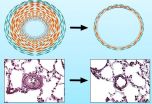
UH research focuses on suicide resilience and vulnerability
2014-10-27
Religious beliefs and practices may reduce thoughts of suicide among African-American adults in stressful life events induced by racial discrimination, according to a new research study conducted at the University of Houston (UH).
"African-Americans experience an inordinate amount of psychological strain through racial discrimination, leading to depression, hopelessness and other high risk factors for suicide, but demonstrate significantly lower rates of suicide relative to European-Americans," said Rheeda Walker, associate professor and director of the Culture, Risk ...
Synapses always on the starting blocks
2014-10-27
This news release is available in German.
While neurons rapidly propagate information in their interior via electrical signals, they communicate with each other at special contact points known as the synapses. Chemical messenger substances, the neurotransmitters, are stored in vesicles at the synapses. When a synapse becomes active, some of these vesicles fuse with the cell membrane and release their contents. To ensure that valuable time is not lost, synapses always have some readily releasable vesicles on standby. With the help of high-resolution, three-dimensional ...
Satellite movie shows Tropical Storm Ana headed to British Columbia, Canada
2014-10-27
VIDEO:
This animation of NOAA's GOES-West satellite imagery from Oct. 1 -27 shows the movement of Tropical Storm Ana as it heads toward British Columbia, Canada. TRT: 00:20.
Click here for more information.
An animation of imagery from NOAA's GOES-West satellite taken over the period of Oct.19 to 26 shows the movement, intensification, weakening and movement toward British Columbia, Canada. On Oct. 27, wind warnings were posted along some coastal sections of British Columbia.
During ...
Prostate cancer, kidney disease detected in urine samples on the spot
2014-10-27
When you flush the toilet, you may be discarding microscopic warning signs about your health.
But a cunningly simple new device can stop that vital information from "going to waste."
Brigham Young University chemist Adam Woolley and his students made a device that can detect markers of kidney disease and prostate cancer in a few minutes. All you have to do is drop a sample into a tiny tube and see how far it goes.
That's because the tube is lined with DNA sequences that will latch onto disease markers and nothing else. Urine from someone with a clean bill of health ...
Lack of transcription factor FoxO1 triggers pulmonary hypertension
2014-10-27
This news release is available in German.
Pulmonary hypertension is characterised by uncontrolled division of cells in the blood vessel walls. As a result, the vessel walls become increasingly thick.
Scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Heart and Lung Research in Bad Nauheim and Giessen University have discovered that transcription factor FoxO1 regulates the division of cells and plays a key role in the development of pulmonary hypertension. The researchers were able to cure pulmonary hypertension in rats by activating FoxO1. The study findings could ...
Study documents millions in unused medical supplies in US operating rooms each year
2014-10-27
A Johns Hopkins research team reports that major hospitals across the U.S. collectively throw away at least $15 million a year in unused operating room surgical supplies that could be salvaged and used to ease critical shortages, improve surgical care and boost public health in developing countries.
A report on the research, published online Oct. 16 in the World Journal of Surgery, highlights not only an opportunity for U.S. hospitals to help relieve the global burden of surgically treatable diseases, but also a means of reducing the cost and environmental impact of medical ...
Syracuse physicists closer to understanding balance of matter, antimatter in universe
2014-10-27
Physicists in Syracuse University's College of Arts and Sciences have made important discoveries regarding Bs meson particles—something that may explain why the Universe contains more matter than antimatter.
Distinguished Professor Sheldon Stone and his colleagues recently announced their findings at a workshop at CERN in Geneva, Switzerland. Titled "Implications of LHCb Measurements and Their Future Prospects," the workshop enabled him and other members of the Large Hadron Collider beauty (LHCb) Collaboration to share recent data results.
The LHCb Collaboration ...
Discovery of how newborn mice repair bone fractures could improve treatments
2014-10-27
If you've ever broken a bone, there's a good chance you needed surgery, braces, or splints to realign the bone. Severe fractures in infants, on the other hand, can heal on their own through a process that has eluded scientists. A study published by Cell Press on October 27 in Developmental Cell reveals that a fractured arm bone in newborn mice can rapidly realign through a previously unknown mechanism involving bone growth and muscle contraction. The findings provide new insights into how human infants and other young vertebrates may repair broken bones and pave the way ...
Ibuprofen better choice to relieve fracture pain in children than oral morphine
2014-10-27
Although Ibuprofen and oral morphine both provide effective pain relief for children with broken limbs, ibuprofen is the recommended choice because of adverse events associated with oral morphine, according to a randomized trial published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal)
Fractures make up between 10% and 25% of all children's injuries, and the most severe pain is felt during the first 48 hours after the injury. Because of concerns about the safety of codeine for children, there is limited choice for medications to relieve pain for these patients.
"Evidence ...
New prostate cancer screening guideline recommends not using PSA test
2014-10-27
A new Canadian guideline recommends that the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test should not be used to screen for prostate cancer based on evidence that shows an increased risk of harm and uncertain benefits. The guideline is published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal)
"Some people believe men should be screened for prostate cancer with the PSA test but the evidence indicates otherwise," states Dr. Neil Bell, member of the Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care and chair of the prostate cancer guideline working group. "These recommendations balance ...
Imaging the genome: Cataloguing the fundamental processes of life
2014-10-27
The team of researchers, led by Dr Rafael Carazo Salas from the Department of Genetics, combined high-resolution 3D confocal microscopy and computer-automated analysis of the images to survey the fission yeast genome with respect to three key cellular processes simultaneously: cell shape, microtubule organisation and cell cycle progression. Microtubules are small, tube-like structures which help cells divide and give them their structure.
Of the 262 genes whose functions the team report in a study published today in the journal Developmental Cell, two-thirds are linked ...
New RCT: KoACT® beats calcium and vitamin D for optimal bone strength
2014-10-27
ity of Industry, CA – October 28, 2014 – A new randomized controlled trial (RCT) of post-menopausal women demonstrates that a proprietary blend of collagen and calcium, KoACT®, was far superior to calcium and vitamin D in slowing down the leaching of calcium from bones and rebuilding new bone strength. An Abstract of the article appears on PubMed at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25314004, ahead of print in The Journal of Medicinal Food.
The research was conducted by Bahram H. Arjmandi, PhD, RDN, who is currently Margaret A. Sitton Named Professor ...
GW researcher adapting breakthrough technologies to combat parasitic worm infections
2014-10-27
WASHINGTON (Oct. 27, 2014) — Recent breakthroughs may pave the way for vaccines and new drugs for those infected by parasitic helminths. These flatworms, including tapeworms that cause hydatid diseases and neurocysticercosis, liver flukes, and blood flukes (schistosomes), infect more than 300 million people and cause approximately four million disability-adjusted life years lost due to chronic illness and death each year.
Paul Brindley, Ph.D., professor of microbiology, immunology, and tropical medicine, and scientific director of the Research Center for Neglected ...
Boosting biogasoline production in microbes
2014-10-27
In the on-going effort to develop advanced biofuels as a clean, green and sustainable source of liquid transportation fuels, researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Joint BioEnergy Institute (JBEI) have identified microbial genes that can improve both the tolerance and the production of biogasoline in engineered strains of Escherichia coli.
Aindrila Mukhopadhyay, a chemist who directs the host engineering program for JBEI's Fuels Synthesis Division, led a study in which transcriptomic data and a synthetic metabolic pathway were used to identify several genes ...
NASA sees a 'Zombie' tropical storm kick off Halloween week
2014-10-27
NASA's Terra satellite spotted a "zombie" tropical storm as Halloween week kicks off. Tropical Depression 9 made landfall in Mexico's Yucatan Peninsula late last week and lingered as a remnant low pressure area on Saturday and Sunday, Oct. 25 and 26. Satellite data revealed that those remnants had reformed quickly and jumped up to tropical storm status, where it became "zombie" storm named Tropical Storm Hanna off the coast of Nicaragua. NASA's Terra satellite spotted strong thunderstorms around the zombie storm's center as it passed overhead.
At 9:30 a.m. EDT on Oct. ...
Ultrasound guides tongue to pronounce 'r' sounds
2014-10-27
Using ultrasound technology to visualize the tongue's shape and movement can help children with difficulty pronouncing "r" sounds, according to a small study by NYU's Steinhardt School of Culture, Education, and Human Development and Montclair State University.
The ultrasound intervention was effective when individuals were allowed to make different shapes with their tongue in order to produce the "r" sound, rather than being instructed to make a specific shape. The findings appear online in the Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research.
The "r" sound is one ...
Slowing the biological clock
2014-10-27
Difficulty in conceiving a child is a major challenge for one in seven heterosexual couples in America, especially for those over the age of 35. Now a new discovery by researchers at Tel Aviv University and Chaim Sheba Medical Center at Tel Hashomer could boost the chances of conception in women undergoing in vitro fertilization (IVF) treatments.
Their new research reveals a linkage between the genes of the innate immune system — immunity with which human beings are born, rather than immunity they acquire during their lives — and ovarian longevity. The study, ...
'Sticky' ends start synthetic collagen growth
2014-10-27
Rice University researchers have delivered a scientific one-two punch with a pair of papers that detail how synthetic collagen fibers self-assemble via their sticky ends.
Collagen is the most common protein in mammals, a major component of bone and the fibrous tissues that support cells and hold organs together. Discovering its secrets may lead to better synthetic collagen for tissue engineering and cosmetic and reconstructive medicine.
The Rice lab of Jeffrey Hartgerink has been studying synthetic collagen for a decade, teasing out the details of how it starts as three ...
Hot on the trail of the Asian tiger mosquito
2014-10-27
The Asian tiger mosquito (Aedes albopictus), which is native to Southeast Asia, was spotted in Houston in 1985. By 1986 it had reached St. Louis and Jacksonville, Fla. Today it can be found in all of the southern states and as far north as Maine.
An aggressive daytime biter, Ae. albopictus has an affinity for humans and is also a vector for human disease, said Kim Medley, PhD, interim director of the Tyson Research Center at Washington University in St. Louis.
The mosquito arrived in the U.S. in a shipment of used tires from Japan. Ae. albopictus lays eggs that can ...
University of Delaware study connects penguin chick weights to local weather conditions
2014-10-27
Adélie penguins are an indigenous species of the West Antarctic Peninsula (WAP), one of the most rapidly warming areas on Earth. Since 1950, the average annual temperature in the Antarctic Peninsula has increased 2 degrees Celsius on average, and 6 degrees Celsius during winter.
As the WAP climate warms, it is changing from a dry, polar system to a warmer, sub-polar system with more rain.
University of Delaware oceanographers recently reported a connection between local weather conditions and the weight of Adélie penguin chicks in an article in Marine Ecology ...
Cost of informal caregiving for US elderly is $522 billion annually, study finds
2014-10-27
The price tag for informal caregiving of elderly people by friends and relatives in the United States comes to $522 billion a year, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
Replacing that care with unskilled paid care at minimum wage would cost $221 billion, while replacing it with skilled nursing care would cost $642 billion annually.
The study, published online by the journal Health Services Research, improves on earlier estimates about the value of informal caregiving by making use of the 2011 and 2012 American Time Use Survey, a new and unique database, to provide ...
PET scans reveal how psychodynamic therapy for depression may change brain function
2014-10-27
A study from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) investigators has identified for the first time changes in the metabolic activity of a key brain region in patients successfully treated for depression with psychodynamic psychotherapy, suggesting a mechanism of action behind one of the most historically important and widely practiced forms of therapy. They also found evidence that pretreatment metabolism in a different brain structure might predict which patients are likely to respond to that form of therapy. Their report will appear in the journal Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics ...
Blood vessel growth in the brain relies on a protein found in tumor blood vessels
2014-10-27
Do blood vessels that feed tumors differ from other blood vessels? Fourteen years ago, experiments designed to answer that question led to the discovery of several genes that are more active in tumor-associated blood vessels than in normal blood vessels. New research now reveals the normal function of one of those genes and suggests it could be a good target for anticancer drug therapy.
A summary of the research appears in the journal Developmental Cell on Oct. 27.
The mystery of the gene, TEM5, began in 2000 with research conducted by Brad St. Croix, Ph.D., working ...
Using microscopic bugs to save the bees
2014-10-27
For decades, honeybees have been battling a deadly disease that kills off their babies (larvae) and leads to hive collapse. It's called American Foulbrood and its effects are so devastating and infectious, it often requires infected hives to be burned to the ground.
Treating Foulbrood is complicated because the disease can evolve to resist antibiotics and other chemical treatments. Losing entire hives not only disrupts the honey industry, but reduces the number of bees for pollinating plants.
Now researchers at BYU have produced a natural way to eliminate the scourge, ...
Group classes teach parents effective autism therapy, Stanford/Packard study finds
2014-10-27
Parents can learn to use a scientifically validated autism therapy with their own children by taking a short series of group classes, a new study by researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine and Lucile Packard Children's Hospital Stanford has found.
The therapy helped children improve their language skills, an area of deficiency in autism, according to the study, which will be published Oct. 27 in the Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry. The study is the first randomized, controlled trial to test whether group classes are a good way to train parents ...
[1] ... [3239]
[3240]
[3241]
[3242]
[3243]
[3244]
[3245]
[3246]
3247
[3248]
[3249]
[3250]
[3251]
[3252]
[3253]
[3254]
[3255]
... [8826]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.