International Alzheimer’s prevention trial in young adults begins
2025-02-04
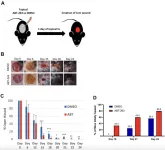
The first participants in an international clinical trial aimed at preventing Alzheimer’s disease in young adults at high risk of the disease have been enrolled. The trial, led by Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, aims to determine whether stopping the early molecular changes that lead to symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease can prevent the disease from ever taking hold. The study is enrolling people as young as 18 who have few or no detectable Alzheimer’s-related molecular changes in their brains, up to 25 years before the expected onset ...
Why your headphone battery doesn't last
2025-02-04
Ever notice that batteries in electronics don't last as long as they did when they were brand new?
An international research team led by The University of Texas at Austin took on this well-known battery challenge, called degradation, with a twist. They're focusing their work on real-world technology that many of us use daily: wireless earbuds. They deployed x-ray, infrared, and other imaging technologies to understand the complexities of all the technology packed in these tiny devices and learn why their battery lives erode over time.
"This started with my personal headphones; I only wear the right one, and I found ...
Study probes how to predict complications from preeclampsia
2025-02-04
The existing prediction models for severe complications of preeclampsia are most accurate only in the two days after hospital admission, with deteriorating performance over time, according to a new study published February 4th in the open-access journal PLOS Medicine by Henk Groen of University of Groningen, the Netherlands, and colleagues.
Preeclampsia is a potentially life-threatening condition that can occur during pregnancy; of women diagnosed with preeclampsia, 5-20% will develop severe complications. Two existing PIERS (Pre-eclampsia Integrated ...
CNIC scientists design an effective treatment strategy to prevent heart injury caused by a class of anticancer drugs
2025-02-04
A team of scientists at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC), working in collaboration with international partners, has designed a strategy for preventing the cardiotoxic effects of anthracyclines, a widely used class of anticancer drugs. Cardiotoxicity is a frequent adverse secondary effect of cancer therapy with these drugs. The study, published in JACC: CardioOncology, demonstrates that treatment with the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin can mitigate the cardiac injury associated with anthracycline therapy.
Anthracyclines are first-line medications in the treatment of cancer, but in 5% of patients their use is associated ...
NYU’s Yann LeCun a winner of the 2025 Queen Elizabeth Prize for Engineering
2025-02-04
New York University’s Yann LeCun has been selected as a winner of the 2025 Queen Elizabeth Prize for Engineering—one of seven recognized for contributions to the advancement of Modern Machine Learning, which has fueled advances in artificial intelligence.
“This year, we celebrate the remarkable achievements that these seven engineers have contributed to Modern Machine Learning, a field that has revolutionized artificial intelligence by uniting algorithms, hardware, and data,” said Lord Vallance, chair of the Queen Elizabeth Prize for Engineering Foundation. “The impact of this innovation is felt across industries, economies, and the planet, ...
New study assesses impact of agricultural research investments on biodiversity, land use
2025-02-04
New study assesses impact of agricultural research investments on biodiversity and land use
Data analysis spans 1960s Green Revolution to 2015
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. — New, groundbreaking research shows how, at a local scale, agricultural research and development led to improved crop varieties that resulted in global benefits to the environment and food system sustainability. The Purdue University study appears in the latest issue of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“At the global level, we see a reduction in cropland use from these technology ...
High-precision NEID spectrograph helps confirm first Gaia astrometric planet discovery
2025-02-04
NEID (rhymes with fluid) is a high-precision radial-velocity spectrograph that is designed to measure the extremely minute wobble of nearby stars using the radial velocity effect. This effect results from the mutual gravitational force between a planet and its host star which causes the star’s position to shift very slightly as the planet travels around it. With this powerful capability, one of NEID’s main science goals is to confirm exoplanet candidates found by other exoplanet missions.
NEID is funded by the NASA/NSF Exoplanet Exploration Program (NN-EXPLORE) and is mounted on the WIYN 3.5-meter Telescope at ...
ABT-263 treatment rejuvenates aged skin and enhances wound healing
2025-02-04
“[…] topical ABT-263 effectively reduced several senescence markers in aged skin, thereby priming the skin for improved subsequent wound healing.”
BUFFALO, NY—February 4, 2025 — A new research paper was published by Aging (Aging-US) on December 3, 2024, in Volume 17, Issue 1, titled “Topical ABT-263 treatment reduces aged skin senescence and improves subsequent wound healing.”
Researchers Maria Shvedova, Rex Jeya Rajkumar Samdavid Thanapaul, Joy Ha, Jannat ...
The challenge of pursuit – how saccades enable mammals to simultaneously chase prey and navigate through complex environments
2025-02-04
How do predators use their vision to both navigate through the terrain whilst tracking prey running for its life? Pursuing prey through a complex environment is a major challenge for the visual system as not only do the prey constantly change direction, sometimes in the opposite direction to the pursuer, but running after something evokes self-induced motion-blur which degrades vision. In a study, published in Current Biology, researchers reconstructed the visual fields of freely moving ferrets as they chased a fleeing target. They discovered that the eye saccades, like those that normally track objects when sitting still, aligned the motion of the environment, ...
Music can touch the heart, even inside the womb
2025-02-04
WASHINGTON, Feb. 4, 2025 – Playing music has long been a way for expectant parents to connect with their children in the womb, but a group of researchers has found evidence it can calm fetal heart rates, potentially providing developmental benefits.
In Chaos, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the Autonomous University of the State of Mexico, the Metropolitan Autonomous University, the General Hospital Nicolás San Juan, and the National Institute of Cardiology Ignacio Chávez studied the effect of classical music on a fetal heartbeat. The team used mathematical analysis tools to identify patterns in heart rate variability.
Typical measures ...
Contribution of cannabis use disorder to new cases of schizophrenia has almost tripled over the past 17 years
2025-02-04
Ottawa, ON, February 4, 2025 – The proportion of new cases of schizophrenia associated with a cannabis use disorder has risen from 4% pre-legalization to 10% after cannabis legalization in Ontario, according to new research.
A new study from researchers at ICES, The Ottawa Hospital, University of Ottawa’s Department of Family Medicine, and Bruyère Health Research Institute and published in the journal JAMA Network Open used data capturing the healthcare visits of everyone living in Ontario, Canada to track whether the liberalization of medical cannabis in 2015 and legalization of non-medical ...
Listening for multiple mental health disorders
2025-02-04
WASHINGTON, Feb. 4, 2025 – It’s no secret that there is a mental health crisis in the United States. As of 2021, 8.3% adults had major depressive disorder (MDD) and 19.1% had anxiety disorders (AD), and the COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated these statistics. Despite the high prevalence of AD/MDD, diagnosis and treatment rates remain low – 36.9% for AD and 61.0% for MDD – due to a variety of social, perceptual, and structural barriers. Automated screening tools can help.
In JASA Express Letters, published on behalf of the Acoustical Society ...
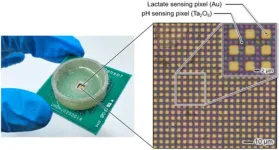
Visualization of chemical phenomena in the microscopic world using semiconductor image sensor
2025-02-04
<Overview>
A research team led by Professor Kazuaki Sawada and Project Assistant Professor Hideo Doi of the Department of Electrical and Electronic Information Engineering, Toyohashi University of Technology has developed a semiconductor sensor enabling the real-time observation of two types of biomolecule dynamics in solutions. By using semiconductor technology to pattern a thin metal film functioning as a neurotransmitter-sensitive membrane on sensor pixels arranged two-dimensionally in a 2 µm pitch, the sensor captures the movement of hydrogen ions and lactate ...
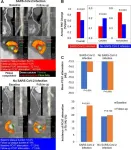
Virus that causes COVID-19 increases risk of cardiac events
2025-02-04
OAK BROOK, Ill. – A new study found severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection was associated with the rapid growth of plaque in the coronary arteries and an increased risk of cardiovascular events. The results were published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
“COVID-19, caused by SARS-CoV-2, is initially characterized by acute lung injury and respiratory failure,” said the study’s senior author, Junbo Ge, M.D., professor and director of the Cardiology Department at Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University in Shanghai, ...
Half a degree rise in global warming will triple area of Earth too hot for humans
2025-02-04
New assessment warns area the size of the USA will become too hot during extreme heat events for even healthy young humans to maintain a safe body temperature if we hit 2°C above preindustrial levels.
For those aged over 60, the same 2°C rise would see more than a third of the planet’s land mass cross this critical ‘overheating’ threshold
An international group of scientists, led by King’s College London, has revealed how continued global warming will lead to more parts of the planet becoming too ...
Identifying ED patients likely to have health-related social needs
2025-02-04
INDIANAPOLIS -- Addressing patients’ health-related social needs such as housing instability, food insecurity, transportation barriers and financial strain is important to improving health outcomes yet can be challenging. A new study from Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University Indianapolis Richard M. Fairbanks School of Public Health investigates the best approach to predicting likely need for one or more health-related social need services.
To identify emergency department (E.D.) patients needing these services, researchers ...
Yo-yo dieting may significantly increase kidney disease risk in people with type 1 diabetes
2025-02-04
WASHINGTON—Body-weight cycling (also known as yo-yo dieting) has been shown to significantly increase the risk of kidney disease in people with type 1 diabetes, regardless of body mass index (BMI) and other traditional risk factors, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society’s Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Yo-yo dieting is defined as repeatedly losing and gaining weight multiple times over the years. Its prevalence is reported to be as high as 35% in men and 55% in women.
This patten of dieting has been shown to increase risks of cardiovascular events ...
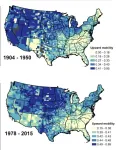
Big cities fuel inequality
2025-02-04
A study combining remote sensing and administrative data finds that since the mid-20th century, large, growing cities have ceased to be centers of upward social and economic mobility.
Cities have been celebrated as places of innovation and social mobility but also as hotspots of inequality and poverty. Dylan Shane Connor and colleagues measured how the size, density, and connectedness of urban areas in an American’s birth county predicted their social mobility across the 20th century. The results tell a tale of a waning relationship between ...
Financial comfort and prosociality
2025-02-04
People who feel financially comfortable are more likely to report prosocial actions like donating money and prosocial attitudes than people in a tough financial situation, according to a study. Prosociality—preferences and behaviors that benefit others—is essential to human society. In practice, it is determined by both the desire and the ability to help. Paul Vanags and colleagues analyzed data from the Global Preferences Survey and the Gallup World Poll, including 80,337 people in 76 countries with incomes ranging from about $200 a year to about $380,000 per year, adjusted to be equivalent across the different countries ...
Painted lady butterflies migrations and genetics
2025-02-04
A broadly distributed migratory butterfly travels varying distances, influenced by environmental conditions rather than following genetically coded instructions, according to a study. The Afro-Palearctic population of the painted lady butterfly, Vanessa cardui, is a single freely interbreeding, or ‘panmictic’ population.
Vanessa cardui is a renowned world traveler, undertaking multigenerational migrations throughout Africa, Asia, Europe, and North America. The winter breeding range of painted ladies in the Afro-Palearctic includes areas north and south of the Sahara ...
Globetrotting not in the genes
2025-02-04
Painted lady butterflies are world travelers. The ones we encounter in Europe fly from Africa to Sweden, ultimately returning to areas north and south of the Sahara. But what determines whether some butterflies travel long distances while others travel short distances? A group of scientists, including from the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA), shows that the different migration strategies are shaped by environmental conditions rather than being encoded in the butterfly’s DNA.
It is a warm summer day in June. A group of scientists with sunhats and nets is hiking along a trail in the Catalan mountains. They meticulously search for painted ladies—vibrant orange ...
Patient advocates from NCCN guidelines panels share their ‘united by unique’ stories for world cancer day
2025-02-04
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [February 4, 2025] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®) is joining people and organizations across the globe to commemorate World Cancer Day today. World Cancer Day is a global initiative to improve awareness and knowledge of cancer risks and actions for better prevention, detection, and treatment. It is led and organized by the Union of International Cancer Control (UICC) every February 4.
World Cancer Day 2025 marks the start of the ‘United by Unique’ campaign to highlight how every experience with cancer is unique, even as people touched by cancer ...
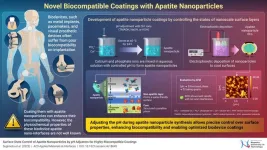
Innovative apatite nanoparticles for advancing the biocompatibility of implanted biodevices
2025-02-04
Medical implants have transformed healthcare, offering innovative solutions with advanced materials and technologies. However, many biomedical devices face challenges like insufficient cell adhesion, leading to inflammatory responses after their implantation in the body. Apatite coatings, particularly hydroxyapatite (HA)—a naturally occurring form of apatite found in bones, have been shown to promote better integration with surrounding tissues. However, the biocompatibility of artificially synthesized apatite nanoparticles often falls short of expectations, primarily due to the nanoparticles’ limited ability to bind effectively with biological tissues.
To overcome ...
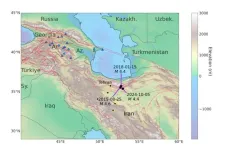
Study debunks nuclear test misinformation following 2024 Iran earthquake
2025-02-04
A new study debunks claims that a magnitude 4.5 earthquake in Iran was a covert nuclear weapons test, as widely alleged on social media and some mainstream news outlets in October 2024, a period of heightened geopolitical tensions in the Middle East.
Led by Johns Hopkins University scientists, the study warns about the potential consequences of mishandling and misinterpreting scientific information, particularly during periods of international conflict. The findings appear in the journal Seismica.
“There was a concerted misinformation and disinformation campaign around this event that promoted the idea this was a nuclear test, ...
Quantum machine offers peek into “dance” of cosmic bubbles
2025-02-04
Physicists have performed a groundbreaking simulation they say sheds new light on an elusive phenomenon that could determine the ultimate fate of the Universe.
Pioneering research in quantum field theory around 50 years ago proposed that the universe may be trapped in a false vacuum – meaning it appears stable but in fact could be on the verge of transitioning to an even more stable, true vacuum state. While this process could trigger a catastrophic change in the Universe's structure, experts agree that predicting the timeline ...
[1] ... [691]
[692]
[693]
[694]
[695]
[696]
[697]
[698]
699
[700]
[701]
[702]
[703]
[704]
[705]
[706]
[707]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.