Centipede's genome reveals how life evolved on our planet
2014-11-25
Centipedes, those many-legged creatures that startle us in our homes and gardens, have been genetically sequenced for the first time. In a new study in the journal PLoS Biology, an international team of over 100 scientists today reveals how this humble arthropod's DNA gave them new insight into how life developed on our planet.
Centipedes are members of the arthropods, a group with numerous species including insects, spiders and other animals. Until now, the only class of arthropods not represented by a sequenced genome was the myriapods, which include centipedes and ...
Mere expectation of treatment can improve brain activity in Parkinson's patients
2014-11-25
Learning-related brain activity in Parkinson's patients improves as much in response to a placebo treatment as to real medication, according to a new study by researchers at the University of Colorado Boulder and Columbia University.
Past research has shown that while Parkinson's disease is a neurological reality, the brain systems involved may also be affected by a patient's expectations about treatment. The new study, published in the journal Nature Neuroscience, explains how the placebo treatment -- when patients believe they have received medication when they have ...
Endangered species success: Idaho salmon regaining fitness advantage
2014-11-25
Endangered Snake River sockeye salmon are regaining the fitness of their wild ancestors, with naturally spawned juvenile sockeye migrating to the ocean and returning as adults at a much higher rate than others released from hatcheries, according to a newly published analysis. The analysis indicates that the program to save the species has succeeded and is now shifting to rebuilding populations in the wild.
Biologists believe the increased return rate of sockeye spawned naturally by hatchery-produced parents is high enough for the species to eventually sustain itself in ...
Homeless, mentally ill women face vicious cycle in India
2014-11-25
MAYWOOD, Il. - An award-winning study by a Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine researcher has documented how homeless, mentally ill women in India face a vicious cycle:
During psychotic episodes, they wander away from home, sometimes for long distances, and wind up in homeless shelters. They then are returned to their families before undergoing sufficient psychosocial rehabilitation to deal with their illness. Consequently, they suffer mental illness relapses and wind up homeless again.
"The study illustrates how there must be a balance between reintegrating ...
Another reason to be thankful: Turkeys may be lifesavers
2014-11-25
While the turkey you eat on Thursday will bring your stomach happiness and could probably kick-start an afternoon nap, it may also save your life one day.
That's because the biological machinery needed to produce a potentially life-saving antibiotic is found in turkeys. Looks like there is one more reason to be grateful this Thanksgiving.
"Our research group is certainly thankful for turkeys," said BYU microbiologist Joel Griffitts, whose team is exploring how the turkey-born antibiotic comes to be. "The good bacteria we're studying has been keeping turkey farms healthy ...
Vultures evolved an extreme gut to cope with disgusting dietary habits
2014-11-25
How is it that vultures can live on a diet of carrion that would at least lead to severe food-poisoning, and more likely kill most other animals? This is the key question behind a recent collaboration between a team of international researchers from Denmark's Centre for GeoGenetics and Biological Institute at the University of Copenhagen, Aarhus University, the Technical University of Denmark, Copenhagen Zoo and the Smithsonian Institution in the USA. An "acidic" answer to this question is now published in the scientific journal Nature Communications.
When vultures eat ...
Blu-ray disc can be used to improve solar cell performance
2014-11-25
Who knew Blu-ray discs were so useful? Already one of the best ways to store high-definition movies and television shows because of their high-density data storage, Blu-ray discs also improve the performance of solar cells -- suggesting a second use for unwanted discs -- according to new research from Northwestern University.
An interdisciplinary research team has discovered that the pattern of information written on a Blu-ray disc -- and it doesn't matter if it's Jackie Chan's "Supercop" or the cartoon "Family Guy" -- works very well for improving light absorption across ...
Long-term testosterone therapy does not increase the risk of prostate cancer
2014-11-25
New York, NY, November 25, 2014 - Testosterone (T) therapy is routinely used in men with hypogonadism, a condition in which diminished function of the gonads occurs. Although there is no evidence that T therapy increases the risk of prostate cancer (PCa), there are still concerns and a paucity of long-term data. In a new study in The Journal of Urology®, investigators examined three parallel, prospective, ongoing, cumulative registry studies of over 1,000 men. Their analysis showed that long-term T therapy in hypogonadal men is safe and does not increase the risk of ...
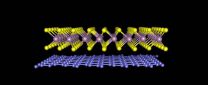
Physicists bind single-atom sheets with the same force geckos use to climb walls
2014-11-25
LAWRENCE -- Physicists at the University of Kansas have fabricated an innovative substance from two different atomic sheets that interlock much like Lego toy bricks. The researchers said the new material -- made of a layer of graphene and a layer of tungsten disulfide -- could be used in solar cells and flexible electronics. Their findings are published today by Nature Communications.
Hsin-Ying Chiu, assistant professor of physics and astronomy, and graduate student Matt Bellus fabricated the new material using "layer-by-layer assembly" as a versatile bottom-up nanofabrication ...
Vegetable oil ingredient key to destroying gastric disease bacteria
2014-11-25
The bacterium Helicobacter pylori is strongly associated with gastric ulcers and cancer. To combat the infection, researchers at University of California, San Diego School of Medicine and Jacobs School of Engineering developed LipoLLA, a therapeutic nanoparticle that contains linolenic acid, a component in vegetable oils. In mice, LipoLLA was safe and more effective against H. pylori infection than standard antibiotic treatments.
The results are published online Nov. 24 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"Current H. pylori treatments are facing ...
A link between DNA transcription and disease-causing expansions
2014-11-25
Medford/Somerville, Mass--Researchers in human genetics have known that long nucleotide repeats in DNA lead to instability of the genome and ultimately to human hereditary diseases such Freidreich's ataxia and Huntington's disease.
Scientists have believed that the lengthening of those repeats occur during DNA replication when cells divide or when the cellular DNA repair machinery gets activated. Recently, however, it became apparent that yet another process called transcription, which is copying the information from DNA into RNA, could also been involved.
A Tufts ...
Missing gene linked to autism
2014-11-25
Researchers at the University of Leeds have shed light on a gene mutation linked to autistic traits.
The team already knew that some people with autism were deficient in a gene called neurexin-II. To investigate whether the gene was associated with autism symptoms, the Leeds team studied mice with the same defect.
They found behavioural features that were similar to autism symptoms, including a lack of sociability or interest in other mice.
Dr Steven Clapcote, Lecturer in Pharmacology in the University's Faculty of Biological Sciences, who led the study published ...
Breakthrough in flexible electronics enabled by inorganic-based laser lift-off
2014-11-25
Flexible electronics have been touted as the next generation in electronics in various areas, ranging from consumer electronics to bio-integrated medical devices. In spite of their merits, insufficient performance of organic materials arising from inherent material properties and processing limitations in scalability have posed big challenges to developing all-in-one flexible electronics systems in which display, processor, memory, and energy devices are integrated. The high temperature processes, essential for high performance electronic devices, have severely restricted ...
Researchers identify new ways to drain cancer's 'fuel tank'
2014-11-25
Cancer stem cells are particularly difficult to eradicate and are at the heart of why it is so hard to more effectively treat cancer patients, as the post-treatment survival of cancer stem cells drives tumour recurrence, the systemic spread of cancer and, ultimately, treatment failure.
The researchers, based at the University's Institute of Cancer Sciences and the Cancer Research UK Manchester Institute - both part of the Manchester Cancer Research Centre - investigated the role of mitochondria which produce and release energy within cells. In this context, the new ...
Using wash cloths in jails shows promise for reducing costly infections
2014-11-25
CHICAGO (November 25, 2014) - New research shows providing detainees wash cloths treated with a skin cleanser could reduce the prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) bacteria in U.S. jails. Researchers looked at the effect on transmission of S. aureus of using wash cloths treated with chlorhexidine gluconate (CHG) compared with wash cloths with only plain water in detainees at Dallas County Jail. The study was published in the December issue of Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology, the journal of the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA). ...
Superbug in SE Michigan shows recent decline
2014-11-25
CHICAGO (November 25, 2014) - A new study finds a decrease in an emergent strain of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) that is resistant to last line defense antibiotics. Researchers examined the prevalence of vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA) infections in southeastern Michigan, where the majority of these infections have occurred in the U.S. The study is published in the December issue of Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology, the journal of the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA).
"Vancomycin is one of the few antimicrobial ...
Vanderbilt team uses e-health records to search for hidden drug benefits
2014-11-25
With research and development costs for many drugs reaching well into the billions, pharmaceutical companies want more than ever to determine whether their drugs already at market have any hidden therapeutic benefits that could warrant putting additional indications on the label and increase production.
Such repurposing of drugs requires evidence of efficacy, and to find candidate drugs for randomized controlled repurposing trials, investigators can use computer simulation and scans of health care billing data, in addition to in vitro and in vivo testing.
A study led ...
Trojan horse tactic gives parasites edge over immune systems
2014-11-25
Parasites use Trojan horse subterfuge to suppress the immunity of their victims when causing infection, according to a study.
The finding, which shows a new trick parasites can play, paves the way to possible treatments for infectious diseases and allergies.
Scientists have shown that parasites are able to secrete tiny sealed packages of genetic material into the cells of their victims, in order to suppress the immune response to infection.
The packages, known as vesicles, mimic those that are produced naturally in most organisms to carry out everyday functions such ...
Researchers shed new light on the genetics of memory performance
2014-11-25
(Boston)-- In the largest study of the genetics of memory ever undertaken, an international researcher team including scientists from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM), have discovered two common genetic variants that are believed to be associated with memory performance. The findings, which appear in the journal Biological Psychiatry, are a significant step towards better understanding how memory loss is inherited.
Longer life spans and the increased prevalence of memory impairment and dementia world-wide underscore the critical public health importance of ...
A hybrid vehicle that delivers DNA
2014-11-25
BUFFALO, N.Y. - A new hybrid vehicle is under development.
Its performance isn't measured by the distance it travels, but rather the delivery of its cargo: vaccines that contain genetically engineered DNA to fight HIV, cancer, influenza and other maladies.
Described recently in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the technology is a biomedical advancement that could help unleash the potential of DNA vaccines, which despite two decades of research, have yet to make a significant impact in the treatment of major illnesses.
"The technology that we're developing ...
Pathology specialist contributes to debate on breast cancer gene screening
2014-11-25
There has been much recent debate on the benefits and risks of screening for breast cancer using BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations in the general adult population. With an estimated 235,000 new breast cancer diagnoses each year in the U.S. and more than 40,000 deaths, it is clearly important to be able to determine which women may be genetically predisposed to breast cancer.
Glenn E. Palomaki, PhD, associate director of the Division of Medical Screening and Special Testing in the Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine at Women & Infants Hospital of Rhode Island has ...
Study supports free 'super Wi-Fi'
2014-11-25
This news release is available in German.
Wireless data transmission largely takes place via WLAN networks, such as WiFi. However, these networks are currently limited to high frequency ranges at 2 GHz and above and, hence, have a limited range. The authors of the study, Arnd Weber of the Institute for Technology Assessment and Systems Analysis (ITAS) of KIT and Jens Elsner, a former member of the staff of the KIT Communications Engineering Lab, propose to extend the frequencies for free communication to include lower ranges and even increased transmission power. ...
Athletes' testosterone surges not tied to winning, study finds
2014-11-25
A higher surge of testosterone in competition, the so-called "winner effect," is not actually related to winning, suggests a new study of intercollegiate cross country runners.
The International Journal of Exercise Science published the research, led by David Edwards, a professor of psychology at Emory University, and his graduate student Kathleen Casto.
"Many people in the scientific literature and in popular culture link testosterone increases to winning," Casto says. "In this study, however, we found an increase in testosterone during a race regardless of the athletes' ...
Mining can damage fish habitats far downstream, study shows
2014-11-25
Anglers across the nation wondering why luck at their favorite fishing spot seems to have dried up may have a surprising culprit: a mine miles away, even in a different state.
Scientists at Michigan State University (MSU) have taken a first broad look at the impacts of mines across the country- and found that mining can damage fish habitats miles downstream, and even in streams not directly connected to the mines.
The work is published in this week's issue of the journal Ecological Indicators.
"We've been surprised that even a single mine in headwaters might influence ...
Incomes fall as stressed economy struggles
2014-11-25
Australian average incomes are falling with the country's population growth "masking underlying economic weakness", according to a QUT economist.
Dr Mark McGovern, a senior lecturer in QUT's Business School, said while it was regularly proclaimed Australia had experienced positive economic growth for more than 20 years, there had been periodic per capita declines, indicating the economy was not as healthy as assumed.
"Looking at national income figures in recent years shows our economy is under stress," Dr McGovern, whose research was recently published in the Economic ...
[1] ... [3168]
[3169]
[3170]
[3171]
[3172]
[3173]
[3174]
[3175]
3176
[3177]
[3178]
[3179]
[3180]
[3181]
[3182]
[3183]
[3184]
... [8824]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.