Cost of World Cup may be too high for Brazil
2014-07-21
Brazil's World Cup has been estimated to be the priciest of any yet, with a projected cost of $11.5 billion. Some predictions even claim that the Brazilian government will have spent up to $14 billion on building and renovating 12 stadiums; upgrading federal, state and city infrastructure; and ensuring security.
In a country with many economic and social issues that need to be addressed, such amounts of spending—more than three times the amount spent on the last World Cup—seem irresponsible to Brazilian citizens who are eager to understand the benefits of such spending, ...
Filter bed substrates, plant types recommended for rain gardens
2014-07-21
RALEIGH, NC – Urban stormwater runoff is causing problems for the world's water sources. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency found stormwater runoff to be one of the top 10 causes of compromised environments in rivers, streams, lakes, ponds, reservoirs, bays, and estuaries. The pollutants from urban stormwater runoff can harm fish and wildlife populations, foul drinking water, and make recreational areas unsafe.
Researchers from North Carolina State University are looking to rain gardens as one way to remediate the water quality concerns caused by ...
Organic apple orchards benefit from green compost applications
2014-07-21
FAYETTEVILLE, AR – In traditional apple orchards, effective management practices rely on two interrelated components: finding ways to manage competitive vegetation under the trees, and supplying important supplemental nutrition to trees. These factors are further complicated in organic management systems where limited tools are available, and producers need to meet the stringent soil fertility and crop nutrient management standards of the National Organic Program. University of Arkansas scientists published a study that includes recommendations for the use of various groundcover ...
LEDs shine in bedding plant production study
2014-07-21
WEST LAFAYETTE, IN – Growers of annual bedding plant seedlings or plugs work to produce compact, fully rooted transplants with a large stem diameter and high root dry mass--qualities that make seedlings less susceptible to damage during shipping and transplant. To achieve these desirable qualities, greenhouse growers in northern latitudes must rely on supplemental lighting from high-pressure sodium lamps during winter months. A new study shows that light-emitting diodes (LEDs) can give greenhouse growers other lighting options that produce favorable results.
Previously, ...
Typhoon Rammasun made final landfall near China and Vietnam border
2014-07-21
Typhoon Rammasun made landfall in southern China on July 19 bringing heavy rain and typhoon-strength winds to the south China/Vietnam border. NASA and NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite captured an infrared image the typhoon that showed strong thunderstorms with heavy rain potential.
Rammasun made landfall in southern China just north of the Vietnam border on July 18 at 8 p.m. EDT (July 19 at 0000 UTC). The Joint Typhoon Warning Center placed Rammasun's center near 21.9 north and 108.1 east, about 134 nautical miles (154.2 miles/248.2 km) east-northeast of Hanoi, Vietnam. Maximum ...
New research from Africa on pharmacomicrobiomics
2014-07-21
New Rochelle, NY -- The Human Microbiome Project (HMP) is a global initiative to identify and characterize the microorganisms present at multiple sites in the human body. An international team of researchers reports on new ways to harness the results of the HMP and discusses how changes in the microbiome might affect human health, disease, immunity, and importantly, the safety and effectiveness of drug treatment in a Review article that is part of the special issue "OMICS in Africa: Moving 21st Century Integrative Biology from Lab to Village to Innovation Ecosystems," of ...
Fires in Indonesia, July 2014
2014-07-21
Terra and Aqua satellites detected 154 hotspots in areas across Riau province on Sunday, July 20, indicating forest and land fires had increased again following a decline in rainfall. The number of detected hotspots in Sunday's report was far higher than what had been reported one day prior, which had reached only 75 spots.
The hotspots were scattered in six regencies and municipalities, most of which were in northern Riau coastal areas. Smoke and the related haze it creates could potentially spread via winds to Malaysia and Singapore as it seems to be doing in this ...
Tropical Storm Wali no more, but remnants soaked Hawaii
2014-07-21
On July 19, NOAA's Central Pacific Hurricane Center noted that Wali didn't even make it to the Big Island, but moisture associated with the storm did. NOAA's GOES-West satellite captured an image of the remnant low southwest of the Big Island, and a moisture stream that extended over it.
That remnant moisture was enough to cause the local National Weather Service office to issue an early morning flash flood watch on July 19. An infrared image from NOAA's GOES-West satellite showed the moisture stream as a diagonal line of clouds extending from what was the center of the ...
Parents want info about circumcision, not directives from health-care providers
2014-07-21
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – Most parents expect healthcare providers to answer their questions about circumcision, but they don't want a specific recommendation on the procedure, according to a new University of Michigan C.S. Mott Children's Hospital National Poll on Children's Health.
More than half of male infants born in the United States are circumcised, but the rates of circumcision continue to decline.
"Both pro- and anti-circumcision advocates feel strongly about their views, which can create anxiety for new or expectant parents who are trying to find objective information ...
Another advancement in imaging from INRS professor François Légaré's team
2014-07-21
François Légaré's team at the INRS Énergie Matériaux Télécommunications Research Centre successfully imaged a chemical reaction with a spatial and temporal resolution greatly exceeding that obtained to date using microscopes. The team used a femtosecond laser source to shoot a molecular movie of how an acetylene molecule turns into vinylidene. An article presenting the advancement was recently published in the scientific journal Nature Communications.
"The approach we developed combines multiphoton ionization and Coulomb explosion imaging. With the significantly improved ...
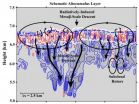
NRL reveals new meteorological insight into mid-level clouds
2014-07-21
WASHINGTON -- Research meteorologists at the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) Marine Meteorology Division (MMD) and Scripps Institution of Oceanography, employing the Navy's Mid-Course Doppler Radar (MCR) at Cape Canaveral, were able to characterize mid-level, mixed-phase altocumulus clouds.
In altocumulus clouds, at medium altitudes ranging from 6,000 feet to 20,000 feet above mean sea level, water droplets can remain in a supercooled liquid phase at temperatures below zero degrees Celsius, the freezing point of water. The supercooled liquid water found at temperatures ...
Mental health issues in children with relatives who participated in manhunt after Boston Marathon
2014-07-21
Children with relatives who were called upon to participate in the interagency manhunt following the Boston Marathon attack carried a particularly heavy mental health burden, according to a Depression and Anxiety study that included surveys of Boston-area parents and other caretakers.
Researchers found that the proportion of youth with likely PTSD was 5.7 times higher among youth with relatives in the manhunt than among youth without. Children with relatives in the manhunt also experienced more emotional symptoms and hyperactivity or inattention.
"Beyond informing our ...
Researchers simplify process to purify water using seed extracts
2014-07-21
Researchers have streamlined and simplified a process that uses extracts from seeds of Moringa oleifa trees to purify water, reducing levels of harmful bacteria by 90% to 99%. The hardy trees that are drought resistant are cultivated widely throughout many countries of Africa, Asia, and Latin America.
The protocol, which is outlined in a Current Protocols in Microbiology review, is low-cost and efficient, making it especially useful for people living in extreme poverty in developing countries who are presently drinking highly turbid and contaminated water. Of these, some ...
Replacing coal and oil with natural gas will not help fight global warming
2014-07-21
Both shale gas and conventional natural gas have a larger greenhouse gas footprint than do coal or oil, especially for the primary uses of residential and commercial heating.
Dr. Robert Howarth, a professor of ecology and environmental biology, came to this conclusion after assessing the best available data and analyzing greenhouse gas footprints for both methane (including shale gas and conventional gas) and carbon dioxide over a timescale of 20-years following emissions. The findings are published in Energy Science & Engineering.
"While emissions of carbon dioxide ...
Mothers of children with autism benefit from peer-led intervention
2014-07-21
Peer-led interventions that target parental well-being can significantly reduce stress, depression and anxiety in mothers of children with disabilities, according to new findings released today in the journal Pediatrics.
In a first-of-its-kind study, researchers from Vanderbilt University examined two treatment programs in a large number of primary caregivers of a child with a disability. Participants in both groups experienced improvements in mental health, sleep and overall life satisfaction and showed less dysfunctional parent-child interactions.
"The well-being ...
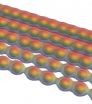
Carbyne morphs when stretched
2014-07-21
Applying just the right amount of tension to a chain of carbon atoms can turn it from a metallic conductor to an insulator, according to Rice University scientists.
Stretching the material known as carbyne -- a hard-to-make, one-dimensional chain of carbon atoms -- by just 3 percent can begin to change its properties in ways that engineers might find useful for mechanically activated nanoscale electronics and optics.
The finding by Rice theoretical physicist Boris Yakobson and his colleagues appears in the American Chemical Society journal Nano Letters.
Until recently, ...
Philosopher uses game theory to understand how words, actions acquire meaning
2014-07-21
MANHATTAN, KANSAS -- Why does the word "dog" have meaning? If you say "dog" to a friend, why does your friend understand you?
Kansas State University philosopher Elliott Wagner aims to address these types of questions in his latest research, which focuses on long-standing philosophical questions about semantic meaning. Wagner, assistant professor of philosophy, and two other philosophers and a mathematician are collaborating to use game theory to analyze communication and how it acquires meaning.
"If I order a cappuccino at a coffee shop, I usually don't think about ...
New technique uses 'simulated' human heart to screen drugs
2014-07-21
A Coventry University scientist has developed a pioneering new way – using samples of beating heart tissue – to test the effect of drugs on the heart without using human or animal trials.
The breakthrough is the work of Dr Helen Maddock – an expert in cardiovascular physiology and pharmacology from the University's Centre for Applied Biological and Exercise Sciences – and could lead to the lives of hundreds of future patients being saved and the quality of their treatments improved.
Adverse effects of drugs on the cardiovascular system are a major cause of many medical ...
Age-related macular degeneration occurs much earlier than previously assumed
2014-07-21
It is widely accepted that age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the most common cause of visual impairment and blindness in industrialized countries. However, it is questionable whether it can continue to be defined as a disease in people in their 50s and beyond. Investigations to determine the incidence of age-related macular degeneration undertaken as part of the Gutenberg Health Study of the University Medical Center of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) have shown that even persons under the age of 50 years may be affected by an early form of the eye disease. ...
Our daily bread
2014-07-21
Bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) is the most widely cultivated cereal crop in the world and provides 20 percent of the food calories consumed by humans. A polyploid species, hexaploid bread wheat contains six duplicated copies of its genome and is more than five times larger than the human genome. This makes genome research in wheat particularly difficult.
Dr. Klaus Mayer, Head of the Research Unit Plant Genome and Systems Biology at HMGU, in collaboration with his colleagues Matthias Pfeifer, Dr. Karl Kugler and Manuel Spannagl, succeeded in gaining insights into complex ...
Described novel regulator of a protein inactive in over 50 percent of human tumors
2014-07-21
Researchers at the Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBELL) and the University of Barcelona have discovered the interaction between HERC2 proteins with another protein called p53 that is inactivated in more than half of human tumors. The study results were published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
Regulation of the activity of p53 by HERC2
The team of José Luis Rosa, at the growth factors and cell differentiation research group at IDIBELL studies the molecular mechanisms of HERC family proteins. These proteins are ubiquitin ligases that regulate the ...
Potential new flu drugs target immune response, not virus
2014-07-21
The seriousness of disease often results from the strength of immune response, rather than with the virus, itself. Turning down that response, rather than attacking the virus, might be a better way to reduce that severity, says Juliet Morrison of the University of Washington, Seattle. She and her collaborators have now taken the first step in doing just that for the H7N9 influenza, and their work has already led to identification of six potential therapeutics for this highly virulent strain. The research is published ahead of print in the Journal of Virology.
"We set ...
More than glitter
2014-07-21
A special class of tiny gold particles can easily slip through cell membranes, making them good candidates to deliver drugs directly to target cells.
A new study from MIT materials scientists reveals that these nanoparticles enter cells by taking advantage of a route normally used in vesicle-vesicle fusion, a crucial process that allows signal transmission between neurons. In the July 21 issue of Nature Communications, the researchers describe in detail the mechanism by which these nanoparticles are able to fuse with a membrane.
The findings suggest possible strategies ...
Mammals metabolize some pesticides to limit their biomagnification
2014-07-21
The concentrations of many historically used, and now widely banned, pesticides and other toxic chemicals—called legacy contaminants—can become magnified in an animal that eats contaminated food; however, a new Environmental Toxicology & Chemistry study has found that Arctic mammals metabolize some currently used pesticides, preventing such 'biomagnification.'
Researchers who studied the vegetation-caribou-wolf food chain in the Bathurst region of Canada say that currently use pesticides enter the food chain and become concentrated in vegetation, but the evidence shows ...
Examining the causes of a devastating debris flow
2014-07-21
Storm-triggered landslides cause loss of life, property damage, and landscape alterations. For instance, the remnants of Hurricane Camille in 1969 caused 109 deaths in central Virginia, after 600 mm of rain fell in mountainous terrain in 6 hours. More recently, on 8 August 2010, a rainstorm-induced landslide devastated the Chinese county of Zhouqu, causing more than 1000 deaths. A new modeling study by Ren (Geophysical Research Letters) examines the multiple factors, both natural and human caused, that came together to produce this event. The triad of storm-triggered landslides ...
[1] ... [3473]
[3474]
[3475]
[3476]
[3477]
[3478]
[3479]
[3480]
3481
[3482]
[3483]
[3484]
[3485]
[3486]
[3487]
[3488]
[3489]
... [8831]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.