Physicists and chemists work to improve digital memory technology
2014-11-24
Lincoln, Neb., Nov. 24, 2104 -- The improvements in random access memory that have driven many advances of the digital age owe much to the innovative application of physics and chemistry at the atomic scale.
Accordingly, a team led by University of Nebraska-Lincoln researchers has employed a Nobel Prize-winning material and common household chemical to enhance the properties of a component primed for the next generation of high-speed, high-capacity RAM.
The team, which published its findings in the Nov. 24 edition of the journal Nature Communications, engineered and tested ...
Babies remember nothing but a good time, study says
2014-11-24
Parents who spend their time playing with and talking to their five-month-old baby may wonder whether their child remembers any of it a day later.
Thanks to a new BYU study, we now know that they at least remember the good times.
The study, published in Infant Behavior and Development, shows that babies are more likely to remember something if there is a positive emotion, or affect, that accompanies it.
"People study memory in infants, they study discrimination in emotional affect, but we are the first ones to study how these emotions influence memory," said BYU psychology ...
Can stress management help save honeybees?
2014-11-24
Honeybee populations are clearly under stress--from the parasitic Varroa mite, insecticides, and a host of other factors--but it's been difficult to pinpoint any one of them as the root cause of devastating and unprecedented losses in honeybee hives. Researchers writing in the Cell Press journal Trends in Parasitology on November 24th say that the problem likely stems from a complex and poorly understood interplay of stresses and their impact on bee immunity and health. It's a situation they suspect might be improved through stress management and better honeybee nutrition.
As ...
Study finds most older adults qualify for statin therapy under new cholesterol guidelines
2014-11-24
MINNEAPOLIS, MN - November 24, 2014 - Nearly all individuals in their late 60s and early 70s -- including 100 percent of men -- now qualify for and should consider starting a statin medication to reduce their risk of cardiovascular disease, under the recently released cholesterol guidelines from the American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Heart Association (AHA).
That's according to a research letter published today in the 11/20/2014 (JAMA-IM) by Michael D. Miedema, MD, MPH, a research cardiologist at Minneapolis Heart Institute Foundation and cardiologist ...
Selenium compounds boost immune system to fight against cancer
2014-11-24
The immune system is designed to remove things not normally found in the body. Cells undergoing change, e.g. precursors of cancer cells, are therefore normally recognised and removed by the immune system. Unfortunately, the different cancer cells contain mechanisms that block the immune system's ability to recognise them, allowing them to freely continue cancer development.
Certain cancer cells overexpress immunostimulatory molecules in liquid form. Such over-stimulation has a negative impact on the immune system:
"You can say that the stimulating molecules over-activate ...
Bad news for kids
2014-11-24
The degree to which parents sacrifice themselves for their children depends on a variety of factors. On the one hand nest predators pose a threat to the young and the parent birds. But also the time of hatching plays a role. Earlier studies have shown that birds born late in the season are more likely to be protected by their parents, as the adult birds often do not have the chance to produce replacement clutches. Older offspring also tend to be protected more readily than younger ones, as much more parental care and energy have already been invested.
"Studies on the ...
Asteroid impacts on Earth make structurally bizarre diamonds
2014-11-24
Scientists have argued for half a century about the existence of a form of diamond called lonsdaleite, which is associated with impacts by meteorites and asteroids. A group of scientists based mostly at Arizona State University now show that what has been called lonsdaleite is in fact a structurally disordered form of ordinary diamond.
The scientists' report is published in Nature Communications, Nov. 20, by Péter Németh, a former ASU visiting researcher (now with the Research Centre of Natural Sciences of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences), together with ASU's ...
Lionfish analysis reveals most vulnerable prey as invasion continues
2014-11-24
CORVALLIS, Ore. - If you live in lionfish territory in the Atlantic Ocean, the last thing you want to be is a small fish with a long, skinny body, resting by yourself at night, near the bottom of the seafloor.
If so, your chances of being gobbled up by a lionfish increase by about 200 times.
Findings of a study on lionfish predation behavior, which may also apply to some other fish and animal species, have shed some new light on which types of fish are most likely to face attack by this invasive predator, which has disrupted ecosystems in much of the Caribbean Sea and ...
Preconception care for diabetic women could potentially save $5.5 billion
2014-11-24
Philadelphia, PA, November 24, 2014 - Pregnant women with diabetes are at an increased risk for many adverse birth outcomes. Preconception care (PCC) can significantly lower these risks by helping pregnant mothers with diabetes control their glucose levels, resulting in healthier babies and less money spent on complicated deliveries and lifelong medical complications. Effective, universal PCC for diabetic mothers could avert an estimated $5.5 billion in health expenditures and lost employment productivity over affected children's lifetimes, according to a new study published ...
Ultra-short X-ray pulses explore the nano world
2014-11-24
This news release is available in German.
X-ray flashes are a unique scientific tool. They are generated by accelerating electrons to very high energy levels in kilometer-long vacuum tubes, so-called linear accelerators, and then deflecting them with specially arranged magnets. In the process the particles emit X-ray radiation that is amplified until an ultra-short and intensive X-ray flash is released.
Researchers use these X-ray flashes to resolve structures as small as one ten billionth of a meter (0.1 nanometer) in size. That is roughly the diameter of a ...
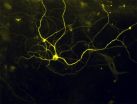
Pain and itch in a dish
2014-11-24
LA JOLLA, CA--November 24, 2014--A team led by scientists from The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) has found a simple method to convert human skin cells into the specialized neurons that detect pain, itch, touch and other bodily sensations. These neurons are also affected by spinal cord injury and involved in Friedreich's ataxia, a devastating and currently incurable neurodegenerative disease that largely strikes children.
The discovery allows this broad class of human neurons and their sensory mechanisms to be studied relatively easily in the laboratory. The "induced ...
Scientists identify bone cells that could help children who need corrective facial surgery
2014-11-24
ANN ARBOR--Our bones are smart. Bones know that by adolescence it's time to stop growing longer and stronger, and from that point on bones keep their shape by healing injuries.
This question of why bones grow longer and stronger in children, but stay static in adults--yet retain the ability to heal themselves, has long perplexed scientists in the bone regeneration field. But researchers from the University of Michigan, Kyoto University and Harvard University believe they may have unearthed a big piece of this puzzle.
The team discovered that a certain subset of cartilage-making ...
Drugs to block angiogenesis could provide new treatment for TB
2014-11-24
VIDEO:
When zebrafish are infected with bright blue Mycobacterium marinum, bright red immune cells quickly surround the bacteria to form tightly organized nuggets called granulomas (vessels green, bacteria blue, immune cells...
Click here for more information.
DURHAM, N.C. -- The body responds to tuberculosis infection by locking the bacterial offenders into tiny clusters of immune cells called granulomas, which are a hallmark of the disease. This containment strategy succeeds ...
Research reveals how our bodies keep unwelcome visitors out of cell nuclei
2014-11-24
The structure of pores found in cell nuclei has been uncovered by a UCL-led team of scientists, revealing how they selectively block certain molecules from entering, protecting genetic material and normal cell functions. The discovery could lead to the development of new drugs against viruses that target the cell nucleus and new ways of delivering gene therapies, say the scientists behind the study.
At the heart of every cell in our body is a cell nucleus, a dense structure that contains our DNA. For a cell to function normally, it needs to surround its nucleus with a ...
Underwater robot sheds new light on Antarctic sea ice
2014-11-24
The first detailed, high-resolution 3-D maps of Antarctic sea ice have been developed using an underwater robot. Scientists from the UK, USA and Australia say the new technology provides accurate ice thickness measurements from areas that were previously too difficult to access.
The results, published this week in the journal Nature Geoscience (Monday 24 November 2014), step up the pace of research in the polar regions aimed at understanding the dramatic sea ice changes in the context of climate change.
Scientists use a range of technologies and techniques to measure ...
New research discovers gene that reduces risk of stroke
2014-11-24
Scientists have discovered a gene that protects people against one of the major causes of stroke in young and middle-aged adults and could hold the key to new treatments.
Researchers from Royal Holloway, University of London, together with an international team from across the United States and Europe, have found that people with a specific variant of a gene, known as PHACTR1, are at reduced risk of suffering cervical artery dissection, which is caused by a tear in an artery that leads to the brain.
The new discovery, published in the journal Nature Genetics, could ...
Magnetic fields and lasers elicit graphene secret
2014-11-24
Scientists at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) have studied the dynamics of electrons from the "wonder material" graphene in a magnetic field for the first time. This led to the discovery of a seemingly paradoxical phenomenon in the material. Its understanding could make a new type of laser possible in the future. Together with researchers from Berlin, France, the Czech Republic and the United States, the scientists precisely described their observations in a model and have now published their findings in the scientific journal Nature Physics.
Graphene ...
Excessive contact between cellular organelles disrupts metabolism in obesity
2014-11-24
Boston, MA - Researchers at Harvard School of Public Health (HSPH) have found a novel mechanism causing type 2 diabetes that could be targeted to prevent or treat the disease. The research highlights a previously unrecognized molecular pathway that contributes to the malfunction of liver cells in obesity, leading to insulin resistance and diabetes.
The study appears online November 24, 2014 in Nature Medicine.
"While it is well-established that obesity generates cellular and molecular stress leading to abnormal functioning of many cellular processes, the mechanisms ...
New device could make large biological circuits practical
2014-11-24
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Researchers have made great progress in recent years in the design and creation of biological circuits -- systems that, like electronic circuits, can take a number of different inputs and deliver a particular kind of output. But while individual components of such biological circuits can have precise and predictable responses, those outcomes become less predictable as more such elements are combined.
A team of researchers at MIT has now come up with a way of greatly reducing that unpredictability, introducing a device that could ultimately allow such ...
Pain in a dish
2014-11-24
After more than six years of intensive effort, and repeated failures that made the quest at times seem futile, Harvard Stem Cell Institute (HSCI) researchers at Boston Children's Hospital (BCH) and Harvard's Department of Stem Cell and Regenerative Biology (HSCRB) have successfully converted mouse and human skin cells into pain sensing neurons that respond to a number of stimuli that cause acute and inflammatory pain.
This "disease in a dish" model of pain reception may advance the understanding of different types of pain, identify why individuals differ in their pain ...
Masking HIV target cells prevents viral transmission in animal model
2014-11-24
Cloaking immune cells with antibodies that block T cell trafficking to the gut can substantially reduce the risk of viral transmission in a non-human primate model of HIV infection, scientists report.
The findings suggest that drugs that are already in clinical trials for inflammatory bowel diseases might be effective in the treatment or prevention of HIV infection.
The results are scheduled for publication in Nature Medicine.
"We were surprised by the effects that we observed," says senior author Aftab Ansari, PhD, professor of pathology and laboratory ...
Animals steal defenses from bacteria
2014-11-24
It's a dog eat dog world, and bacteria have been living in it for a long time. It's of no surprise that bacteria have a sophisticated arsenal to compete with each other for valuable resources in the environment. In 2010, work led by University of Washington Department of Microbiology Associate Professor Joseph Mougous uncovered a weaponry system used in this warfare between bacteria. The combatants inject deadly toxins into rival cells.
Now, in a surprising twist, Mougous and colleagues have found that many animals have taken a page from the bacterial playbook. They steal ...
Global warming cynics unmoved by extreme weather
2014-11-24
EAST LANSING, Mich. --- What will it take to convince skeptics of global warming that the phenomenon is real? Surely, many scientists believe, enough droughts, floods and heat waves will begin to change minds.
But a new study led by a Michigan State University scholar throws cold water on that theory.
Only 35 percent of U.S. citizens believe global warming was the main cause of the abnormally high temperatures during the winter of 2012, Aaron M. McCright and colleagues report in a paper published online today in the journal Nature Climate Change.
"Many people already ...
Cooling with the coldest matter in the world
2014-11-24
Physicists at the University of Basel have developed a new cooling technique for mechanical quantum systems. Using an ultracold atomic gas, the vibrations of a membrane were cooled down to less than 1 degree above absolute zero. This technique may enable novel studies of quantum physics and precision measurement devices, as the researchers report in the journal Nature Nanotechnology.
Ultracold atomic gases are among the coldest objects in existence. Laser beams can be used to trap atoms inside a vacuum chamber and slow down their motion to a crawl, reaching temperatures ...
Italian natural history museums on the verge of collapse?
2014-11-24
Are Italian natural history museums (NHMs) on the verge of collapse? A new analysis published in the open access journal ZooKeys points out that these institutions are facing a critical situation due to progressive loss of scientific relevance, decreasing economic investments and scarcity of personnel.
The study proposes that existing museums associate and collaborate to form a diffused structure, able to better manage their scientific collections and share resources and personnel.
"Italy is universally known for its history, culture, food and art. The list of Italian ...
[1] ... [3171]
[3172]
[3173]
[3174]
[3175]
[3176]
[3177]
[3178]
3179
[3180]
[3181]
[3182]
[3183]
[3184]
[3185]
[3186]
[3187]
... [8824]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.