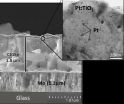
Artificial photosynthesis: New, stable photocathode with great potential
2015-05-12
Many of us are familiar with electrolytic splitting of water from their school days: if you hold two electrodes into an aqueous electrolyte and apply a sufficient voltage, gas bubbles of hydrogen and oxygen are formed. If this voltage is generated by sunlight in a solar cell, then you could store solar energy by generating hydrogen gas.This is because hydrogen is a versatile medium of storing and using "chemical energy". Research teams all over the world are therefore working hard to develop compact, robust, and cost-effective systems that can accomplish this challenge. ...
Researchers theoretically demonstrate detection of spin of atoms at room temperature
2015-05-12
For the first time, a researcher at the University of Waterloo has theoretically demonstrated that it is possible to detect a single nuclear spin at room temperature, which could pave the way for new approaches to medical diagnostics.
Published in the journal Nature nanotechnology this week, Amir Yacoby from the University of Waterloo, along with colleagues from University of Basel and RWTH Aachen University, propose a theoretical scheme that could lead to enhanced Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) imaging of biological materials in the near future by using weak magnetic ...
Astrophysicists prepare weather forecasts for planets beyond our solar system
2015-05-12
TORONTO, ON -- "Cloudy for the morning, turning to clear with scorching heat in the afternoon."
While this might describe a typical late-summer day in many places on Earth, it may also apply to planets outside our solar system, according to a new study by an international team of astrophysicists from the University of Toronto, York University and Queen's University Belfast.
Using sensitive observations from the Kepler space telescope, the researchers have uncovered evidence of daily weather cycles on six extra-solar planets seen to exhibit different phases. Such phase ...
Exogenous microRNAs in maternal food pass through placenta, regulate fetal gene expression
2015-05-12
In a new study published in the Protein & Cell, Chen-Yu Zhang's group at Nanjing University reports that small non-coding RNAs in maternal food can transfer through placenta to regulate fetal gene expression.
MicroRNAs (miRNA) are a class of noncoding RNAs with lengths of approximately 22 nucleotides that bind to target messenger RNAs to inhibit protein translation. In previous studies, the same group has found that plant miRNAs can enter into the host blood and tissues via the route of food-intake. The food-derived exogenous miRNAs are absorbed, packaged into microvesical ...
Bacterial communities can act as precise biosensors of environmental damage
2015-05-12
WASHINGTON, DC -- May 12, 2015-- A multidisciplinary group of US-based researchers has shown that the mixture of species found within natural bacterial communities in the environment can accurately predict the presence of contaminants such as uranium, nitrate, and oil. The findings, published this week in mBio, the online open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology, show that the rapid sequencing of microbiomes in place at environmental sites can be used to monitor damage caused by human activity.
"This approach might be a general way for us to see anthropogenic ...
Nerve cells in the fast lane
2015-05-12
Nerve cells that produce dopamine for the purpose of transmitting signals to other cells affect numerous crucial brain functions. This becomes evident in diseases such as Parkinson's and schizophrenia, where dopamine transmission in the brain is impaired. In collaboration with researchers from Bonn, RUB scientists at the Mercator Research Group "Structure of Memory" have now identified in what way a specific form of this important cell is generated and which networks it forms in the course of brain development. In the process, the researchers discovered a data highway of ...
E-skin and pocket-sized diagnostic machines give patients the power back
2015-05-12
Amsterdam, May 12, 2015 - Wearable E-skin that can measure heart rate and blood pressure, and paper diagnostic machines the size of a credit card that can give instant readings on blood and saliva samples are two new bio-sensing technologies presented at Elsevier's 4th International Conference on Bio-Sensing Technology in Lisbon, Portugal on 12 May 2015.
Bio-sensors can detect and analyze data to give patients information on their heart rate and blood pressure, blood sugar and hormone levels, and even test whether they are infected with antibiotic-resistant bacteria. ...
Scientists regenerate bone tissue using only proteins secreted by stem cells
2015-05-12
SAN FRANCISCO, CA--MAY 11, 2015--Scientists have discovered a way to regrow bone tissue using the protein signals produced by stem cells. This technology could help treat victims who have experienced major trauma to a limb, like soldiers wounded in combat or casualties of a natural disaster. The new method improves on older therapies by providing a sustainable source for fresh tissue and reducing the risk of tumor formation that can arise with stem cell transplants.
The new study, published in Scientific Reports, is is the first to extract the necessary bone-producing ...
Using microbial communities to assess environmental contamination
2015-05-12
First there were canaries in coal mines, now there are microbes at nuclear waste sites, oil spills and other contaminated environments. A multi-institutional team of more than 30 scientists has found that statistical analysis of DNA from natural microbial communities can be used to accurately identify environmental contaminants and serve as quantitative geochemical biosensors. This study was sponsored by ENIGMA, a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science "Scientific Focus Area Program" based at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab).
"Changes ...
siRNA-toting nanoparticles inhibit breast cancer metastasis
2015-05-12
Researchers at Case Western Reserve University combined finely crafted nanoparticles with one of nature's potent disrupters to prevent the spread of triple-negative breast cancer in mouse models.
The highly aggressive cancer subtype is difficult to manage and, currently, the FDA has no approved targeted treatments. But striking results from a new study, published in the journal Cancer Research make the researchers optimistic they have a potential game-changer for triple negative cancer and more.
"There are multiple targets within a cell," said William Schiemann, professor ...
Prenatal exercise lowers risks of C-sections, higher birth weights
2015-05-12
Pregnant women who exercise can significantly lower the risk of undergoing Caesarean sections and giving birth to large babies, a University of Alberta study has found.
Prenatal exercise has been suggested to be a means to prevent childhood obesity through a "normalization" in birth weight (ie. reducing the risk of having a large baby at birth). University of Alberta researchers conducted a meta-analysis to analyze 28 randomized control studies encompassing 5,322 women that looked at the influence of maternal exercise on baby outcomes.
"We found that women who exercised ...
How the presence of conservation researchers affects wildlife
2015-05-12
In a study that compared three sites within the Dja Conservation Complex in Cameroon, Africa, investigators found that the presence of a conservation research project acts as a deterrent to chimpanzee and gorilla poachers, and community awareness and involvement in research lead to an increased value of apes and intact forests to local people, thus limiting hunting practices.
The results provide evidence that the mere existence of research programs exerts a positive impact on the conservation of wildlife in their natural habitats.
"It's important to recognize the effectiveness ...
Psychotic hallucinations, delusions rarely precede violence
2015-05-12
Mass shootings at the hands of unhinged loners - such as those in Aurora, Colorado; Santa Barbara, California, and Newtown, Connecticut - perpetuate a commonly held belief that mental illness triggers violent crimes.
But a new study from the University of California, Berkeley, shows that hallucinations and delusions associated with psychiatric disorders seldom foreshadow acts of aggression.
In a painstaking review of 305 violent incidents in the United States, the researchers found that only 12 percent were preceded by psychosis. While numerous studies have found that ...
Ants' movements hide mathematical patterns
2015-05-12
When ants go exploring in search of food they end up choosing collective routes that fit statistical distributions of probability. This has been demonstrated by a team of mathematicians after analysing the trails of a species of Argentine ant. Studies like this could be applied to coordinate the movement of micro-robots in cleaning contaminated areas for example.
Scientists have yet to discover the mechanisms explaining how flocks of birds, shoals of fish, lines of ants and other complex natural systems organise themselves so well when moving collectively.
To tackle ...
New device provides chikungunya test results in an hour
2015-05-12
Scientists at a U.S. Army research center have modified an assay that tests whether or not a sample of mosquitoes harbors the virus responsible for the disease known as chikungunya (CHIKV), long a problem in the Old World tropics but recently established in the Americas. Their assay is described in an article in the Journal of Medical Entomology.
Health workers now have a quick way to detect the presence of the CHIKV virus within an hour, rather than waiting for results of laboratory tests that take days, or even weeks. It's done with a chemical dipstick, the same kind ...
Bacteria the newest tool in detecting environmental damage
2015-05-12
KNOXVILLE--The reaction most people have when they hear the word bacteria is rarely a good one.
While it's true that food- and water-borne bacteria cause untold illnesses and even death around the world, a team of researchers from the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, and Oak Ridge National Laboratory has found a way to use bacteria to help prevent some of the very symptoms most people associate with them.
Terry Hazen, the Governor's Chair for Environmental Biotechnology, a joint UT-ORNL appointment, is working with a team of researchers who have developed a method ...
Survival from rare bone cancer remains low
2015-05-12
MAYWOOD, IL - Among the deadliest cancers is a rare malignancy called mesenchymal chondrosarcoma, which begins in cartilage around bones and typically strikes young adults.
Ten-year survival has been reported to be as low as 20 percent. But a Loyola University Medical Center study has found survival is not as dismal as prior reports. Among 205 cases examined, more than half (51 percent) of patients survived at least five years, and 43 percent survived at least 10 years, the study found.
The study by senior author Lukas Nystrom, MD, and colleagues was reported at the Mid-America ...
Rethinking the rebound: Unexpected effects of rejection
2015-05-12
May 12, 2015 - It's portrayed in movies again and again - a character gets rejected by someone attractive and then falls willingly into the arms of someone perhaps less attractive. According to a new study, it's not so simple: Rejection by an attractive man actually led women to socially distance themselves from an unattractive man, even when he offered acceptance.
"We hadn't expected to see derogation of the unattractive male when women had been rejected by the attractive male," says Geoff MacDonald of the University of Toronto and lead author of the new study in Social ...
Cause of regression in individuals with down syndrome identified
2015-05-12
COLUMBIA, Mo. - Down syndrome, the most common chromosomal disorder in America, can be complicated by significant deterioration in movement, speech and functioning in some adolescents and young adults. Physicians previously attributed this regression to depression or early-onset Alzheimer's, and it has not responded to treatments. Now, a researcher at the University of Missouri has found that Catatonia, a treatable disorder, may cause regression in patients with Down syndrome. Individuals with regressive Down syndrome who were treated for Catatonia showed improvement, the ...
The weakest magnetic field in the solar system
2015-05-12
This news release is available in German.
Magnetic fields easily penetrate matter. Creating a space practically devoid of magnetic fields thus presents a great challenge. An international team of physicists has now developed a shielding that dampens low frequency magnetic fields more than a million-fold. Using this mechanism, they have created a space that boasts the weakest magnetic field of our solar system. The physicists now intend to carry out precision experiments there.
Magnetic fields exist everywhere in the universe. Here on the Earth, we are permanently ...
Out with heavy metal
2015-05-12
RICHLAND, Wash - Researchers have demonstrated a new process for the expanded use of lightweight aluminum in cars and trucks at the speed, scale, quality and consistency required by the auto industry. The process reduces production time and costs while yielding strong and lightweight parts, for example delivering a car door that is 62 percent lighter and 25 percent cheaper than that produced with today's manufacturing methods.
In partnership with General Motors, Alcoa and TWB Company LLC, researchers from the Department of Energy's Pacific Northwest National Laboratory ...
Children exposed to multiple languages may be better natural communicators
2015-05-12
Young children who hear more than one language spoken at home become better communicators, a new study from University of Chicago psychologists finds. Effective communication requires the ability to take others' perspectives. Researchers discovered that children from multilingual environments are better at interpreting a speaker's meaning than children who are exposed only to their native tongue. The most novel finding is that the children do not even have to be bilingual themselves; it is the exposure to more than one language that is the key for building effective social ...
New research will help forecast bad ozone days over the western US
2015-05-12
New research published in Nature Communications led by Meiyun Lin of NOAA's Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory and NOAA's cooperative institute at Princeton University, reveals a strong connection between high ozone days in the western U.S. during late spring and La Niña, an ocean-atmosphere phenomena that affects global weather patterns.
Recognizing this link offers an opportunity to forecast ozone several months in advance, which could improve public education to reduce health effects. It would also help western U.S. air quality managers prepare to track these ...
Political talk on Facebook mirrors political talk offline
2015-05-12
LAWRENCE -- Political discussions conducted on social networking sites like Facebook mirror traditional offline discussions and don't provide a window into previously untapped participants in the political process, according to a new study that includes two University of Kansas researchers.
"Social networking is important, but what we've shown in political science is that the people who are using the Internet, be it Facebook, Twitter or whatever else for political activities, are really the same people who are politically active offline anyway," said Patrick Miller, a ...
CU Anschutz researchers create microscope allowing deep brain exploration
2015-05-12
AURORA, Colo. (May 12, 2015) - A team of neuroscientists and bioengineers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus have created a miniature, fiber-optic microscope designed to peer deeply inside a living brain.
The researchers, including scientists from the University of Colorado Boulder, published details of their revolutionary microscope in the latest issue of Optics Letters journal.
"Microscopes today penetrate only about one millimeter into the brain but almost everything we want to see is deeper than that," said Prof. Diego Restrepo, PhD, one of the ...
[1] ... [2982]
[2983]
[2984]
[2985]
[2986]
[2987]
[2988]
[2989]
2990
[2991]
[2992]
[2993]
[2994]
[2995]
[2996]
[2997]
[2998]
... [8822]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.