New method to determine antibiotic resistance fast
2014-11-24
Scientists from Uppsala University, the Science for Life Laboratory (SciLifeLab) in Stockholm and Uppsala University Hospital have developed a new method of rapidly identifying which bacteria are causing an infection and determining whether they are resistant or sensitive to antibiotics. The findings are now being published in the Journal of Clinical Microbiology.
'Clinical use of the method would mean that the right antibiotic treatment could be started straightaway, reducing unnecessary use of antibiotics,' says Professor Dan I. Andersson of Uppsala University, who ...
Cell's skeleton is never still
2014-11-24
HOUSTON - (Nov. 24, 2014) - New computer models that show how microtubules age are the first to match experimental results and help explain the dynamic processes behind an essential component of every living cell, according to Rice University scientists.
The results could help scientists fine-tune medications that manipulate microtubules to treat cancer and other diseases. Rice theoretical biophysicist Anatoly Kolomeisky and postdoctoral researcher Xin Li reported their results in the Journal of Physical Chemistry B.
Microtubules are cylinders made of 13 protein strands ...
Sleep apnea linked to poor aerobic fitness
2014-11-24
People with moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea may have an intrinsic inability to burn high amounts of oxygen during strenuous aerobic exercise, according to a new study led by researchers at University of California, San Diego School of Medicine.
The study, reported in the current issue of Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, shows that people with sleep apnea, in which breathing repeatedly starts and stops during slumber, have a lower peak oxygen uptake during aerobic activity than those who do not suffer from the sleep disorder.
People who suffer from apnea ...
Avoiding ecosystem collapse
2014-11-24
From coral reefs to prairie grasslands, some of the world's most iconic habitats are susceptible to sudden collapse due to seemingly minor events. A classic example: the decimation of kelp forests when a decline of otter predation unleashes urchin population explosions. Three studies published in the Nov. 24 special issue of Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society Biological Science hold the promise of helping resource managers predict, avoid, and reverse the tipping points that lead to degraded habitats, economic losses, and social upheaval.
The studies are the ...
Has a possible new lead been found in the fight against neurodegenerative diseases?
2014-11-24
Good communication between brain cells is vital for optimal (mental) health. Mutations in the TBC1D24 gene inhibit this process, thereby causing neurodegeneration and epilepsy. Fruit flies with a defect in Skywalker, the fruit fly variant of TBC1D24, are being used as a model for neurodegeneration. Researchers from VIB and KU Leuven have succeeded in completely suppressing neurodegeneration in such fruit flies, by partially inhibiting the breakdown of 'defective' proteins in brain cells.
Patrik Verstreken (VIB/KU Leuven): "These unexpected results offer us a new line ...
High-dose interleukin-2 effective in mRCC pre-treated with VEGF-targeted therapies
2014-11-24
VIDEO:
High-dose interleukin-2 can be effective in selected metastatic renal cell cancer patients pre-treated with VEGF-targeted agents, reveals research presented today at the ESMO Symposium on Immuno-Oncology in Geneva, Switzerland....
Click here for more information.
Lugano/Geneva, Switzerland, 24 November 2014 - High-dose interleukin-2 can be effective in selected metastatic renal cell cancer patients pre-treated with VEGF-targeted agents, reveals research presented ...
Discovery by NUS researchers contributes towards future treatment of multiple sclerosis
2014-11-24
A multi-disciplinary research team from the National University of Singapore (NUS) has made a breakthrough discovery of a new type of immune cells that may help in the development of a future treatment for multiple sclerosis (MS).
Led by Professor Xin-Yuan Fu, Senior Principal Investigator from CSI Singapore and Professor at the Department of Biochemistry at the NUS Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, and Dr Wanqiang Sheng, post-doctoral fellow at CSI Singapore, the team found that a new type of immune T helper cells named TH-GM cells play a crucial role in the immune system ...
Survivors of childhood eye cancer experience normal cognitive functioning as adults
2014-11-24
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. - November 24, 2014) Most long-term survivors of retinoblastoma, particularly those who had been diagnosed with tumors by their first birthdays, have normal cognitive function as adults, according to a St. Jude Children's Research Hospital study. The research, which appears in the current issue of the journal Cancer, found that the vast majority of survivors work full time, live independently and fulfill other milestones of adult life.
The study is the first to examine how adult survivors of retinoblastoma fare cognitively and socially decades after their ...
Important element in the fight against sleeping sickness found
2014-11-24
Researchers from Aarhus University have taken an important step in the fight against sleeping sickness, a disease that is a major problem in parts of Africa. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the disease threatens approximately 60 million people and the treatment options are poor.
The deadly disease is caused by a parasite that is transferred to people via the bite of the African tsetse fly. The parasite lives in the bloodstream where it absorbs haemoglobin from human red blood cells. However, if left untreated it can infect the central nervous system ...
Study finds provider-focused intervention improves HPV vaccination rates
2014-11-24
(Boston)--Changing the way doctors practice medicine is difficult, however a new study has shown that combining traditional education with quality improvement and incentives improves Human Papilloma virus (HPV) vaccination rates in boys and girls. The study, which appears on-line in the journal Vaccine, has the potential to produce sustained improvements in these vaccination rates.
Every year, approximately three million Americans seek treatment for HPV related diseases. Twenty-seven thousand Americans develop HPV-related cancer while more than 5,000 people die from this ...
'Good fat' could help manage type 2 diabetes
2014-11-24
A special type of fat found in some people could be used to manage type 2 diabetes.
Scientists from Monash University and Stockholm University have discovered that brown fat, nicknamed the 'good fat' because it warms up the body in cold temperatures, burning up calories in the process, also 'hoovers up' excess sugar.
The findings, published in The Journal of Cell Biology, are significant for people with type 2 diabetes, whose bodies are unable to respond to insulin properly, resulting in elevated blood glucose levels. Researchers believe that if brown fat cells can ...
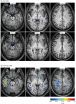
Football players found to have brain damage from mild 'unreported' concussions
2014-11-24
Beer-Sheva, Israel, Nov. 24, 2014 - A new, enhanced MRI diagnostic approach was, for the first time, able to identify significant damage to the blood-brain barrier (BBB) of professional football players following "unreported" trauma or mild concussions. Published in the current issue of JAMA Neurology, this study could improve decision making on when an athlete should "return to play."
According to Dr. Alon Friedman, from the Ben-Gurion University Brain Imaging Research Center and discoverer of the new diagnostic, "until now, there wasn't a diagnostic capability to identify ...
Breaking with tradition: The 'personal touch' is key to cultural preservation
2014-11-24
"Memetics," or the study of memes, is a very popular discipline among cultural researchers now, particularly as it concerns new media like viral videos. But no one seems to know what a meme really is.
Originally coined by evolutionary biologist Richard Dawkins, the "meme" transfers cultural information much the way that genes inherit biological properties. Pharrell Williams' feel-good hit "Happy" (2013), one of the top-selling singles of all time, is a recent example of a wildly popular meme. Originally tucked away in the soundtrack of the film Despicable Me 2, the song ...
Teens prescribed anti-anxiety or sleep medications more likely to abuse those drugs illegally
2014-11-24
WASHINGTON - Teens prescribed anti-anxiety or sleep medications may be up to 12 times more likely to abuse those drugs illegally than teens who have never received a prescription, often by obtaining additional pills from friends or family members, according to new research published by the American Psychological Association.
Based on surveys of more than 2,700 high school and middle school students from the Detroit area, almost 9 percent had been prescribed a potentially addictive benzodiazepine anti-anxiety medication (e.g., Xanax, Valium or Klonopin) or sleep medication ...
Sorting through recycling bins to learn about alcohol use
2014-11-24
COLUMBUS, Ohio - When researchers wanted to verify alcohol-use survey results at a senior housing center, they came up with a novel way to measure residents' drinking: Count the empty bottles in recycling bins.
Scientists compared the recycling bin results with two residential surveys gauging drinking habits of people living in a San Diego complex for low-income, older adults.
"We were able to check how much the residents said they were drinking with the empty beer, wine and liquor containers they were actually putting in the recycling bins," said John Clapp, co-author ...
Mimics do not substitute for the 'real thing' for bomb-sniffing dogs
2014-11-24
When it comes to teaching dogs how to sniff out explosives, there's nothing quite like the real thing to make sure they're trained right. That's the message from William Kranz, Nicholas Strange and John Goodpaster of Indiana University-Purdue University Indianapolis (IUPUI) in the US, after finding that dogs that are trained with so-called "pseudo-explosives" could not reliably sniff out real explosives (and vice versa). Their findings are published online in Springer's journal Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry.
Genuine explosive materials are traditionally used ...
Experience with family verbal conflict as a child can help in stressful situations as an adult
2014-11-24
Washington, DC (November 26, 2014) - The holiday season gives people the opportunity to reconnect with friends and family each year. Sometimes these interactions can be stressful, especially around the Thanksgiving table where a heated debate can occur. How come some people are better at handling these stressful interactions than others? A recent study published in the journal Human Communication Research by researchers at Rollins College and The Pennsylvania State University found that individuals who were exposed to intense verbal aggression as children are able to handle ...
New treatments for cancer, diabetes, and heart disease -- you may have a pig to thank
2014-11-24
New Rochelle, NY, November 24, 2014--Genetically engineered pigs, minipigs, and microminipigs are valuable tools for biomedical research, as their lifespan, anatomy, physiology, genetic make-up, and disease mechanisms are more similar to humans than the rodent models typically used in drug discovery research. A Comprehensive Review article entitled "Current Progress of Genetically Engineered Pig Models for Biomedical Research," describing advances in techniques to create and use pig models and their impact on the development of novel drugs and cell and gene therapies, is ...
New volume documents the science at the legendary snowmastodon fossil site in Colorado
2014-11-24
DENVER--Nov. 24, 2014-- Four years ago, a bulldozer operator turned over some bones during construction at Ziegler Reservoir near Snowmass Village, Colorado. Scientists from the Denver Museum of Nature & Science were called to the scene and confirmed the bones were those of a juvenile Columbian mammoth, setting off a frenzy of excavation, scientific analysis, and international media attention. This dramatic and unexpected discovery culminates this month with the publication of the Snowmastodon Project Science Volume in the international journal Quaternary Research.
Fourteen ...
An inside job: UC-designed nanoparticles infiltrate, kill cancer cells from within
2014-11-24
Conventional treatment seeks to eradicate cancer cells by drugs and therapy delivered from outside the cell, which may also affect (and potentially harm) nearby normal cells.
In contrast to conventional cancer therapy, a University of Cincinnati team has developed several novel designs for iron-oxide based nanoparticles that detect, diagnose and destroy cancer cells using photo-thermal therapy (PTT). PTT uses the nanoparticles to focus light-induced heat energy only within the tumor, harming no adjacent normal cells.
The results of the UC work will be presented at the ...
For important tumor-suppressing protein, context is key
2014-11-24
Scientists from the US Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have learned new details about how an important tumor-suppressing protein, called p53, binds to the human genome. As with many things in life, they found that context makes a big difference.
The researchers mapped the places where p53 binds to the genome in a human cancer cell line. They compared this map to a previously obtained map of p53 binding sites in a normal human cell line. These binding patterns indicate how the protein mobilizes a network of genes that quell tumor ...
Developing a noninvasive test for endometriosis
2014-11-24
Researchers at UC San Francisco have identified patterns of genetic activity that can be used to diagnose endometriosis and its severity, a finding that may offer millions of women an alternative to surgery through a simple noninvasive procedure.
The study is online in the journal Endocrinology.
"This promising molecular diagnostic approach would not have been possible without advances in genomics and bioinformatics," said senior author Linda Giudice, MD, PhD, distinguished professor and chair of obstetrics, gynecology and reproductive sciences at UCSF.
"Importantly, ...
Protein that rouses the brain from sleep may be target for Alzheimer's prevention
2014-11-24
A protein that stimulates the brain to awaken from sleep may be a target for preventing Alzheimer's disease, a study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis suggests.
In recent years, scientists at Washington University have established links between sleep problems and Alzheimer's. For example, they have shown in people and in mice that sleep loss contributes to the growth of brain plaques characteristic of Alzheimer's, and increases the risk of dementia.
The new research, in mice, demonstrates that eliminating that protein - called orexin ...
Too much turkey: What happens when you overeat? (video)
2014-11-24
WASHINGTON, Nov. 24, 2014 -- The season of giving is often also the season of over-indulging at the dinner table. As Thanksgiving approaches, Reactions takes a look down at our stomachs to find out what happens when you overeat. Put on your "eating pants" and enjoy the video here:
Subscribe to the series at Reactions YouTube, and follow us on Twitter @ACSreactions to be the first to see our latest videos.
INFORMATION:The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. With more than 161,000 members, ACS is the world's largest scientific ...
Scientists do glass a solid -- with new theory on how it transitions from a liquid
2014-11-24
How does glass transition from a liquid to its familiar solid state? How does this common material transport heat and sound? And what microscopic changes occur when a glass gains rigidity as it cools?
A team of researchers at NYU's Center for Soft Matter Research offers a theoretical explanation for these processes in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Our understanding of glasses as they change state is relatively limited. This is because, unlike other materials such as metals, their constituent particles--which can be as small as a billionth of a meter ...
[1] ... [3172]
[3173]
[3174]
[3175]
[3176]
[3177]
[3178]
[3179]
3180
[3181]
[3182]
[3183]
[3184]
[3185]
[3186]
[3187]
[3188]
... [8824]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.