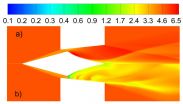
Supersonic laser-propelled rockets
2014-10-29
WASHINGTON, Oct. 29, 2014—Scientists and science fiction writers alike have dreamt of aircrafts that are propelled by beams of light rather than conventional fuels. Now, a new method for improving the thrust generated by such laser-propulsion systems may bring them one step closer to practical use.
The method, developed by physicists Yuri Rezunkov of the Institute of Optoelectronic Instrument Engineering, Russia and Alexander Schmidt of the Ioffe Physical Technical Institute in Saint Petersburg, Russia is described today in The Optical Society's (OSA) journal Applied ...
Can plants edge out petroleum as raw material for textiles and plastics?
2014-10-29
Your next pair of spandex pants could be made out of corn — or, more precisely, from dextrose derived from corn. This option is part of a new wave, albeit a small one, of consumer goods that are being produced from plants rather than petroleum-based materials. But a complete transition to a biobased economy won't be easy, according to an article in Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), the weekly newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society.
Melody M. Bomgardner, a senior editor at C&EN, notes that a range of companies, from start-up firms to industrial giants, have ...
Nanosafety research: The quest for the gold standard
2014-10-29
Researching the safety of nanoparticles is all the rage. Thousands of scientists worldwide are conducting research on the topic, examining the question of whether titanium dioxide nanoparticles from sun creams can get through the skin and into the body, whether carbon nanotubes from electronic products are as hazardous for the lungs as asbestos used to be or whether nanoparticles in food can get into the blood via the intestinal flora, for instance. Public interest is great, research funds are flowing – and the number of scientific projects is skyrocketing: between ...
Free urban data -- what's it good for?
2014-10-29
New Rochelle, October 29, 2014 –Cities around the world are increasingly making urban data freely available to the public. But is the content or structure of these vast data sets easy to access and of value? A new study of more than 9,000 data sets from 20 cities presents encouraging results on the quality and volume of the available data and describes the challenges and benefits of analyzing and integrating these expanding data sets, as described in an article in Big Data, the highly innovative, peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The Open ...
To reap the brain benefits of physical activity, just get moving!
2014-10-29
This news release is available in French. Everyone knows that exercise makes you feel more mentally alert at any age. But do you need to follow a specific training program to improve your cognitive function? Science has shown that the important thing is to just get moving. It's that simple. In fact, this was the finding of a study conducted at the Institut universitaire de gériatrie de Montréal (IUGM), an institution affiliated with Université de Montréal, by Dr. Nicolas Berryman, PhD, Exercise Physiologist, under the supervision of Dr. Louis Bherer, ...
Meiotic cell division 'the other way round'
2014-10-29
This news release is available in German. Meiosis is not like another: Gabriela Cabral and Peter Schlögelhofer at the Max F. Perutz Laboratories (MFPL) of the University of Vienna and the Medical University of Vienna dived into the process of meiosis in specific plant species and revealed that these plants display an inversion of the standard meiotic phases. The researchers describe the detailed mechanisms in the scientific journal Nature Communications.
Meiosis is the two-step series of cell divisions that make sexual reproduction and genetic diversity possible.The ...
A mechanism that allows a differentiated cell to reactivate as a stem cell revealed
2014-10-29
One kind of stem cell, those referred to as 'facultative', form part—together with other cells—of tissues and organs. There is apparently nothing that differentiates these cells from the others. However, they have a very special characteristic, namely they retain the capacity to become stem cells again. This phenomenon is something that happens in the liver, an organ that hosts cells that stimulate tissue growth, thus allowing the regeneration of the organ in the case of a transplant. Knowledge of the underlying mechanism that allows these cells to retain this ...
Cinema-like environment helps audiences immerse in movies even on small screens & displays
2014-10-29
If the surroundings are designed to be sufficiently stimulating, even a simple computer screen is enough to generate an intense cinematic experience. After observing some 300 study subjects, researchers at the Institute of Psychology of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) in Germany concluded that the angle of viewing does not play a vital role in the cinematic experience, thus disproving various hypotheses. According to the results of their study, the presence of so-called contextual visual cues plays a greater role in actually drawing viewers into a movie. When ...
Projecting a robot's intentions
2014-10-29
In a darkened, hangar-like space inside MIT's Building 41, a small, Roomba-like robot is trying to make up its mind.
Standing in its path is an obstacle — a human pedestrian who's pacing back and forth. To get to the other side of the room, the robot has to first determine where the pedestrian is, then choose the optimal route to avoid a close encounter.
As the robot considers its options, its "thoughts" are projected on the ground: A large pink dot appears to follow the pedestrian — a symbol of the robot's perception of the pedestrian's position in space. ...
Walking workstations improve physical and mental health, builds healthier workplace
2014-10-29
Walking workstations can improve not only physical, but also mental health during the workday, a new study released this week found. The research was conducted by faculty and student researchers from the Department of Psychology in the School of Science at Indiana University-Purdue University Indianapolis (IUPUI).
With growing concerns regarding obesity in the United States, Michael Sliter, assistant professor of psychology, hopes the study encourages employers to examine methods to assist workers in in healthy living.
"We found that the walking workstations, regardless ...
Go straight and publish: From Barcode of Life Data Systems to scholarly publishing systems
2014-10-29
An innovative workflow reveals new research potential of the Barcode of Life Data Systems (BOLD). A recently published article in the Biodiversity Data Journal (BDJ) used specimen records downloaded from BOLD in tabular format and imported these into a human-readable text developed in manuscript within the Pensoft Writting Tool (PWT). Data were used to study the species distributions of ten Nearctic species of braconid wasps from the Microgastrinae subfamily.
BOLD is originally designed to support the generation and application of DNA barcode data. However, the repository ...
Saving lots of computing capacity with a new algorithm
2014-10-29
The control of modern infrastructure such as intelligent power grids needs lots of computing capacity. Scientists of the Interdisciplinary Centre for Security, Reliability and Trust (SnT) at the University of Luxembourg have developed an algorithm that might revolutionise these processes. With their new software the SnT researchers are able to forego the use of considerable amounts of computing capacity, enabling what they call micro mining. Their achievements, which the team headed by Prof. Yves Le Traon published in the International Conference on Software Engineering ...
NYU research: Tourism as a driver of illicit drug use, HIV risk in the DR
2014-10-29
The Caribbean has the second highest global human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) prevalence in the world outside of Sub-Saharan Africa, with HIV/AIDS as leading cause of death among people aged 20–59 years within the region. Particularly hard-hit are the Dominican Republic (DR) and Haiti, on the island of Hispaniola, accounting for approximately 70% of all people living with HIV in the Caribbean region.
Insufficient attention has been paid to the intersection of drugs and tourism as contributing factors for the region's elevated HIV/AIDS risk. Caribbean studies ...
Prenatal phthalate exposures and anogenital distance in Swedish boys
2014-10-29
The first study to examine prenatal exposure to the phthalate DiNP finds it is associated with a shorter anogenital distance (AGD) in Swedish boys at the age of 21 months. These findings raise concern since animal research has linked DiNP exposure to a shorter AGD, and studies on humans have related shorter AGD to male genital birth defects as well as impaired reproductive function in adult males, and the levels of DiNP metabolites in humans are increasing globally.
Background
Phthalates are used as plasticizers in soft polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and found in a large ...
Largest ever dataset of individual deaths in Africa & SE Asia reveals changing health
2014-10-29
More than 110,000 individual deaths and their causes across 13 countries, including Ghana, South Africa, Kenya, Bangladesh and Vietnam, are contained in the new INDEPTH dataset. The data, collected by hundreds of researchers over two decades, are the first meaningful community-based information about cause of death in countries where individual deaths are not recorded automatically by national governments.
The INDEPTH cause of death findings are published in a special issue of the journal Global Health Action, which is fully open access. There are six multisite papers ...
Aortic valve replacement appears safe, effective in very elderly patients
2014-10-29
Chicago, October 29, 2014 – Aortic valve replacement (AVR) can safely be used to treat severe aortic stenosis in patients age 90 years and older and is associated with a low risk of operative stroke and mortality, according to a study in the November 2014 issue of The Annals of Thoracic Surgery.
Key points
Aortic valve replacement appears to be safe and effective for patients over age 90 years with severe aortic stenosis.
Four out of five (81.3%) patients were alive 1 year following AVR.
TAVR had similar rates of morbidity and mortality as traditional surgical ...
Support for fecal testing in familial colorectal cancer screening
2014-10-29
Bethesda, MD (Oct. 29, 2014) — Fecal immunochemical tests (FIT) may be as effective as colonoscopies when it comes to detecting colorectal cancer among first-degree relatives of patients with colorectal cancer, according to a new study in Gastroenterology1, the official journal of the American Gastroenterological Association.
"In our study, repeat FIT screening detected all colorectal cancers in asymptomatic first-degree relatives of patients with colorectal cancer," said lead study authors Enrique Quintero, MD, PhD, and Marta Carrillo, MD, from Hospital Universitario ...
Georgia Tech releases 2015 Emerging Cyber Threats Report
2014-10-29
In its latest Emerging Cyber Threats Report, Georgia Tech warns about loss of privacy; abuse of trust between users and machines; attacks against the mobile ecosystem; rogue insiders; and the increasing involvement of cyberspace in nation-state conflicts.
Such topics are discussed at length in the annual report, which is published by the Georgia Tech Information Security Center (GTISC) and the Georgia Tech Research Institute (GTRI). The report will be released this week at the 12th Georgia Tech Cyber Security Summit (GT CSS), which has become the Atlanta IT community's ...
New technology shows promise for delivery of therapeutics to the brain
2014-10-29
A new technology that may assist in the treatment of brain cancer and other neurological diseases is the subject of an article in a recent issue of the journal Technology, published by World Scientific Publishing Company.
According to the authors, the current medical use of chemotherapy to treat brain cancer can be inefficient because of the blood-brain-barrier that impedes the delivery of drugs out of blood vessels and into the tumor.
The researchers from the Virginia Tech – Wake Forest University School of Biomedical Engineering and Sciences described in their ...
Smoke and haze over China
2014-10-29
Smoke and haze hang over a large portion of eastern China in this image captured by the Aqua satellite on October 29, 2014. China uses the method of "slash and burn" agriculture to rid their fields of leftover plants. Farmers often use fire to return nutrients to the soil and to clear the ground of unwanted plants. While fire helps enhance crops and grasses for pasture, the fires also produce smoke that degrades air quality as seen in this image.
The U.S. Consulate in Beijing records an air quality index of 226 for October 29 putting it in the "Very Unhealthy" region. ...
Microrockets fueled by water neutralize chemical and biological warfare agents
2014-10-29
With fears growing over chemical and biological weapons falling into the wrong hands, scientists are developing microrockets to fight back against these dangerous agents, should the need arise. In the journal ACS Nano, they describe new spherical micromotors that rapidly neutralize chemical and biological agents and use water as fuel.
Joseph Wang and colleagues point out that titanium dioxide is one of the most promising materials available for degrading chemical and biological warfare agents. It doesn't require harsh chemicals or result in toxic by-products. Current ...
Why plants don't get sunburn
2014-10-29
Plants rely on sunlight to make their food, but they also need protection from its harmful rays, just like humans do. Recently, scientists discovered a group of molecules in plants that shields them from sun damage. Now, in an article in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, one team reports on the mechanics of how these natural plant sunscreens work.
Timothy Zwier and colleagues at Purdue University note that the harsh ultraviolet radiation plants are exposed to daily can cause serious damage to plant DNA and, as a result, hinder plant growth. Biochemical tests ...
Scientists rank thousands of substances according to potential exposure level
2014-10-29
An overwhelming number of chemicals from household and industrial products are in the environment – and hundreds are in our bodies. But for most of them, scientists have yet to determine whether they cause health problems. Now they've taken the first step toward doing that by estimating which substances people are exposed to the most. Their new method is published in the ACS journal Environmental Science & Technology.
John F. Wambaugh and colleagues note that the risks to human health of any given substance depend primarily on two factors: the potential hazards ...
Nestling birds struggle in noisy environments
2014-10-29
WASHINGTON, D.C., October 29, 2014--Unable to fly, nestling birds depend on their parents for both food and protection: vocal communication between parents and offspring helps young birds to determine when they should beg for food and when they should crouch in the nest to avoid a predator seeking an easy meal.
A group of researchers from Dalhousie University in Halifax, Nova Scotia has found that ambient, anthropomorphic noise – from traffic, construction and other human activities – can break this vital communications link, leaving nestlings vulnerable ...
Integrins losing their grip lead to activation of T cell immune response
2014-10-29
Integrins are adhesion molecules expressed on the surface of cells. They play a crucial role in "integrating" the cell exterior and the interior cytoskeleton in cells. The beta2-integrin family members are highly expressed in dendritic cells that are very important in immune responses. Dendritic cells pick up antigens in inflamed tissues and move to lymph nodes where they present the antigen to T cells and activate them to help fight infection.
Dr Susanna Fagerholm's groups at the Institute of Biotechnology in Helsinki, Finland, and at the University of Dundee, UK, found ...
[1] ... [3233]
[3234]
[3235]
[3236]
[3237]
[3238]
[3239]
[3240]
3241
[3242]
[3243]
[3244]
[3245]
[3246]
[3247]
[3248]
[3249]
... [8826]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.