Obesity before pregnancy linked to earliest preterm births, Stanford/Packard study finds
2014-06-25
Women who are obese before they become pregnant face an increased risk of delivering a very premature baby, according to a new study of nearly 1 million California births.
The findings from the Stanford University School of Medicine provide important clues as to what triggers extremely preterm births, specifically those that occur prior to 28 weeks of pregnancy.
The study, published in the July issue of Paediatric and Perinatal Epidemiology, found no link between maternal obesity and premature births that happen between 28 and 37 weeks of the normal 40-week gestation ...
Earlier snowmelt prompting earlier breeding of Arctic birds
2014-06-25
A new collaborative study that included the work of Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) biologists has revealed that migratory birds that breed in Arctic Alaska are initiating nests earlier in the spring, and that snowmelt occurring earlier in the season is a big reason why.
The report, "Phenological advancement in arctic bird species: relative importance of snow melt and ecological factors," appears in the current on-line edition of the journal Polar Biology. Lead author Joe Liebezeit (formerly with WCS) and co-author Steve Zack of WCS have conducted research on Arctic ...
UMN research uncovers structure, protein elements critical to human function and disease
2014-06-25
MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (June 23, 2014) – New structures discovered within cilia show a relationship between certain proteins and juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. The discovery, made at the University of Minnesota, was named paper of the week in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, and sheds new light on the microstructure of cilia.
Cilia are microscopic, hair-like structures occurring in large numbers on the surface of some of the body's cells and are involved in movement and perception. Cilia are composed of double microtubules, which are in turn composed of protofilaments.
Richard ...
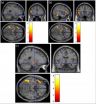
Chronic brain damage not as prevalent in NFL players, say researchers
2014-06-25
ROSEMONT, IL – A study published online today in Sports Health: A Multidisciplinary Approach provides a different take on previous information regarding the prevalence of chronic brain damage in retired NFL players.
Researchers performed in-depth neurological examinations of 45 retired NFL players, ranging in age from 30-to 60-years old. The analysis included state-of-the-art magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI), diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) along with comprehensive neuropsychological and neurological examinations, interviews, blood ...
Stanley Miller's forgotten experiments, analyzed
2014-06-25
VIDEO:
Graduate student and study first author Eric Parker talks about the famous spark discharge experiment and the latest findings from a first-ever analysis of Miller's samples from 1958.
Click here for more information.
Stanley Miller, the chemist whose landmark experiment published in 1953 showed how some of the molecules of life could have formed on a young Earth, left behind boxes of experimental samples that he never analyzed. The first-ever analysis of some of Miller's ...
Restoring thyroid hormones in heart may prevent heart disease from diabetes
2014-06-25
Old Westbury, N.Y. (June 25, 2014) –Administering low doses of a thyroid hormone to rats with diabetes helps restore hormone levels in their hearts and prevented deterioration of heart function and pathology, according to a new study by NYIT College of Osteopathic Medicine professor A. Martin Gerdes.
The study, published in the online edition of Molecular Medicine provides the first clear indication that low thyroid hormone levels in cardiac tissue of diabetic individuals may be the major cause of their associated heart disease, says Gerdes.
The study finds that diabetes ...
Neural sweet talk: Taste metaphors emotionally engage the brain
2014-06-25
So accustomed are we to metaphors related to taste that when we hear a kind smile described as "sweet," or a resentful comment as "bitter," we most likely don't even think of those words as metaphors. But while it may seem to our ears that "sweet" by any other name means the same thing, new research shows that taste-related words actually engage the emotional centers of the brain more than literal words with the same meaning.
Researchers from Princeton University and the Free University of Berlin report in the Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience the first study to experimentally ...
Special edition of the Red Journal highlights the need for radiation oncology services in LMICs
2014-06-25
Fairfax, Va., June 25, 2014—The July 1, 2014 edition of the International Journal of Radiation Oncology ● Biology ● Physics (Red Journal), the official scientific journal of the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO), features a special section of 10 articles focusing on global health and radiation oncology in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs.)
Three papers examine the overall need for more and the current opportunities to provide radiation oncology in LMICs, C. Norman Coleman, MD, FASTRO, highlights the work and the four main principles of ...
Study highlights carbon monoxide hazards on houseboats
2014-06-25
FALLS CHURCH, Va. (June 25, 2014) — Boaters and marina workers should exercise caution this summer before taking to the seas. A study published online in the Journal of Occupational and Environmental Hygiene (JOEH) outlines hazards posed by carbon monoxide levels on houseboats that use gasoline-powered generators without emission controls, along with controls that are available to reduce exposure to carbon monoxide from the generators.
The study, conducted by researchers at the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), found that uncontrolled generators ...
New treatment option in development for individuals with food allergy
2014-06-25
New Rochelle, NY, June 25, 2014—For some children an allergic reaction to common foods such as milk, eggs, or peanuts can cause an anaphylactic reaction. At present no effective treatment for food allergy exists, and strict dietary avoidance of known food triggers is the only preventive option available. Ongoing trials are exploring options for oral immunotherapy (OIT) for desensitization in the treatment of Immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated food allergy, as described in a Review article in Pediatric Allergy, Immunology, and Pulmonology, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary ...
Deploying midwives in poorest nations could avert millions of maternal and newborn deaths
2014-06-25
A modest increase in the number of skilled midwives in the world's poorest nations could save the lives of a substantial number of women and their babies, according to new analyses by researchers from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
Maternal mortality is a leading cause of death for women in many developing countries and public health efforts to avert it have only made headway in a few countries. Elsewhere, progress has either never started or has stalled in recent years. Poor nations also have troubling rates of infant and fetal deaths. Midwives ...
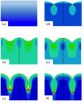
Mathematical models explain how a wrinkle becomes a crease
2014-06-25
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Wrinkles, creases and folds are everywhere in nature, from the surface of human skin to the buckled crust of the Earth. They can also be useful structures for engineers. Wrinkles in thin films, for example, can help make durable circuit boards for flexible electronics.
A new mathematical model developed by researchers from Brown University could help engineers control the formation of wrinkle, crease, and fold structures in a wide variety of materials. It may also help scientists understand how these structures form in nature. The ...
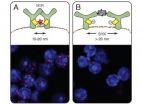
Nanoscale ruler reveals organization of the cell membrane
2014-06-25
This news release is available in German.
After a ten-year effort, Prof. Dr. Michael Reth from the Institute of Biology III of the University of Freiburg and the Max Planck Institute of Immunobiology and Epigenetics has developed a method to investigate the cell surface's organization on a nanometer scale. This allows him to monitor how the antigen receptor, which B cells of the immune system use to recognize foreign substances, changes after activation. This study shows that the receptor components dissociate from each other– rather than assemble, as previously ...
New study quantifies the effects of climate change in Europe
2014-06-25
If no further action is taken and global temperature increases by 3.5°C, climate damages in the EU could amount to at least €190 billion, a net welfare loss of 1.8% of its current GDP. Several weather-related extremes could roughly double their average frequency. As a consequence, heat-related deaths could reach about 200 000, the cost of river flood damages could exceed €10 billion and 8000 km2 of forest could burn in southern Europe. The number of people affected by droughts could increase by a factor of seven and coastal damage, due to sea-level rise, could more than ...
Using math to analyze movement of cells, organisms, and disease
2014-06-25
Traveling waves model tumor invasion
Cell migration, which is involved in wound healing, cancer and tumor growth, and embryonic growth and development, has been a topic of interest to mathematicians and biologists for decades.
In a paper published recently in the SIAM Journal on Applied Dynamical Systems, authors Kristen Harley, Peter van Heijster, Robert Marangell, Graeme Pettet, and Martin Wechselberger study a model describing cell invasion through directional outgrowth or movement in the context of malignant tumors, in particular, melanoma or skin cancer. Tumor ...
Freedom of choice: When rejection and discrimination hinder minority entrepreneurs
2014-06-25
When it comes to The American Dream, freedom of choice is a central value for entrepreneurs. According to a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research, when a person's choices are limited due to rejection and discrimination, they are more likely to fail at business and in their personal lives.
"Not only does restricting a person's choices threaten the success of a new business, it also has swift and damaging effects on the individual's self-esteem and their personal sense of control and power in the world," write authors Sterling A. Bone (Utah State University), Glenn ...
Money in the bank: Why does feeling powerful help people save more?
2014-06-25
In a materialistic culture, saving money is a challenge many of us face long before our retirement years. While many people think education, upbringing, and self-control are major contributors to a person's savings habits, a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research reveals that people save more when they feel powerful.
"We were interested in knowing whether the decision to save or not save money was affected by how someone was feeling during the time they were making a savings decision," write authors Emily N. Garbinsky (Stanford University), Anne-Kathrin Klesse ...
Army leads collaborative effort to establish standards for sequencing viral genomes
2014-06-25
Scientists at the U.S. Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases (USAMRIID) have proposed a set of standards aimed at developing a common "language" among investigators working to sequence viral genomes and characterize viral stocks.
According to USAMRIID senior author Gustavo Palacios, Ph.D., the proposed system, published last week as an editorial in the journal mBio, is the result of a collaborative effort involving scientists from many of the world's leading institutions. Contributors include the Broad Institute, the J. Craig Venter Institute, Los Alamos ...
Achieving Your Goals: Does removing yourself from the big picture help?
2014-06-25
Consider the case of the adult student attending night school to earn a degree that will result in a better job with higher pay. From sacrificing time with friends and family to missing a relaxing evening watching TV, this type of long-term gain often comes with short-term pain. According to a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research, people are more likely to achieve their goals and avoid temptations when they are able to remove themselves from the big picture.
"Past research on personal achievement has focused on whether someone sets nearsighted or farsighted ...
Distorting the past: Why do impulsive consumers forget their past indulgences?
2014-06-25
Activities like dieting, saving money, and studying require goal setting and self-control. But even the most disciplined person falls prey to temptation every once in a while. According to a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research, people who distort past memories of their indulgences are more likely to indulge in the future.
"We investigated the possibility that individuals may distort memories of past behavior in order to allow for indulgence in the present. In other words, people may trick themselves into thinking something like, 'I've been good on my diet lately, ...
Downside to disaster relief: Why do photos of attractive children backfire?
2014-06-25
When it comes to asking a stranger for help, being young, pretty, and the opposite sex greatly improve your odds. But when it comes to children suffering from the likes of natural disaster, poverty, or homelessness, a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research reveals that less attractive children receive more help than their cuter counterparts.
"Many charitable organizations use children in advertising and promotional materials. Our research examines how the facial attractiveness of the children in these campaigns affects the empathy and help received from adults," ...
Double standard? The use of performance-enhancing products
2014-06-25
When professional athletes are found to be using performance-enhancing drugs, many people consider this an unfair advantage and say they are cheating. But when another person uses the same drug to overcome a disease or behavioral issue, society is more forgiving. A new study in the Journal of Consumer Research shows that people are more forgiving when the benefit is personal.
"Our research shows that when people see others using ability-boosting products, they are more likely to see this behavior as morally unacceptable than if they were using the products themselves," ...
Marriage and healthy hearts
2014-06-25
PITTSBURGH—The affairs of the heart may actually affect the affairs of the heart in ways previously not understood.
"Growing evidence suggests that the quality and patterns of one's social relationships may be linked with a variety of health outcomes, including heart disease," says Thomas Kamarck, professor of psychology and Biological and Health Program Chair in the University of Pittsburgh Kenneth P. Dietrich School of Arts and Sciences. He is an author of a new study that correlates unhappy marital interaction with thicker carotid arteries and a higher risk of cardiovascular ...
When does rude service at luxury stores make consumers go back for more?
2014-06-25
For many people, the idea of purchasing a luxury product in a high-end boutique comes with the stigma of snobbery and rude salesclerks. But when they are rejected in real life, a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research reveals that a person's desire for brand affiliation and willingness to purchase and display the item actually increases.
"Our research highlights the fact that we are profoundly attuned to social threats and are driven to buy, wear, and use products from the very people who are disrespectful to us," write authors Morgan K. Ward (Southern Methodist ...
Home sweet messy home: How do consumers cope with disorder at home?
2014-06-25
From hanging up our coats to organizing our bookshelves and kitchen cupboards, some people keep their homes tidy and others seem to live in complete chaos. According to a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research, understanding how we organize our homes can help us cope with contradictions and disruptions occurring in our daily lives.
"Tidying a home is an activity that goes beyond moving objects from one place to another or putting them in specific places. Rather, it is a process of building a meaningful domestic environment. Through their tidying activities, people ...
[1] ... [3524]
[3525]
[3526]
[3527]
[3528]
[3529]
[3530]
[3531]
3532
[3533]
[3534]
[3535]
[3536]
[3537]
[3538]
[3539]
[3540]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.