Nail stem cells prove more versatile than press ons
2014-11-21
There are plenty of body parts that don't grow back when you lose them. Nails are an exception, and a new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) reveals some of the reasons why.
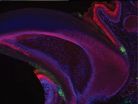
A team of USC Stem Cell researchers led by principal investigator Krzysztof Kobielak and co-first authors Yvonne Leung and Eve Kandyba has identified a new population of nail stem cells, which have the ability to either self-renew or undergo specialization or differentiation into multiple tissues.
To find these elusive stem cells, the team used a sophisticated ...
Mental disorders due to permanent stress
2014-11-21
Stress activates the immune system
The team focused mainly on a certain type of phagocytes, namely microglia. Under normal circumstances, they repair synapses between nerves cells in the brain and stimulate their growth. Once activated, however, microglia may damage nerve cells and trigger inflammation processes. The studies carried out in Bochum have shown that the more frequently microglia get triggered due to stress, the more they are inclined to remain in the destructive mode - a risk factor for mental diseases such as schizophrenia.
Susceptibility for stress effects ...
Novel regulatory mechanism for cell division found
2014-11-21
A protein kinase or enzyme known as PKM2 has proven to control cell division, potentially providing a molecular basis for tumor diagnosis and treatment.
A study, led by Zhimin Lu, M.D., Ph.D., professor of neuro-oncology at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, showcased the non-metabolic abilities of PKM2 (pyruvate kinase M2) in promoting tumor cell proliferation when cells produce more of the enzyme.
The study results were published in today's issue of Nature Communications.
Dr. Lu's group previously demonstrated that PKM2 controls gene expression ...
Researchers tease out glitches in immune system's self-recognition
2014-11-21
Immunity is a thankless job. Though the army of cells known as the immune system continuously keeps us safe from a barrage of viruses, bacteria and even precancerous cells, we mainly notice it when something goes wrong: "Why did I get the flu this year even though I got vaccinated?" "Why does innocent pollen turn me into a red-eyed, sniffling mess?"
A new study from Johns Hopkins takes a big step toward answering this and other questions about immunity, shedding light on how the body recognizes enemies on the molecular level -- and how that process can go wrong. The results ...
Tapeworms on the brain expand our knowledge of their genome
2014-11-21
A genome of a rare species of tapeworm found living inside a patient's brain has been sequenced for the first time, in research published in the open access journal Genome Biology. The study provides insights into potential drug targets within the genome for future treatments.
Tapeworms are parasites that are most commonly found living in the gut, causing symptoms such as weakness, weight loss and abdominal pain. However, the larvae of some species of tapeworm are able to travel further afield to areas such as the eyes, the brain and spinal cord.
A 50-year-old man ...
Brain-dwelling worm in UK man's head sequenced
2014-11-21
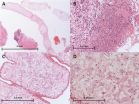
For the first time, the genome of a rarely seen tapeworm has been sequenced. The genetic information of this invasive parasite, which lived for four years in a UK resident's brain, offers new opportunities to diagnose and treat this invasive parasite.
The tapeworm, Spirometra erinaceieuropaei, has been reported only 300 times worldwide since 1953 and has never been seen before in the UK. The worm causes sparganosis: inflammation of the body's tissues in response to the parasite. When this occurs in the brain, it can cause seizures, memory loss and headaches. The worm's ...
The Lancet: Worldwide action needed to address hidden crisis of violence against women and girls
2014-11-21
Current efforts to prevent violence against women and girls are inadequate, according to a new Series published in The Lancet. Estimates suggest that globally, 1 in 3 women has experienced either physical or sexual violence from their partner, and that 7% of women will experience sexual assault by a non-partner at some point in their lives.
Yet, despite increased global attention to violence perpetrated against women and girls, and recent advances in knowledge about how to tackle these abuses (Paper 1, Paper 3), levels of violence against women - including intimate ...
Effectiveness of campaigns addressing violence against women and girls examined
2014-11-21
WASHINGTON--Levels of violence against women and girls--such as female genital mutilation, trafficking, forced marriage and intimate partner violence--remain high across the world despite the global attention the issue has received. The focus needs to shift to preventing violence, rather than just dealing with the consequences, according to a new series on violence against women and girls published Friday in The Lancet.
Mary Ellsberg, director of the George Washington University's Global Women's Institute (GWI), co-authored one of the five papers published in the special ...
Results of new drug, ASP8273, show response in patients with treatment-resistant NSCLC
2014-11-21
Barcelona, Spain: In a second presentation looking at new ways of treating non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that has both the EGFR and T790M mutations, researchers will tell the 26th EORTC-NCI-AACR [1] Symposium on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics in Barcelona, Spain, that an oral drug called ASP8273 has caused tumour shrinkage in patients in a phase I clinical trial in Japan.
Mutations of the epidermal growth factor (EGFR) occur in about 30-35% of Asian patients with NSCLC (and in 10-15% of Caucasian patients). EGFR inhibitors called tyrosine kinase inhibitors ...
US policy that gives priority to prior organ donors who need a transplant is working
2014-11-21
Highlights
Living organ donors who later need kidney transplants have much shorter waiting times, and they receive higher quality kidneys compared with similar people on the waiting list who were not organ donors.
In 2010, a total of 16,900 kidney transplants took place in the U.S. Of those, only 6,278 were from living donors.
Washington, DC (November 20, 2014) -- Prior organ donors who later need a kidney transplant experience brief waiting times and receive excellent quality kidneys, according to a study appearing in an upcoming issue of the Journal of the American ...
Exercise may improve physical function, lessen pain in patients with kidney disease
2014-11-21
Highlights
A 12-week course of aerobic exercise improved physical function and quality of life in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease.
The exercise program also decreased patients' pain.
More than 20 million people in the United States have chronic kidney disease.
Washington, DC (November 20, 2014) -- Simple yet structured exercise can significantly improve kidney disease patients' quality of life as well as decrease their pain, according to a study appearing in an upcoming issue of the Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (CJASN). The ...
Pain, magnet displacement in MRI in patients with cochlear implants
2014-11-20
Pain, discomfort and magnet displacement were documented in a small medical records review study of patients with cochlear implants (CIs) who underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), according to a report published online by JAMA Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery.
A CI can help patients with severe to profound hearing loss and about 300,000 people worldwide have the device. However, undergoing MRI can pose concerns for patients with CI because of exposure of the internal magnet to a strong electromagnetic field. There have been previous reports of adverse events, ...
When vaccines are imperfect
2014-11-20
Philadelphia, PA--The control of certain childhood diseases is difficult, despite high vaccination coverage in many countries. One of the possible reasons for this is "imperfect vaccines," that is, vaccines that fail either due to "leakiness," lack of effectiveness on certain individuals in a population, or shorter duration of potency.
In a paper publishing today in the SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, authors Felicia Magpantay, Maria Riolo, Matthieu Domenech de Celles, Aaron King, and Pejman Rohani use a mathematical model to determine the consequences of vaccine ...
New survey of employers about the health insurance market
2014-11-20
A new nationally representative survey of employers--the largest purchasers of health care in the country-- shows that most are unfamiliar with objective metrics of health plan quality information. The survey, conducted by The Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research, also found that employers are looking to the Affordable Care Act (ACA) as they make significant decisions on the benefits they offer, with the costs of health plans as a key consideration. Funding for the survey was provided by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation.
"There appears to be a serious ...
Time-lapse photos and synched weather data unlock Antarctic secrets
2014-11-20
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- In preparation for his upcoming fieldwork, Brown University research analyst Jay Dickson took 10,000 pictures of the inside of his freezer. He wasn't investigating disappearing food or making sure the light went off when he closed the door. Dickson was making sure his new camera and timer would function properly for long periods in sub-freezing temperatures.
"Everything worked great in the freezer for five weeks," Dickson said, "so hopefully it will all work in the field."
That camera's next stop: a remote Antarctic outpost, where ...
New study: Aggressive conifer removal benefits Sierra aspen
2014-11-20
Chester, CA-- A study just published by Point Blue Conservation Science shows the benefits of an aggressive approach to restoring Sierra Nevada aspen stands (Populus tremuloides).
Most of the aspen stands that dotted the Sierra Nevada less than a century ago are gone or in poor health. Aspen stands can increase groundwater, enrich soils and support a higher diversity of plants and wildlife, relative to adjacent forest types. Keeping aspen stands as part of our forests is critical to maintaining a healthy Sierra Nevada forest ecosystem for people and wildlife.
The ...
UC Irvine-Italian researchers create first inhibitor for enzyme linked to cancers
2014-11-20
Irvine, Calif., Nov. 20, 2014 -- Recent studies showing acid ceramidase (AC) to be upregulated in melanoma, lung and prostate cancers have made the enzyme a desired target for novel synthetic inhibitor compounds. This week in Angewandte Chemie, a top journal in chemistry, UC Irvine and Italian Institute of Technology scientists describe the very first class of AC inhibitors that may aid in the efficacy of chemotherapies.
AC, which is encoded by the ASAH1 gene, plays an important role in the regulation of cell fate, setting the balance between pro-aging/death and pro-life ...
Cost of meeting basic needs rising faster than wages in Washington state
2014-11-20
A Washington family of four must spend 46 percent more on average to make ends meet today than 13 years ago, according to a new report from the University of Washington.
The Self-Sufficiency Standard for Washington State 2014, released Thursday (Nov. 20), provides a sobering look at how much it costs individuals and families statewide to meet basic needs -- and how far short they're falling.
The study found that Washington families with two adults, a preschooler and a school-aged child saw the costs of meeting their most basic requirements jump as much as 72 percent ...
Discovery sheds light on nuclear reactor fuel behavior during a severe event
2014-11-20
A new discovery about the atomic structure of uranium dioxide will help scientists select the best computational model to simulate severe nuclear reactor accidents.
Using the Advanced Photon Source (APS), a Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science User Facility, researchers from DOE's Argonne National Laboratory and Brookhaven National Laboratory, along with Materials Development, Inc., Stony Brook University, and Carnegie Institution of Washington, found that the atomic structure of uranium dioxide (UO2) changes significantly when it melts.
UO2 is the primary ...
Economic burden of prediabetes up 74 percent over five years
2014-11-20
The economic burden of diabetes in America continues to climb, exceeding more than $322 billion in excess medical costs and lost productivity in 2012, or more than $1,000 for every American, according to a study being published in the December issue of Diabetes Care that also includes a state-by-state breakdown of the prevalence and costs associated with diabetes. Additionally, increased costs associated with prediabetes and undiagnosed diabetes highlight the growing importance of prevention and early intervention.
The study, which follows up on a similar report published ...
Moffitt researchers use evolutionary principles to model cancer mutations
2014-11-20
TAMPA, Fla. - Moffitt Cancer Center researchers are taking a unique approach to understanding and investigating cancer by utilizing evolutionary principles and computational modeling to examine the role of specific genetic mutations in the Darwinian struggle among tumor and normal cells during cancer growth.
Cells become malignant by acquiring genetic mutations that lead to increased survival and reproduction. Many researchers in the past have viewed cancer progression as the result of unlimited accumulation of these genetic mutations. However, Moffitt researchers ...
Study: Obesity fuels silent heart damage
2014-11-20
Fast facts:
The study shows that obesity leads to subclinical heart muscle injury and increases the risk for heart failure even among people without overt heart disease and independently of other cardiovascular risk factors such as diabetes, high blood pressure and high cholesterol.
The silent heart damage was detected by using an ultrasensitive test that measures the levels of a protein released by the cells of the heart muscle during injury.
The findings suggest that obesity is an independent driver of heart muscle damage, and that obese individuals, even when free ...
Mass. General-developed system reveals how our brains and bodies change as we fall asleep
2014-11-20
Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) investigators have developed a system to accurately track the dynamic process of falling asleep, something has not been possible with existing techniques. In their report in the October issue of the open-access journal PLOS Computational Biology, the research team describes how combining key physiologic measurements with a behavioral task that does not interfere with sleep onset gives a better picture of the gradual process of falling asleep. In addition to being a powerful tool for future research, the system could provide valuable ...
Deep-earth carbon offers clues on origin of life on Earth
2014-11-20
New findings by a Johns Hopkins University-led team reveal long unknown details about carbon deep beneath the Earth's surface and suggest ways this subterranean carbon might have influenced the history of life on the planet.
The team also developed a new, related theory about how diamonds form in the Earth's mantle.
For decades scientists have had little understanding of how carbon behaved deep below the Earth's surface even as they learned more and more about the element's vital role at the planet's crust. Using a model created by Johns Hopkins geochemist Dimitri ...
A global report card: Are children better off than they were 25 years ago?
2014-11-20
Twenty-five years ago this month, the countries that compose the United Nations reached a landmark agreement that laid the foundation for much-needed strengthening of children's rights and protections in nearly every country around the world.
Today, the Convention on the Rights of the Child remains the only formal global effort to improve children's rights and the most widely ratified human rights treaty in history. Only three U.N. member nations have not ratified the treaty: Somalia, South Sudan and the United States.
"The Convention on the Rights of the Child is a ...
[1] ... [3175]
[3176]
[3177]
[3178]
[3179]
[3180]
[3181]
[3182]
3183
[3184]
[3185]
[3186]
[3187]
[3188]
[3189]
[3190]
[3191]
... [8824]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.