015-05-14
The Aqua satellite's MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) instrument took this image of the fires in Siberia. The top image shows the full sized false color image of the area highlighting the burn scars from previous fires.
The sliding "before and after" image shows the real and false color images side-by-side for comparison. The left side shows current fires burning denoted by the red spots. These spots show areas where the thermal detectors on the MODIS instrument recognized temperatures higher than background. When accompanied by plumes of smoke, ...
CLAIRE brings electron microscopy to soft materials
2015-05-14
Soft matter encompasses a broad swath of materials, including liquids, polymers, gels, foam and - most importantly - biomolecules. At the heart of soft materials, governing their overall properties and capabilities, are the interactions of nano-sized components. Observing the dynamics behind these interactions is critical to understanding key biological processes, such as protein crystallization and metabolism, and could help accelerate the development of important new technologies, such as artificial photosynthesis or high-efficiency photovoltaic cells. Observing these ...
Smoking induces early signs of cancer in cheek swabs
2015-05-14
DNA damage caused by smoking can be detected in cheek swabs, finds research published today in JAMA Oncology. The study provides evidence that smoking induces a general cancer program that is also present in cancers which aren't usually associated with it - including breast and gynaecological cancers.
The research team, led by Professor Martin Widschwendter, Head of the Department of Women's Cancer at the UCL Institute for Women's Health and Dr Andrew Teschendorff (UCL Cancer Institute) looked at epigenetic alterations - changes to the DNA that switch genes on and off. ...
[1] ... [2977]
[2978]
[2979]
[2980]
[2981]
[2982]
[2983]
[2984]
2985
[2986]
[2987]
[2988]
[2989]
[2990]
[2991]
[2992]
[2993]
... [8822]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.