The bee's knees for identifying genetic triggers of novel adult traits
2014-10-29
Scientists have long sought to identify the specific DNA changes that can trigger new traits, allowing species to adapt. But when animals develop a new trait, are the mutations within the part of the DNA that makes proteins, or, in the master switches that control the gene, modulating its activity to turn on or off?
For development of the embryo, it is usually the master control regions of a gene that dominate, but what about in an adult?
Jasper et al. found that adults play by a different set of rules, relying on the contributions of novel genes---called taxonomically ...
A battle for ant sperm
2014-10-29
And you thought the sexual battles between people could get weird and fierce? Try ants. In a new study, biologists at the University of Vermont have discovered some queen ants that make sexual bondage into a life and death fight.
In a discovery new to science, their research shows that sexual conflict between two species can drive an evolutionary bedroom-battle royal, leading to competing adaptations in which female ants of one species manage to manhandle sperm away from the unwitting males of a different species during intercourse. The study was published in the October ...
High milk intake linked with higher fractures and mortality
2014-10-29
A high milk intake in women and men is not accompanied by a lower risk of fracture and instead may be associated with a higher rate of death, suggests observational research published in The BMJ this week.
This may be explained by the high levels of lactose and galactose (types of sugar) in milk, that have been shown to increase oxidative stress and chronic inflammation in animal studies, say the researchers.
However, they point out that their study can only show an association and cannot prove cause and effect. They say the results "should be interpreted ...
UK medical schools are not attracting enough GPs
2014-10-29
Richard Wakeford, Life Fellow at Hughes Hall in the University of Cambridge, warns that the NHS needs more GPs immediately – and that without a complete reorganisation of student recruitment, medical schools "will continue to overproduce graduates inclined to hospital specialties and research."
Workforce reports show that we need at least half of UK medical graduates to become GPs, yet UK medical schools "are not recruiting students with this career inclination in anything like sufficient numbers," he writes.
He points out that Labour has announced plans for 8,000 ...
The Lancet: Neglect of culture in medicine is 'single biggest barrier' to achieving better health
2014-10-29
The systematic neglect of culture is the single biggest barrier to advancing the highest attainable standard of health worldwide, say the authors of a major new report on culture and health, led by Professor David Napier, a leading medical anthropologist from University College London (UCL), UK, and published in The Lancet.
Bringing together experts from many different fields, including anthropologists, social scientists, and medics, the Commission is the first ever detailed appraisal of the role of culture in health. The authors argue that cultures of all kinds – ...
New findings show that different brain tumors have the same origin
2014-10-28
Glioma is a common name for serious brain tumours. Different types of glioma are usually diagnosed as separate diseases and have been considered to arise from different cell types in the brain. Now researchers at Uppsala University, together with American colleagues, have shown that one and the same cell of origin can give rise to different types of glioma. This is important for the basic understanding of how these tumours are formed and can contribute to the development of more efficient and specific glioma therapies. The results have been published in Journal of Neuroscience.
The ...
Adolescent binge drinking reduces brain myelin, impairs cognitive and behavioral control
2014-10-28
AMHERST, Mass. – Binge drinking can have lasting effects on brain pathways that are still developing during adolescence, say neuroscience researcher Heather N. Richardson and her colleagues at the University of Massachusetts Amherst and Louisiana State University. Results of their study using a rodent model of adolescent drinking appear in the October 29 issue of The Journal of Neuroscience.
Richardson says, "Adverse effects of this physical damage can persist long after adolescent drinking ends. We found that the effects of alcohol are enduring." She adds, "The ...
Animal study suggests heavy drinking in adolescence associated with lasting brain changes
2014-10-28
WASHINGTON, DC — Heavy drinking during adolescence may lead to structural changes in the brain and memory deficits that persist into adulthood, according to an animal study published October 29 in The Journal of Neuroscience. The study found that, even as adults, rats given daily access to alcohol during adolescence had reduced levels of myelin — the fatty coating on nerve fibers that accelerates the transmission of electrical signals between neurons. These changes were observed in a brain region important in reasoning and decision-making. Animals that were ...
NASA's LRO spacecraft captures images of LADEE's impact crater
2014-10-28
NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) spacecraft has spied a new crater on the lunar surface; one made from the impact of NASA's Lunar Atmosphere and Dust Environment Explorer (LADEE) mission.
"The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera (LROC) team recently developed a new computer tool to search Narrow Angle Camera (NAC) before and after image pairs for new craters, the LADEE impact event provided a fun test, said Mark Robinson, LROC principal investigator from Arizona State University in Tempe. "As it turns there were several small surface changes found in the predicted ...
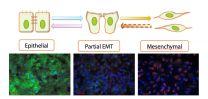
Modeling cancer: Virginia Tech researchers prove models can predict cellular processes
2014-10-28
How does a normal cellular process derail and become unhealthy?
A multi-institutional, international team led by Virginia Tech researchers studied cells found in breast and other types of connective tissue and discovered new information about cell transitions that take place during wound healing and cancer.
The results were published in a September issue of the journal Science Signaling.
During development, cells change forms and regroup from tight packs of epithelial cells to more mobile, loose arrays of mesenchymal cells.
The cell changes, known as an epithelial ...
The effect of statins influenced by gene profiles
2014-10-28
Montreal, October 28, 2014 – The Montreal Heart Institute Research Centre is once again pushing the limits of knowledge in personalized medicine. A meta-analysis combining the results of several pharmacogenomic studies and involving over 40,000 research subjects now makes it possible to demonstrate a different response to statins according to the patient's gene profile. This important contribution of two Montreal researchers from the Montreal Heart Institute (MHI), Dr. Jean-Claude Tardif, Director of the Research Centre and Dr. Marie-Pierre Dubé, Director of ...
Fewer women than men receive hemodialysis treatment
2014-10-28
Fewer women than men are treated with dialysis for end-stage kidney disease, according to a new comprehensive analysis of sex-specific differences in treatment published this week in PLOS Medicine. The results of the study, conducted by Manfred Hecking with Friedrich Port and colleagues from Arbor Research Collaborative for Health in Ann Arbor, Michigan, suggest that these findings call for further detailed study for the reasons underlying the sex-specific differences in end-stage renal disease treatment.
Chronic kidney disease often progresses to end-stage renal disease, ...
Injury prevention intervention cuts distracted driving in half, say trauma surgeons
2014-10-28
SAN FRANCISCO: A simple intervention designed to raise awareness about the use of communication devices while driving reduced the incidence of distracted driving by 50 percent in hospital personnel, according to findings from a single site study presented today at the 2014 Clinical Congress of the American College of Surgeons.
Driving distracted–caused by any activity that steals a driver's attention from the road–is at an all-time high. In 2012, an estimated 421,000 people were injured in accidents involving distracted driving and 3,328 were killed as a result ...
Giant tortoises gain a foothold on a Galapagos Island
2014-10-28
A population of endangered giant tortoises, which once dwindled to just over a dozen, has recovered on the Galapagos island of Española, a finding described as "a true story of success and hope in conservation" by the lead author of a study published today (Oct. 28).
Some 40 years after the first captive-bred tortoises were reintroduced to the island by the Galapagos National Park Service, the endemic Española giant tortoises are reproducing and restoring some of the ecological damage caused by feral goats that were brought to the island in the late 19th century. ...
Text messages could be useful tool in fight against malaria
2014-10-28
New Haven, CT, Oct. 28 2014 – Each year, malaria kills over 600,000 people, more than half of them children. In a study published today in PLOS ONE , researchers with the non-profit Innovations for Poverty Action (IPA) and Harvard University found that simple text message reminders to take malaria medication can help in the fight against the disease by boosting the rates at which patients complete their medication regimen.
One challenge in fighting malaria is that the disease has evolved resistance to many drugs that formerly worked, according to Julia Raifman, ...
Pair bonding reinforced in the brain
2014-10-28
This news release is available in German.
In addition to their song, songbirds also have an extensive repertoire of calls. While the species-specific song must be learned as a young bird, most calls are, as in the case of all other birds, innate. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute in Seewiesen have now discovered that in zebra finches the song control system in the brain is also active during simple communication calls. This relationship between unlearned calls and an area of the brain responsible for learned vocalisations is important for understanding the ...
Scripps Florida scientists uncover major factor in development of Huntington's disease
2014-10-28
JUPITER, FL, October 28, 2014 – Scientists from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have uncovered a major contributor to Huntington's disease, a devastating progressive neurological condition that produces involuntary movements, emotional disturbance and cognitive impairment.
Using an animal model of Huntington's disease, the new study shows that signaling by a specific protein can trigger onset of the disease and lead to exacerbation of symptoms. These findings, published in the October 28, 2014 issue of the journal Science Signaling, offer ...
CHORI scientists identify key factor in relationship between diet, inflammation and cancer
2014-10-28
A connection between inflammation and cancer has been recognized for over a hundred years. This connection is particularly evident in colon carcinogenesis, because patients with IBD have a higher incidence of colon cancer than the general population. There is increasing evidence that inflammation contributes to the earliest stages of carcinogenesis, namely in the process of cell transformation, where the cell acquires many aspects of cancer characteristics. The observation that IBD and colon cancer incidence rise as nations industrialize suggests that changes in diet and ...
Can the wave function of an electron be divided and trapped?
2014-10-28
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — New research by physicists from Brown University puts the profound strangeness of quantum mechanics in a nutshell — or, more accurately, in a helium bubble.
Experiments led by Humphrey Maris, professor of physics at Brown, suggest that the quantum state of an electron — the electron's wave function — can be shattered into pieces and those pieces can be trapped in tiny bubbles of liquid helium. To be clear, the researchers are not saying that the electron can be broken apart. Electrons are elementary particles, ...
Politics can interact with evolution to shape human destiny
2014-10-28
Politics can have unintentional evolutionary consequences that may cause hastily issued policies to cascade into global, multigenerational problems, according to political scientists.
"Most western democracies look at policies as if they are bandages, we fix what we can and then move on," said Pete Hatemi, associate professor of political science, Penn State. "But we need to consider generational policies so that we can fix what we can now, but also be prepared for what comes next."
The researchers said that there is an interaction between political and cultural forces ...
Identifying 'stance taking' cues to enable sophisticated voice recognition
2014-10-28
WASHINGTON, D.C., October 28, 2014 – In the future, computers may be capable of talking to us during meetings just like a remote teleconference participant. But to help move this science-fiction-sounding goal a step closer to reality, it's first necessary to teach computers to recognize not only the words we use but also the myriad meanings, subtleties and attitudes they can convey.
During the 168th Meeting of the Acoustical Society of America (ASA), to be held October 27-31, 2014, at the Indianapolis Marriott Downtown Hotel, Valerie Freeman, a Ph.D. candidate in ...
Improving breast cancer chemo by testing patient's tumors in a dish
2014-10-28
One of the tragic realities of cancer is that the drugs used to treat it are highly toxic and their effectiveness varies unpredictably from patient to patient. However, a new "tumor-in-a-dish" technology is poised to change this reality by rapidly assessing how effective specific anti-cancer cocktails will be on an individual's cancer before chemotherapy begins.
A team of biomedical engineers at Vanderbilt University headed by Assistant Professor Melissa Skala has developed the technique, which uses fluorescence imaging to monitor the response of three-dimensional chunks ...
NASA gets a stare from Cyclone Nilofar's 14 mile-wide eye
2014-10-28
Tropical Cyclone Nilofar developed an eye on Oct. 28 that seemed to stare at NASA's Terra satellite as it passed overhead in space. Warnings are already in effect from the India Meteorological Department as Nilofar is forecast to make landfall in northwestern India.
On Oct. 28 at 06:50 UTC (2:50 a.m. EDT) the MODIS instrument aboard Terra captured a visible image of Tropical Cyclone Nilofar after it developed an eye while moving north in the Arabian Sea. The 12 nautical mile (13.8 miles/22.2 km) wide eye was surrounded by powerful thunderstorms and bands of thunderstorms ...
UC Davis scientists discover exact receptor for DEET that repels mosquitoes
2014-10-28
DEET has been the gold standard of insect repellents for more than six decades, and now researchers led by a University of California, Davis, scientist have discovered the exact odorant receptor that repels them.
They also have identified a plant defensive compound that might mimic DEET, a discovery that could pave the way for better and more affordable insect repellents. Findings from the study appear in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
More than 200 million people worldwide use DEET, developed by scientists at the U.S. Department of Agriculture ...
Figuring out how we get the nitrogen we need
2014-10-28
Nitrogen is an essential component of all living systems, playing important roles in everything from proteins and nucleic acids to vitamins. It is the most abundant element in Earth's atmosphere and is literally all around us, but in its gaseous state, N2,, it is inert and useless to most organisms. Something has to convert, or "fix," that nitrogen into a metabolically usable form, such as ammonia. Until about 100 years ago when an industrial-scale technique called the Haber-Bosch process was developed, bacteria were almost wholly responsible for all nitrogen fixation on ...
[1] ... [3235]
[3236]
[3237]
[3238]
[3239]
[3240]
[3241]
[3242]
3243
[3244]
[3245]
[3246]
[3247]
[3248]
[3249]
[3250]
[3251]
... [8826]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.