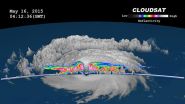
CloudSat analyzed the eye of Typhoon Dolphin
2015-05-21
When Dolphin was a typhoon on May 16, NASA's CloudSat satellite completed a stunning eye overpass of Typhoon Dolphin in the West Pacific at 0412 UTC (12:12 a.m. EDT). By May 22, Dolphin's remnants were moving through the Northern Pacific.
NASA's CloudSat satellite sends pulses of microwave energy through the clouds, and some of the energy in the pulses is reflected back to the spacecraft. The time delay between when the pulse is sent and when the reflected energy is received back at the spacecraft is mapped into a distance of the cloud from the surface of the Earth, and ...
Genetic maps help conservation managers maintain healthy bears
2015-05-21
COLUMBIA, Mo. - Last year, researchers at the University of Missouri published a study on genetic diversity in American black bears in Missouri, Arkansas and Oklahoma and determined that conservation management is needed to maintain healthy populations in the region. Now, those scientists have expanded the study to include black bears throughout North America. They discovered that black bears in Alaska are more closely related to bears in the eastern regions of the U.S. and Canada than those located in western regions. Details from the study revealed ancient movement patterns ...
Low stent thrombosis rates with primary PCI, regardless of antithrombotic choice
2015-05-21
(PARIS, FRANCE) - Stent thrombosis following urgent angioplasty for acute heart attack occurred in less than 1% of patients in a large, "real-world" registry, regardless of whether the antithrombotic treatment used during the procedure was bivalirudin, heparin alone, or a GP IIb/IIIa inhibitor (typically in combination with heparin).*
However, patients who experienced a stent thrombosis between days 2 and 30, regardless of drug regimen, were more likely to die within one year than were patients who developed stent thrombosis within the first 24 hours of their procedure.
"What ...
Pliability, elasticity of skin increase following wrinkle treatment with Botox
2015-05-21
Skin pliability and elasticity improved after treatment with onabotulinum toxin (Botox) for mild facial wrinkles and the effect lasted for up to four months, according to a report published online by JAMA Facial Plastic Surgery.
Human skin has three biomechanical features: strength, pliability (the ability to stretch) and elasticity (the ability to recoil). As people age, these properties change and the loss of skin elasticity appears to be the most prominent. Physicians use a variety of methods to reverse the signs of aging and onabotulinum toxin A injections are among ...
Personalized care during eye visits didn't lower HbA1c levels for diabetics
2015-05-21
Providing personalized education and risk assessment for patients with diabetes when they visit the ophthalmologist did not improve glycemic control as measured by hemoglobin A1c levels compared with patients who received usual care, according to a study published online by JAMA Ophthalmology.
Intensive blood glucose control can reduce the onset and progression of microvascular complications in people with diabetes. However, optimal glycemic control as measured by HbA1c is notoriously difficult to achieve. A potential strategy to improve glycemic control is to leverage ...
Workplace intervention improves sleep of employees' children
2015-05-21
A workplace intervention designed to reduce employees' work-family conflict and increase schedule flexibility also has a positive influence on the sleep patterns of the employees' children.
The intervention, Support-Transform-Achieve-Results (STAR), includes training supervisors to be more supportive of their employees' personal and family lives, changing the structure of work so that employees have more control over their work time, and changing the culture in the workplace so that colleagues are more supportive of each other's efforts to integrate their work and personal ...
Odds are that chronic gamblers are often also depressed
2015-05-21
If a young man is a chronic gambler, the chances are extremely high that he also suffers from depression. This is one of the findings from a study led by Frédéric Dussault of the University of Quebec at Montreal in Canada. Published in Springer's Journal of Gambling Studies, it is the first to investigate the extent to which gambling and depression develop hand-in-hand from the teenage years to early adulthood.
Data were drawn from an ongoing long-term study that began in 1984. It follows a group of 1,162 kindergarten boys from economically disadvantaged areas ...
Fine particulate air pollution associated with increased risk of childhood autism
2015-05-21
PITTSBURGH, May 21, 2015 -- Exposure to fine particulate air pollution during pregnancy through the first two years of a child's life may be associated with an increased risk of the child developing autism spectrum disorder (ASD), a condition that affects one in 68 children, according to a University of Pittsburgh Graduate School of Public Health investigation of children in southwestern Pennsylvania.
The research is funded by The Heinz Endowments and published in the July edition of Environmental Research.
"Autism spectrum disorders are lifelong conditions for which ...
Emoticons may signal better customer service ;)
2015-05-21
Online customer service agents who use emoticons and who are fast typists may have a better chance of putting smiles on their customers' faces during business-related text chats, according to researchers.
In a study, people who text chatted with customer service agents gave higher scores to the agents who used emoticons in their responses than agents who did not use emoticons, said S. Shyam Sundar, Distinguished Professor of Communications and co-director of the Media Effects Research Laboratory. The customers also reported that agents who used emoticons were more personal ...
CWRU dental researchers find some immune cells change to prolong inflammation
2015-05-21
Researchers at Case Western Reserve University School of Dental Medicine have unraveled one of the mysteries of how a small group of immune cells work: That some inflammation-fighting immune cells may actually convert into cells that trigger disease.
Their findings, recently reported in the journal Pathogens, could lead to advances in fighting diseases, said the project's lead researcher Pushpa Pandiyan, an assistant professor at the dental school.
The cells at work
A type of white blood cell, called T-cells, is one of the body's critical disease fighters. Regulatory ...
Premature aging: Scientists identify and correct defects in diseased cells
2015-05-21
Scientists from the Institut Pasteur and CNRS, in collaboration with scientists from the Institut Gustave Roussy and CEA, have succeeded in restoring normal activity in cells isolated from patients with the premature aging disease Cockayne syndrome. They have uncovered the role played in these cells by an enzyme, the HTRA3 protease.
This enzyme is overexpressed in Cockayne syndrome patient cells, and leads to mitochondrial defects, which in turn play a crucial role in the appearance of symptoms leading to aging in affected children. These findings, published in the ...
Team publishes findings about compound with potential for treating rheumatoid arthritis
2015-05-21
BOZEMAN, Mont. -- Montana State University researchers and their collaborators have published their findings about a chemical compound that shows potential for treating rheumatoid arthritis.
The paper ran in the June issue of the Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics (JPET), and one of its illustrations is featured on the cover. JPET is a leading scientific journal that covers all aspects of pharmacology, a field that investigates the effects of drugs on biological systems and vice versa.
"This journal is one of the top journals that reports new types ...
Cost of wages and lack of competence the greatest obstacles to productivity improvement
2015-05-21
According to small and medium-sized enterprises, sizable social security and other wage-related costs still form the single greatest obstacle for improving productivity. Additionally, a lack of competence among supervisors was also seen as an obstacle for productivity. This information is from a newly published survey by the Lappeenranta University of Technology (LUT), which is a follow-up to a study on the obstacles that restrain the productivity of companies published in 1997. A total of 239 representatives from Finnish small and medium-sized enterprises responded to ...
Mayo Clinic, Phoenix Children's Hospital study highlighted during Dog Bite Prevention Week
2015-05-21
PHOENIX -- Prior studies have shown that most dog bite injuries result from family dogs. A new study conducted by Mayo Clinic and Phoenix Children's Hospital shed some further light on the nature of these injuries.
The American Veterinary association has designated this week as Dog Bite Prevention Week.
The study, published last month in the Journal of Pediatric Surgery, demonstrated that more than 50 percent of the dog bites injuries treated at Phoenix Children's Hospital came from dogs belonging to an immediate family member.
The retrospective study looked at a ...
Hiding your true colors may make you feel morally tainted
2015-05-21
The advice, whether from Shakespeare or a modern self-help guru, is common: Be true to yourself. New research suggests that this drive for authenticity -- living in accordance with our sense of self, emotions, and values -- may be so fundamental that we actually feel immoral and impure when we violate our true sense of self. This sense of impurity, in turn, may lead us to engage in cleansing or charitable behaviors as a way of clearing our conscience.
The findings are published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
"Our work ...
Eastern diamondback rattlesnakes' quest for fire
2015-05-21
Two words that arouse immediate fear in some people inspire something else altogether in Jennifer Fill.
"I love snakes and fire," Fill says. "When I was looking at grad schools, I thought, 'if I can just combine those two things, I bet I'll be really happy.'"
It's not about cozy campfires or garden-variety garters for Fill, a biologist who recently defended her dissertation at the University of South Carolina. The fires she's interested in are forest fires, and the snake that was the subject of her doctoral studies is Crotalus adamanteus, commonly called the eastern diamondback ...
Report on expanded success initiative points to changes in schools
2015-05-21
A new report on New York City's Expanded Success Initiative (ESI), which is designed to boost college and career readiness among Black and Latino male students, finds that the schools involved are changing the way they operate and offering students opportunities they would not otherwise have.
"There is strong evidence that these schools are doing something different as a result of ESI," says the study's lead author, Adriana Villavicencio, senior research associate at the Research Alliance for New York City Schools. "We are seeing important shifts in the tone and culture ...
Symbiosis turns messy in 13-year cicadas
2015-05-21
Bacteria that live in the guts of cicadas have split into many separate but interdependent species in a strange evolutionary phenomenon that leaves them reliant on a bloated genome, a new paper by CIFAR Fellow John McCutcheon's lab (University of Montana) has found.
Cicadas subsist on tree sap, which doesn't provide them all the nutrients they need to live. Bacteria in their gut, including one called Hodgkinia, turns the sap into amino acids that sustain them during their unusual lives. Cicadas spend most of their lives underground before emerging in droves, singing loudly, ...
Social structure 'helps birds avoid a collision course'
2015-05-21
The sight of skilful aerial manoeuvring by flocks of Greylag geese to avoid collisions with York's Millennium Bridge intrigued mathematical biologist Dr Jamie Wood. It raised the question of how birds collectively negotiate man-made obstacles such as wind turbines which lie in their flight paths.
It led to a research project with colleagues in the Departments of Biology and Mathematics at York and scientists at the Animal and Plant Health Agency. The study found that the social structure of groups of migratory birds may have a significant effect on their vulnerability ...
Turn that defect upside down
2015-05-21
Most people see defects as flaws. A few Michigan Technological University researchers, however, see them as opportunities. Twin boundaries -- which are small, symmetrical defects in materials -- may present an opportunity to improve lithium-ion batteries. The twin boundary defects act as energy highways and could help get better performance out of the batteries.
This finding, published in Nano Letters earlier this year, turns a previously held notion of material defects on its head. Reza Shahbazian-Yassar helped lead the study and holds a joint appointment at Michigan ...
Experts map surgical approaches for auditory brainstem implantation
2015-05-21
May 21, 2015 -- A technique called auditory brainstem implantation can restore hearing for patients who can't benefit from cochlear implants. A team of US and Japanese experts has mapped out the surgical anatomy and approaches for auditory brainstem implantation in the June issue of Operative Neurosurgery, published on behalf of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons by Wolters Kluwer.
Dr. Albert L. Rhoton, Jr., and colleagues of University of Florida, Gainesville, and Fukuoka University, Japan, performed a series of meticulous dissections to demonstrate and illustrate ...
How supercooled water is prevented from turning into ice
2015-05-21
Water behaves in mysterious ways. Especially below zero, where it is dubbed supercooled water, before it turns into ice. Physicists have recently observed the spontaneous first steps of the ice formation process, as tiny crystal clusters as small as 15 molecules start to exhibit the recognisable structural pattern of crystalline ice. This is part of a new study, which shows that liquid water does not become completely unstable as it becomes supercooled, prior to turning into ice crystals. The team reached this conclusion by proving that an energy barrier for crystal formation ...
Infections can affect your IQ
2015-05-21
New research shows that infections can impair your cognitive ability measured on an IQ scale. The study is the largest of its kind to date, and it shows a clear correlation between infection levels and impaired cognition.
Anyone can suffer from an infection, for example in their stomach, urinary tract or skin. However, a new Danish study shows that a patient's distress does not necessarily end once the infection has been treated. In fact, ensuing infections can affect your cognitive ability measured by an IQ test:
"Our research shows a correlation between hospitalisation ...
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals in baby teethers
2015-05-21
This news release is available in German. FRANKFURT. In laboratory tests, two out of ten teethers, plastic toys used to sooth babies' teething ache, release endocrine disrupting chemicals. One product contains parabens, which are normally used as preservatives in cosmetics, while the second contains six so-far unidentified endocrine disruptors. The findings were reported by researchers at the Goethe University in the current issue of the Journal of Applied Toxicology.
"The good news is that most of the teethers we analyzed did not contain any endocrine disrupting ...
Simulations predict flat liquid
2015-05-21
Computer simulations have predicted a new phase of matter: atomically thin two-dimensional liquid.
This prediction pushes the boundaries of possible phases of materials further than ever before. Two-dimensional materials themselves were considered impossible until the discovery of graphene around ten years ago. However, they have been observed only in the solid phase, because the thermal atomic motion required for molten materials easily breaks the thin and fragile membrane. Therefore, the possible existence of an atomically thin flat liquid was considered impossible.
Now ...
[1] ... [2979]
[2980]
[2981]
[2982]
[2983]
[2984]
[2985]
[2986]
2987
[2988]
[2989]
[2990]
[2991]
[2992]
[2993]
[2994]
[2995]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.