Circumstances are right for weed invasion to escalate, researchers say
2014-11-25
Few agribusinesses or governments regulate the types of plants that farmers use in their pastures to feed their livestock, according to an international team of researchers that includes one plant scientist from Virginia Tech.
The problem is most of these so-called pasture plants are invasive weeds.
In a Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences study this month, the scientists recommended tighter regulations, including a fee for damage to surrounding areas, evaluation of weed risk to the environment, a list of prohibited species based on this risk, and closer ...
NIH scientists determine how environment contributes to several human diseases
2014-11-25
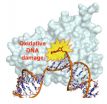
Using a new imaging technique, National Institutes of Health researchers have found that the biological machinery that builds DNA can insert molecules into the DNA strand that are damaged as a result of environmental exposures. These damaged molecules trigger cell death that produces some human diseases, according to the researchers. The work, appearing online Nov. 17 in the journal Nature, provides a possible explanation for how one type of DNA damage may lead to cancer, diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular and lung disease, and Alzheimer's disease.
Time-lapse crystallography ...
Study maps how city neighborhoods affect diabetes risk
2014-11-25
PHILADELPHIA (Nov. 25, 2014) - As the linked epidemics of obesity and diabetes continue to escalate, a staggering one in five U.S. adults is projected to have diabetes by 2050.
Ground zero for identifying ways to slow and stop that rise is Philadelphia, which has the highest diabetes rate among the nation's largest cities. For public health researchers at Drexel University, it is also a prime location to learn how neighborhood and community-level factors -- not just individual factors like diet, exercise and education-- influence people's risk.
A new Drexel study published ...
International team reveals barriers to public health data-sharing; life-saving solutions
2014-11-25
PITTSBURGH, Nov. 24, 2014 -Barriers to the sharing of public health data hamper decision-making efforts on local, national and global levels, and stymie attempts to contain emerging global health threats, an international team led by the University of Pittsburgh Graduate School of Public Health announced today.
The analysis, published in the journal BMC Public Health and funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and the National Institutes of Health (NIH), classifies and examines the barriers in order to open a focused international dialogue on solutions.
"Data on ...
Body size requires hormones under control
2014-11-25
The proper regulation of body size is of fundamental importance, but the mechanisms that stop growth are still unclear. In a study now published in the scientific journal eLife*, a research group from Instituto Gulbenkian de Ciência (IGC), led by Christen Mirth, shed new light on how animals regulate body size. The researchers uncovered important clues about the molecular mechanisms triggered by environmental conditions that ultimately affect final body size. They show that the timing of synthesis of a steroid hormone called ecdysone is sensitive to nutrition in the ...
Feeling -- not being -- wealthy drives opposition to wealth redistribution
2014-11-25
People's views on income inequality and wealth distribution may have little to do with how much money they have in the bank and a lot to do with how wealthy they feel in comparison to their friends and neighbors, according to new findings published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
"Our research shows that subjective feelings of wealth or poverty motivate people's attitudes toward redistribution, quite independently of objective self-interest," says psychological scientist and study co-author Keith Payne of the University ...
Why fruit flies could lead to better beer (video)
2014-11-25
WASHINGTON, Nov. 25, 2014 -- Your beer may attract annoying fruit flies, but listen up before you give them a swat. Researchers found the yeast cells in beer are producing odor compounds -- acetate esters -- that lure flies and that could lead to the best beer you haven't even tasted yet. This week's Speaking of Chemistry explains why. Check it out at http://youtu.be/HQNlGuZvCvA.
Speaking of Chemistry is a production of Chemical & Engineering News, a weekly magazine of the American Chemical Society. The program features fascinating, weird and otherwise interesting chemistry ...
Virtual money: User's identity can be revealed much easier than thought
2014-11-25
Bitcoin is the new money: minted and exchanged on the Internet. Faster and cheaper than a bank, the service is attracting attention from all over the world. But a big question remains: are the transactions really anonymous? Several research groups worldwide have shown that it is possible to find out which transactions belong together, even if the client uses different pseudonyms. However it was not clear if it is also possible to reveal the IP address behind each transaction. This has changed: researchers at the University of Luxembourg have now demonstrated how this is ...
Few operations for epilepsy despite their safety and efficacy
2014-11-25
The study at Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, was based on the Swedish National Epilepsy Surgery Register, which includes all cases since 1990. The researchers reviewed data for the 865 patients who were operated on at Sweden's six epilepsy surgery clinics from 1996 to 2010.
The purpose of surgery is to enable a person with severe epilepsy to be free of seizures or to reduce their frequency to the point that (s)he can enjoy better quality of life.
Downward trend
Only 3% (25) of the patients suffered lasting complications. A comparison with a previous ...
Researchers find way to turn sawdust into gasoline
2014-11-25
Researchers at KU Leuven's Centre for Surface Chemistry and Catalysis have successfully converted sawdust into building blocks for gasoline. Using a new chemical process, they were able to convert the cellulose in sawdust into hydrocarbon chains. These hydrocarbons can be used as an additive in gasoline, or as a component in plastics. The researchers reported their findings in the journal Energy & Environmental Science.
Cellulose is the main substance in plant matter and is present in all non-edible plant parts of wood, straw, grass, cotton and old paper. "At the molecular ...
'Dramatic' early phase 1 results for AG-120 in IDH1 mutated AML
2014-11-25
Results presented November 19 by University of Colorado Cancer Center investigator Daniel Pollyea, MD, MS, at the 26th European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Symposium in Barcelona show "extremely promising" early phase 1 clinical trial results for the investigational drug AG-120 against the subset of patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) harboring mutations in the gene IDH1. The finding builds on phase 1 results of a related drug, AG-221, against IDH2 mutations, presented at the most recent meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research. ...
Johns Hopkins scientists link gene to tamoxifen-resistant breast cancers
2014-11-25
After mining the genetic records of thousands of breast cancer patients, researchers from the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center have identified a gene whose presence may explain why some breast cancers are resistant to tamoxifen, a widely used hormone treatment generally used after surgery, radiation and other chemotherapy.
The gene, called MACROD2, might also be useful in screening for some aggressive forms of breast cancers, and, someday, offering a new target for therapy, says Ben Ho Park, M.D., Ph.D., an associate professor of oncology in the Kimmel Cancer Center's ...
Policing Canada in the 21st century: New policing for new challenges
2014-11-25
A new expert panel report, Policing Canada in the 21st Century: New Policing for New Challenges, released today by the Council of Canadian Academies, details the complexity and global nature of policing in the modern age. Overall, a 12-member Expert Panel determined that safety and security cannot just rest with Canada's policing services. Specialists, public and private security services, and other first responders all have a vital role to play in an interconnected safety and security web. This transition has already begun in Canada and around the world. A central challenge ...
Problem gambling, personality disorders often go hand in hand
2014-11-25
The treatment of people who cannot keep their gambling habits in check is often complicated because they also tend to suffer from personality disorders. So says Meredith Brown of Monash University in Australia, in a review in Springer's Journal of Gambling Studies.
Problem gambling creates a multitude of intrapersonal, interpersonal and social difficulties for the roughly 2.3 percent of the population internationally that suffers from this behavior. Previous research has shown that people with gambling problems suffer from a range of psychiatric disorders affecting their ...
One-two punch of drugs better than either alone against colorectal cancer
2014-11-25
Genes make proteins and proteins tell your body's cells what to do: one talks to the next, which talks to the next, and to the next. Like a game of telephone, researchers call these "signaling pathways". Abnormalities in these signaling pathways can cause the growth and survival of cancer cells. Commonly, mutations or rearrangements of genes in the MAPK signaling pathway create cancer's fast growth, and alterations in the PI3K signaling pathway allow cancer cells to survive into virtual immortality.
Of course, researchers have extensively targeted these two signaling ...
Why cancer cells grow despite a lack of oxygen
2014-11-25
FRANKFURT/GIESSEN. Healthy cells reduce their growth when there is a lack of oxygen (hypoxia). This makes it even more surprising that hypoxia is a characteristic feature of malignant tumours. In two publications in the current edition of the "Nature Communications" journal, researchers from Goethe University and Justus-Liebig-University of Giessen report on how cancer cells succeed at circumventing the genetic program of growth inhibition.
It has long been known that PHD proteins (prolyl-hydroxylase domain proteins) play a key role among the regulators of hypoxia. They ...
New device may ease mammography discomfort
2014-11-25
CHICAGO - Researchers have developed a new device that may result in more comfortable mammography for women. According to a study being presented next week at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), standardizing the pressure applied in mammography would reduce pain associated with breast compression without sacrificing image quality.
Compression of the breast is necessary in mammography to optimize image quality and minimize absorbed radiation dose. However, mechanical compression of the breast in mammography often causes discomfort and ...
Asymptomatic atherosclerosis linked to cognitive impairment
2014-11-25
CHICAGO - In a study of nearly 2,000 adults, researchers found that a buildup of plaque in the body's major arteries was associated with mild cognitive impairment. Results of the study conducted at the University of Texas (UT) Southwestern Medical Center will be presented next week at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
"It is well established that plaque buildup in the arteries is a predictor of heart disease, but the relationship between atherosclerosis and brain health is less clear," said Christopher D. Maroules, M.D., radiology ...
Scientists could save thousands of pounds with student's DIY microscope
2014-11-25
Expensive tests for measuring everything from sperm motility to cancer diagnosis have just been made hundreds of thousands of pounds cheaper by a PhD student from Brunel University London who hacked his own microscope.
Adam Lynch, from the university's College of Health and Life Sciences, created his own inverted microscope by adapting a cheap instrument he bought online to save himself time and money.
The tool is used to measure cell motility - how fast cells move from one place to another - but the high-quality equipment, used to automatically test multiple samples, ...
El Niño stunts children's growth in Peru
2014-11-25
Extreme weather events, such as El Niño, can have long-lasting effects on health, according to research published in the open access journal Climate Change Responses. The study, in coastal Peru, shows that children born during and after the 1997-98 El Niño have a lower height-for-age than others born before the event.
Short stature, otherwise known as stunting, is a measure of chronic malnutrition and this generally persists through to adulthood. The research highlights the need for better understanding of the global health issues that may arise and for the ...
Does a yogurt a day keep diabetes away?
2014-11-25
A high intake of yogurt has been found to be associated with a lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes, according to research published in open access journal BMC Medicine. This highlights the importance of having yogurt as part of a healthy diet.
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that occurs when the body doesn't produce enough insulin, or the body's cells develop resistance to insulin. There is an increased risk of developing it if a relative has the condition or if an individual has an unhealthy lifestyle. Approximately 366 million people are affected by type ...
Lancet article: Afferent's P2X3 inhibitor shows 75 percent reduction in chronic cough frequency
2014-11-25
San Mateo, California, November 25, 2014 - Afferent Pharmaceuticals today announced publication of results from a Phase 2 clinical trial demonstrating that the company's novel drug candidate, AF-219, reduced daytime cough frequency by 75% compared to placebo in patients with treatment-refractory chronic cough. These data are featured in an article titled, "P2X3 Receptor Antagonist (AF-219) in Refractory Chronic Cough: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2 Study," which is appearing online in The Lancet. These results support Afferent's current development ...
News from Annals of Internal Medicine Supplement
2014-11-25
Task Force finds insufficient evidence to recommend for or against routine vitamin D screening
Free content
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) found insufficient evidence to assess the benefits and harms of screening for vitamin D deficiency in asymptomatic adults. The recommendation statement and systematic evidence review are being published together in Annals of Internal Medicine. Vitamin D is obtained through diet (fatty fish, cod liver oil, dairy products, fortified beverages and food, and supplements) and synthesis triggered by sun exposure. There ...
Ambulance risk
2014-11-24
Boston, MA (November 24, 2014)--Lights flash, a siren wails and an ambulance races to help a person whose heart has stopped beating.
In most cases, a 911 dispatcher will have sent an advanced life support, or ALS, ambulance to the scene, equipped with sophisticated gear and staffed with a crew of highly trained paramedics who can deliver specialized care in the field, including intubations and IV interventions.
Unfortunately, according to a new study by health policy researchers at Harvard, those advanced techniques actually increase the patient's risk of death.
People ...
Starting treatment soon after HIV infection improves immune health, study finds
2014-11-24
In many countries outside the United States, decisions on when to start treatment for HIV infection are based on the level of certain white blood cells called CD4+ T cells, which are commonly measured to determine immune health. A study by National Institutes of Health grantees suggests that the best time to start treatment also should be based on how much time has elapsed since becoming HIV-infected. The researchers found that starting treatment within a year of seroconversion--the period within a few weeks of HIV infection when antibodies to the virus are first produced ...
[1] ... [3169]
[3170]
[3171]
[3172]
[3173]
[3174]
[3175]
[3176]
3177
[3178]
[3179]
[3180]
[3181]
[3182]
[3183]
[3184]
[3185]
... [8824]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.