Tracing gas adsorption on “crowns” of platinum and gold connected by nanotunnels
2025-02-08
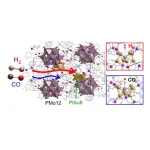
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have elucidated how hydrogen and carbon monoxide is adsorbed into solids containing a crown-motif structure of platinum and gold. Using quick-scan X-ray absorption measurements and theoretical calculations, they studied a solid of [PtAu8(PPh3)8]-H[PMo12O40] called PtAu8-PMo12 and found that gas adsorption is affected strongly by the dimension of nanoscale voids in the structure. This highlights the importance of engineering voids in materials for next generation sensors and gas separation.
Ligand-protected metal clusters have been a source of ...
Rare bird skull from the age of dinosaurs helps illuminate avian evolution
2025-02-08
A new study in Nature describing a fossil of a nearly complete and intact bird skull from Antarctica is shedding light on the early evolution of today’s birds and avian diversity at the end of the Age of Dinosaurs.
The skull is from Vegavis iaai, an extinct duck-like bird that lived during the Late Cretaceous, just before non-avian dinosaurs went extinct. It’s one of very few 3D bird skulls known to science from the Cretaceous — a 79-million-year geological period and the last era when ...
Researchers find high levels of the industrial chemical BTMPS in fentanyl
2025-02-08
A UCLA research team has found that drugs being sold as fentanyl contain high amounts of the industrial chemical bis(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidyl) sebacate, or BTMPS. This new substance of concern emerged in the illicit drug supply nearly simultaneously in multiple U.S. locations from coast-to-coast.
From June through October 2024, the team quantitatively tested samples of drugs sold as fentanyl that had high levels of the chemical, which belongs to a class of compounds called hindered amine light stabilizers ...
Decoding fat tissue
2025-02-08
As many as 40% of Americans are obese, putting them at an increased risk for high blood pressure, diabetes, stroke, heart disease and certain cancers, according to the CDC. New research from the University of Delaware aims to tackle the issue by investigating obesity at the gene level.
Principal investigator Ibra Fancher, assistant professor of kinesiology and applied physiology in UD’s College of Health Sciences, discovered significant differences in gene expression in adipose tissue, more commonly known as fat. Formerly considered fat storage, adipose tissue is now recognized as a vital ...
Solar and electric-powered homes feel the effects of blackouts differently, according to new research from Stevens
2025-02-08
Hoboken, N.J., February 7, 2025 — As winter storms and summer heat waves increasingly stress the nation’s power grids, Stevens researchers have developed a new way to identify the homes most vulnerable to blackouts — without even visiting them.
The timing couldn't be more critical. With more than a quarter of U.S. homes already fully electric, and solar installations set to triple during the next five years, understanding vulnerabilities has become critical for emergency planning and public safety.
"We're ...
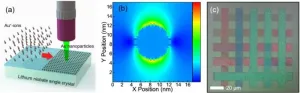
Metal ion implantation and laser direct writing dance together: constructing never-fading physical colors on lithium niobate crystals
2025-02-07
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2025.240193 , discusses a novel approach towards robust construction of physical colors on lithium niobate crystal.
Color has a profound impact on the way humans observe, perceive and understand the world. It is like a silent language, subtly shaping our perception and response to the surrounding environment. From the first ray of sunshine in the morning to the twinkling stars in the night sky, colors are everywhere. They are not only a visual ...
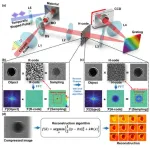
High-frequency enhanced ultrafast compressed photography technology (H-CAP) allows microscopic ultrafast movie to appear at a glance
2025-02-07
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2025.240180 , discusses high-frequency enhanced ultrafast compressed photography technology.
Single-shot ultrafast imaging technology can characterize transient events under a wide range of conditions. It opens the door to explore the unrepeatable or difficult to reproduce ultrafast phenomena such as photosynthesis at the molecular or atomic scale in nature and the precision manufacturing of semiconductor ...
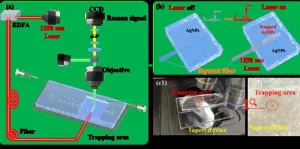
Single-beam optical trap-based surface-enhanced raman scattering optofluidic molecular fingerprint spectroscopy detection system
2025-02-07
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2025.240182 , discusses a single-beam optical trap-based surface-enhanced Raman scattering optofluidic molecular fingerprint spectroscopy detection system.
Raman spectroscopy is a non-destructive analytical technique that allows for precise analysis of substances based on their unique molecular Raman spectral characteristics. However, traditional Raman spectroscopy techniques suffer from weak signal intensity, limiting their sensitivity in high-sensitivity detection applications. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) technology, on the other hand, can amplify Raman signals by several million ...
Removing large brain artery clot, chased with clot-buster shot may improve stroke outcomes
2025-02-07
Research Highlights:
Stroke survivors were more likely to have little or no disability after 90 days if a clot was removed from a large brain artery followed by the injection of the clot-dissolving medication tenecteplase directly into the artery near the blockage, compared to people receiving standard medical treatment after clot removal. In this trial, standard care was clot removal without clot-dissolving medication.
The added treatment may work by dissolving blood clots in the small vessels (microcirculation) near the major blockage, reducing the amount of brain tissue deprived of blood.
The ANGEL-TNK trial found that this approach was ...
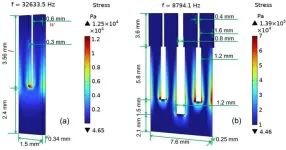
A highly sensitive laser gas sensor based on a four-prong quartz tuning fork
2025-02-07
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2025.240275, discusses A highly sensitive laser gas sensor based on a four-prong quartz tuning fork.
Trace gases, though have a volume fraction much less than 1% of the atmosphere, significantly impact various sectors. Despite their low concentration, typically between 10-12 to 10-6, gases like nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and greenhouse gases contribute to atmospheric pollution, a pressing global issue exacerbated by industrialization and urbanization. Moreover, detecting trace gases is crucial for industrial ...
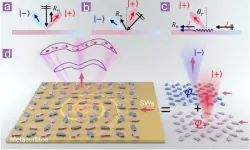
Generation of Terahertz complex vector light fields on a metasurface driven by surface waves
2025-02-07
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Sciences; DOI 10.29026/oes.2025.240024, discusses generation of terahertz complex vector light fields on a metasurface driven by surface waves.
With the rapid development of information and communication technologies, especially in the context of 5G, 6G networks, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things, the development of on-chip optical control devices with high bandwidth, high speed, low power consumption, and miniaturization ...
Clot-busting meds may be effective up to 24 hours after initial stroke symptoms
2025-02-07
Research Highlights:
In a randomized clinical trial in China, giving the clot-busting medication alteplase up to 24 hours after stroke symptoms first appeared increased the odds of better recovery by 50% compared to those who received standard antiplatelet treatment.
The results might extend the time window for patient treatment worldwide, particularly in regions that lack access to advanced medical procedures.
Note: The study featured in this news release is a research abstract. Abstracts presented at the American Heart ...
Texas Tech Lab plays key role in potential new pathway to fight viruses
2025-02-07
Five years removed from the COVID-19 outbreak, scientists around the world are still studying its effects and, more importantly, ways those effects can be mitigated in the future. An international team of researchers may have just found a critical clue in the quest, and a laboratory at Texas Tech University played a key role.
The Ray Laboratory, led by Department of Biological Sciences Professor and Associate Chair David Ray, as part of a study on bat genomes published by the scientific journal Nature, helped identify the components of a genome in a specific species of bats that have shown more genetic adaptations in their immune systems than other animals.
The study revealed that a gene ...
Multi-photon bionic skin realizes high-precision haptic visualization for reconstructive perception
2025-02-07
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2025.240152, discusses how multi-photon bionic skin realizes high-precision haptic visualization for reconstructive perception.
Human palm skin contains more than 20,000 tactile vesicles, depending on the tactile vesicles in the skin depth, activation threshold, trigger mode and other tactile signal pickup differences, as well as cross-synergistic mechanism between them, so that the skin can obtain different types of tactile signals. And then through the brain nerve center on the tactile signal “calculation” ...
Mitochondria may hold the key to curing diabetes
2025-02-07
Mitochondria are essential for generating energy that fuels cells and helps them function.
Mitochondrial defects, however, are associated with the development of diseases such as type 2 diabetes. Patients who suffer from this disorder are unable to produce enough insulin or use the insulin produced by their pancreas to keep their blood sugar at normal levels.
Several studies have shown that insulin-producing pancreatic β-cells of patients with diabetes have abnormal mitochondria and are unable to generate energy. Yet, these studies were unable to explain why the cells behaved this way.
In a study published in Science, ...
Researchers explore ketogenic diet’s effects on bipolar disorder among teenagers, young adults
2025-02-07
UCLA Health is set to begin a multi-site pilot study to explore whether a ketogenic diet, when combined with mood stabilizing medications, helps stabilize mood symptoms in teenagers and young adults who have bipolar disorder.
Preliminary research on the effects of a ketogenic diet in people with bipolar disorder have shown improvements in mood and in overall executive function, but these open trials have been limited to adults. This will be the first study conducted on the diet’s effects among youth and young adults with bipolar disorder.
Set ...
From muscle to memory: new research uses clues from the body to understand signaling in the brain
2025-02-07
Our biceps and our brain cells may have more in common than previously thought.
New research led by the Lippincott-Schwartz Lab shows that a network of subcellular structures similar to those responsible for propagating molecular signals that make muscles contract are also responsible for transmitting signals in the brain that may facilitate learning and memory.
“Einstein said that when he uses his brain, it is like he is using a muscle, and in that respect, there is some parallel here,” says Janelia Senior Group Leader Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz. “The same machinery is operating in both cases ...
New study uncovers key differences in allosteric regulation of cAMP receptor proteins in bacteria
2025-02-07
Washington, D.C. – A new study, “Identifying Allosteric Hotspots in Mycobacterium tuberculosis cAMP Receptor Protein” published in Biochemistry, provides key insights into how bacterial cAMP receptor proteins (CRPs) respond differently to the ubiquitous signaling molecule, cyclic AMP (cAMP). By comparing the allosteric regulation of Escherichia coli CRP (CRPEcoli) and Mycobacterium tuberculosis CRP (CRPMTB), researchers challenge the assumption that structural similarity predicts functional behavior in allosteric proteins.
This ...
Co-located cell types help drive aggressive brain tumors
2025-02-07
A type of aggressive, treatment-resistant brain tumor has a distinct population of immune cells that support its growth, according to new research led by investigators at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center Bloomberg~Kimmel Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy and the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
Searching for subtypes of immune cells seen only in the most serious, grade 4 brain tumors, called glioblastomas, and using a recently developed technology called spatial genomics, ...
Social media's double-edged sword: New study links both active and passive use to rising loneliness
2025-02-07
"The Epidemic of Loneliness: A Nine-Year Longitudinal Study of the Impact of Passive and Active Social Media Use on Loneliness" investigated how social media use impacts loneliness over time. This eye-opening research suggests that the very platforms designed to bring us together contribute to an "epidemic of loneliness."
The findings showed that both passive (PSMU) and active (ASMU) social media use were associated with increased feelings of loneliness over time. While passive social media use—like browsing without ...
An unexpected mechanism regulates the immune response during parasitic infections
2025-02-07
Researchers at the University of Liège (Belgium) have uncovered a previously unknown mechanism that regulates the immune response against parasites. During a parasitic infection, specific immune cells, known as virtual memory T cells (TVM), become activated and express a surface molecule called CD22, which prevents an excessive immune reaction. This discovery could help in better-controlling inflammation and improving immune responses to infections.
Nearly a quarter of the world's population ...
Scientists enhance understanding of dinoflagellate cyst dormancy
2025-02-07
Dinoflagellates play crucial roles in aquatic ecosystems, particularly as major contributors to harmful algal blooms. They can enter a dormant stage, known as the resting cyst stage, that allows them to survive for extended periods—up to 150 years—in marine sediments. This dormancy is essential for their annual population dynamics, blooming cycles, and geographic expansion.
Despite the ecological importance of resting cysts, the molecular mechanisms governing their dormancy, viability maintenance, and germination in natural sediments remain largely unexplored.
To better understand this process, researchers from the Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences ...
PREPSOIL promotes soil literacy through education
2025-02-07
One of the eight key aims of the EU Mission Soil is to enhance soil literacy in society. As part of this effort, the PREPSOIL project is working to inspire teachers across Europe to integrate soil topics into their teaching. By identifying and promoting innovative examples of soil education, PREPSOIL aims to empower educators to engage students in exploring the vital role of soil in natural, urban, and agricultural environments.
In 2023 and 2024, teachers were invited to submit their best practices in soil education targeting primary, secondary, and vocational students. The initiative received over 50 submissions, showcasing a variety of creative and interdisciplinary ...
nTIDE February 2025 Jobs Report: Labor force participation rate for people with disabilities hits an all-time high
2025-02-07
East Hanover, NJ – February 7, 2024 – The latest National Trends in Disability Employment (nTIDE) report revealed a record-breaking Labor Force Participation Rate for people with disabilities, marking an all-time high. These gains build upon a steady upward trend, which exceeded those seen among people without disabilities. nTIDE is issued by Kessler Foundation and the University of New Hampshire’s Institute on Disability (UNH-IOD).
Month-to-Month nTIDE Numbers (comparing December 2024 to January 2025)
Based on data from the ...
Temperamental stars are distorting our view of distant planets
2025-02-07
Most of the information we have about planets beyond our solar system (exoplanets) comes from looking at dips in starlight as these planets pass in front of their host star.
This technique can give clues about the planet’s size (by looking at how much starlight is blocked) and what its atmosphere is made of (by looking at how the planet changes the pattern of starlight that passes through it).
But a new study, published in The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, concluded that fluctuations in ...
[1] ... [683]
[684]
[685]
[686]
[687]
[688]
[689]
[690]
691
[692]
[693]
[694]
[695]
[696]
[697]
[698]
[699]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.