Wasteful tests before surgery: Study shows how to reduce them safely
2025-02-06
For many patients, getting ready to have surgery means getting their blood drawn, their heart rhythm checked, or having other tests in the weeks leading up to their operation.
But not all patients need all those tests -- especially if the results won’t change how their surgical team treats them or how well they do afterward.
Now, a new study shows how hospitals can focus the use of such tests on the patients who truly need them, while safely reducing unnecessary testing in others.
The result: less wasted money and resources for each test, and less wasted time for patients and clinical staff.
The study, published in JAMA ...
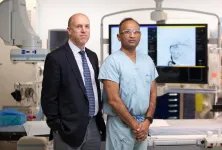
UCalgary researchers confirm best approach for stroke in medium-sized blood vessels
2025-02-06
University of Calgary’s Hotchkiss Brain Institute researchers with the Calgary Stroke Program at Foothills Medical Centre revolutionized treatment for stroke with the ESCAPE Trial, proving that a clot retrieval procedure known as endovascular thrombectomy (EVT) can dramatically improve patient outcomes after an acute ischemic stroke caused by a blockage in a large-sized blood vessel.
Building on that knowledge, the team launched the ESCAPE-MeVO clinical trial to assess whether ischemic stroke patients with blockages in smaller medium-sized vessels could also benefit from EVT. Ischemic strokes are the most common form of stroke. The study, published ...
Nationwide, 34 local schools win NFL PLAY 60 grants to help students move more
2025-02-06
DALLAS, Feb. 6, 2025 — Physical activity positively impacts overall mental and physical wellness which is essential to help children reach their full potential[1]. That is why the American Heart Association, committed to changing the future of health, and the National Football League (NFL) are awarding 34 schools, at least one for each of the NFL teams, with $1,000 grants for physical activity equipment. Through support from the NFL, the NFL PLAY 60 grants are distributed by the American Heart Association annually to recognize those classrooms and ...
New software developed at Wayne State University will help study chemical and biological systems
2025-02-06
DETROIT — Physics-based computer simulations are essential tools for understanding the relationship between atomic-level interactions and physically observable properties of materials. It is from knowledge of these structure-property relationships that new materials can be designed with properties specifically tailored to address the problem of interest.
With the help of a new grant from the National Science Foundation (NSF), a team of Wayne State University College of Engineering researchers are developing new software to support computational materials design. Built on a 15-year collaborative effort, Jeffrey Potoff, Ph.D., chair ...
uOttawa study unveils new insights into how neural stem cells are activated in the adult human brain
2025-02-06
A University of Ottawa neuroscientist has led a Canadian research team to reveal important new insights into the activation dynamics of neural stem cells (NSCs). These are the stem cells that build our central nervous systems and the self-renewing.
The collaborative team led by the University of Ottawa’s Dr. Armen Saghatelyan aimed to shed light on how neural stem cells integrate a multitude of signals from different cell types in the brain – and how they decode these signals.
These are big questions because how NSCs react to signals in their cellular environment controls whether they remain in their ...
Cystic fibrosis damages the immune system early on
2025-02-06
Despite new medication, cystic fibrosis often leads to permanent lung damage. Working with an international team, researchers from the Technical University of Munich (TUM) have discovered that the disease causes changes in the immune system early in life, presumably even in newborns. These changes lead to frequent inflammation and are not affected by drugs targeting the altered mucus production.
Cystic fibrosis is caused by hereditary genetic mutations that impair or halt the production of the CFTR protein. The respiratory tract ...
Novel ‘living’ biomaterial aims to advance regenerative medicine
2025-02-06
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A biomaterial that can mimic certain behaviors within biological tissues could advance regenerative medicine, disease modeling, soft robotics and more, according to researchers at Penn State.
Materials created up to this point to mimic tissues and extracellular matrices (ECMs) — the body’s biological scaffolding of proteins and molecules that surrounds and supports tissues and cells — have all had limitations that hamper their practical applications, according to the team. To overcome some of those limitations, ...
Warding off superbugs with a pinch of turmeric
2025-02-06
In 2017, a tragic incident unfolded in a Nevada hospital. A woman, admitted for pneumonia, tragically succumbed to multiple organ failure and sepsis. The culprit? A strain of bacteria that had developed resistance to a staggering 26 different antibiotics. These superbugs, or antibiotic-resistant bacteria, stand as one of the most pressing public health threats globally.
Joining the effort to fight these deadly pathogens, researchers at Texas A&M have now shown that curcumin, the compound that gives turmeric its characteristic bright yellow color, can potentially be used to reduce antibiotic resistance.
The ...
Ophthalmic complications in patients on antidiabetic GLP-1 medications are concerning neuro-ophthalmologists
2025-02-06
BUFFALO, N.Y. — A small percentage of patients taking the extraordinarily popular GLP-1 medications have experienced vision problems, but a direct causal link with the drugs has not been established. That is the conclusion of a retrospective study published online on Jan. 30 in JAMA Ophthalmology.
The study focused on nine patients who had experienced vision problems while using semaglutide (brand names Wegovy and Ozempic) and tirzepatide (brand names Mounjaro and Zepbound).
The paper is one of several in the past ...
Physicians committee research policy director speaks today at hearing on taxpayer funded animal cruelty
2025-02-06
WASHINGTON, D.C. — Research Policy Director Elizabeth Baker from the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine, a national medical ethics and health advocacy group of 17,000 physicians, spoke today, Feb. 6, at a Congressional hearing focused on ending federally funded animal cruelty in research.
The U.S. House Oversight and Government Reform Subcommittee on Cybersecurity, Information Technology, and Government Innovation Chairwoman Nancy Mace (R-S.C.) announced the hearing in a news release on Monday, with plans to evaluate current animal cruelty funded by the federal government and explore opportunities ...
New technology lights way for accelerating coral reef restoration
2025-02-06
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Scientists have developed a novel tool designed to protect and conserve coral reefs by providing them with an abundance of feeding opportunities.
The device, dubbed the Underwater Zooplankton Enhancement Light Array (UZELA), is an autonomous, programmable underwater light that works to draw in nearby zooplankton, microscopic organisms that coral feed on.
After testing the submersible on two species of coral native to Hawaii over six months, researchers found that UZELA could ...
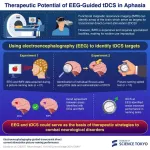
Electroencephalography may help guide treatments for language disorders
2025-02-06
Electroencephalography (EEG) may offer a more accessible alternative to functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) for guiding transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) when treating aphasia. Researchers from Institute of Science Tokyo found an 80% agreement between EEG and fMRI in identifying brain regions activated during language tasks. Furthermore, EEG-guided tDCS improved picture-naming speed in participants, indicating its potential for innovative therapies in language disorders.
Many neurological disorders are directly linked to damage or deterioration in specific regions of the brain. For example, ...
Multinational research project shows how life on Earth can be measured from space
2025-02-06
Measurements and data collected from space can be used to better understand life on Earth.
An ambitious, multinational research project funded by NASA and co-led by UC Merced civil and environmental engineering Professor Erin Hestir demonstrated that Earth’s biodiversity can be monitored and measured from space, leading to a better understanding of terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Hestir led the team alongside University of Buffalo geography Professor Adam Wilson and Professor Jasper Slingsby from the University ...
Essential genome of malaria parasite Plasmodium knowlesi mapped
2025-02-06
Embargoed for release: Thursday, February 6, 2025, 2:00 PM ET
Key points:
Comprehensive genetic mapping of Plasmodium knowlesi, a zoonotic parasite that causes malaria, has revealed the genes required for malaria infection of the blood, and those driving drug resistance.
By identifying specific druggable targets and determinants of resistance, the map provides insights that could help the development of new therapeutics.
Boston, MA—A new, comprehensive map of all the genes essential for blood infections in Plasmodium knowlesi (P. ...
Ice streams move due to tiny ice quakes
2025-02-06
In brief:
• In Greenland, an international team of researchers led by ETH Zurich has discovered that countless tiny ice quakes take place deep inside ice streams.
• These quakes are responsible for the fact that ice streams also move with a continuous stick-slip motion and not only like viscous honey as previously considered.
• The researchers recorded seismic data from inside the ice stream using a fibre-optic cable in a 2,700-metre deep borehole.
The ...
Whale song has remarkable similarities to human speech in terms of efficiency
2025-02-06
Whale song can be as efficient as – and, in some cases, more efficient than – human communication, according to a new study in Science Advances. Meanwhile, new unrelated research in Science further investigates whale song’s adherence to a universal linguistic law, as observed in recordings of humpback whales.
Natural selection favors the pithy over the longwinded. For example, yelling “Duck!” is faster and far more effective than shouting “Be careful, there is an incoming projectile, and you need to move out of the way!” ...
Uncovered: How mice override instinctive fear responses
2025-02-06
Researchers have uncovered a neural mechanism in the brains of mice that enables them to override instinctive fear responses; dysfunction in this mechanism may contribute to inappropriate or excessive fear responses, they say. According to the findings, targeting these circuits could offer new therapeutic avenues for treating fear-related disorders like post-traumatic stress disorder and anxiety. Fear responses to visual threats, such as escaping from an approaching predator, are critical instinctive reactions for survival and are ...
A pathway that contributes to insulin resistance can be targeted, mouse study shows
2025-02-06
The hormone adrenomedullin disrupts insulin signaling in blood vessel cells, contributing to systemic insulin resistance in obesity-associated type 2 diabetes, according to a new study. Blocking adrenomedullin’s effects restores insulin function and improves glucose control in a mouse model, suggesting a potential new target for treating obesity-related metabolic disease. Diabetes is a leading global cause of illness, mortality, and healthcare expenditures, with most cases stemming from obesity-induced insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Insulin resistance primarily ...
Special Issue: The cryosphere
2025-02-06
In this Special Issue of Science, 3 Reviews and a Policy Forum highlight research on Earth’s frozen places – from the Arctic to the Antarctic – and how it’s changing due to climate change and the geopolitical challenges this important work faces. In the first Review, Julienne Stroeve and colleagues provide a preview of what the Arctic region may look like in a warmer world. Without stronger climate action, global temperatures are set to rise +2.7°C above preindustrial levels, ...
Scientists discover brain mechanism that helps overcome fear
2025-02-06
Researchers at the Sainsbury Wellcome Centre (SWC) at UCL have unveiled the precise brain mechanisms that enable animals to overcome instinctive fears. Published today in Science, the study in mice could have implications for developing therapeutics for fear-related disorders such as phobias, anxiety and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
The research team, led by Dr Sara Mederos and Professor Sonja Hofer, mapped out how the brain learns to suppress responses to perceived threats that prove ...
Mantis shrimp clubs filter sound to mitigate damage
2025-02-06
Known for their powerful punch, mantis shrimp can smash a shell with the force of a .22 caliber bullet. Yet, amazingly, these tough critters remain intact despite the intense shockwaves created by their own strikes.
Northwestern University researchers have discovered how mantis shrimp remain impervious to their own punches. Their fists, or dactyl clubs, are covered in layered patterns, which selectively filter out sound. By blocking specific vibrations, the patterns act like a shield against self-generated shockwaves.
The study will be published on Friday (Feb. 7) in the journal Science.
The findings someday could be applied to developing ...
Large differences in water-seeking ability found in U.S. corn varieties
2025-02-06
A corn plant knows how to find water in soil with the very tips of its roots, but some varieties, including many used for breeding high-yielding corn in the U.S., appear to have lost a portion of that ability, according to a Stanford-led study. With climate change increasing droughts, the findings hold potential for developing more resilient varieties of corn.
The study, published in the journal Science, uncovers genetic mechanisms behind root “hydropatterning,” or how plant roots branch toward water and avoid dry spaces in soil. In particular, the researchers ...
Whale song has structure similar to human language
2025-02-06
Humpback whale song is a striking example of a complex, culturally transmitted behavior, but up to now, there was little evidence it has language-like structure. Human language, which is also culturally transmitted, has recurring parts whose frequency of use follows a particular pattern. In humans, these properties help learning and may come about because they help language be passed from one generation to the next. This work innovatively applies methods inspired by how babies discover words in speech to humpback whale recordings, uncovering the same statistical structures found in all human languages. It reveals previously undetected structure in ...
Cracking the Burmese python code: New data zeroes in on game-changing strategies
2025-02-06
In a groundbreaking study, University of Florida scientists statistically analyzed large amounts of data collected by Burmese python contractors, revealing critical insights about how to most efficiently remove the reptiles.
Researchers correlated survey outcomes, including python removals, with survey conditions, using statistical modeling. For example, the researchers examined if factors like time or temperature impacted the chance of removing a python. They also analyzed whether the most surveyed areas aligned with the highest python removals. This allowed the researchers to ...
Risk it or kick it? Study analyzes NFL coaches’ risk tolerance on fourth down
2025-02-06
During the Super Bowl, every decision matters. With millions of fans watching, the game often comes down to a single play call. And no call is more scrutinized than what a coach decides to do on fourth down. Punt? Attempt a field goal? Or go for it?
A new BYU study explains why NFL coaches, including Super Bowl contenders Andy Reid (Kansas City Chiefs) and Nick Sirianni (Philadelphia Eagles), may behave too conservatively on fourth down. Despite growing acceptance of analytics-driven decision-making, most coaches, ...
[1] ... [685]
[686]
[687]
[688]
[689]
[690]
[691]
[692]
693
[694]
[695]
[696]
[697]
[698]
[699]
[700]
[701]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.