A new treatment for post-amputation pain?
2025-02-19
Procedure is simple and could be adopted by most U.S. hospitals
Roughly 2 million people in the U.S. live with limb loss; number is expected to rise
Senior author, a retired U.S. Army colonel, traveled to Ukraine to set up the study
CHICAGO --- A reliable method to treat post-amputation pain remains elusive, but a new Northwestern Medicine study conducted in collaboration with Ukrainian physicians suggests that hydrodissection — a simple procedure that injects fluid around nerves — may reduce residual limb pain and opioid dependence.
The ...
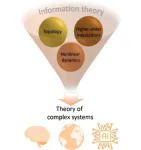
Groundbreaking study reveals how topology drives complexity in brain, climate, and AI
2025-02-19
(Embargo: 19 Feb, 10am GMT) A groundbreaking study led by Professor Ginestra Bianconi from Queen Mary University of London, in collaboration with international researchers, has unveiled a transformative framework for understanding complex systems. Published in Nature Physics, this pioneering study establishes the new field of higher-order topological dynamics, revealing how the hidden geometry of networks shapes everything from brain activity to artificial intelligence.
“Complex systems like the brain, climate, and next-generation artificial intelligence rely on interactions that extend beyond simple pairwise relationships. Our study reveals ...
Lifestyle and environmental factors affect health and ageing more than our genes
2025-02-19
A new study led by researchers from Oxford Population Health has shown that a range of environmental factors, including lifestyle (smoking and physical activity), and living conditions, have a greater impact on health and premature death than our genes.
The researchers used data from nearly half a million UK Biobank participants to assess the influence of 164 environmental factors and genetic risk scores for 22 major diseases on ageing, age-related diseases, and premature death. The study is published today in Nature Medicine.
Key findings
Environmental factors explained 17% of the variation in risk of death, compared to less than 2% explained by genetic predisposition (as ...
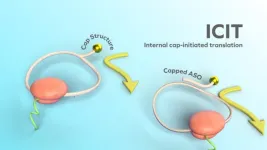
New mRNA produces 200 times more protein: Hope for treatment of cancer and protein disorders
2025-02-19
Imagine a breakthrough in cancer treatment where only malignant cells are targeted, sparing healthy host cells; or patients with abnormal protein synthesis are treated to produce a healthy protein. Hiroshi Abe and his colleagues at Nagoya University have identified two applications, among others, in a new study. Their innovative approach, reported in Nature Biotechnology, called the Internal Cap-Initiated Translation (ICIT) mechanism, introduces a novel way to 'switch on' protein synthesis ...
Magnetic semiconductor preserves 2D quantum properties in 3D material
2025-02-19
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — There is a big problem with quantum technology — it’s tiny. The distinctive properties that exist at the subatomic scale usually disappear at macroscopic scales, making it difficult to harness their superior sensing and communication capabilities for real-world applications, like optical systems and advanced computing. Now, however, an international team led by physicists at Penn State and Columbia University has developed a novel approach to maintain special quantum characteristics, even in three-dimensional (3D) materials.
The researchers published ...
Magnetic switch traps quantum information carriers in one dimension
2025-02-19
Illustration
A quantum "miracle material" could support magnetic switching, a team of researchers at the University of Regensburg and University of Michigan has shown.
This recently discovered capability could help enable applications in quantum computing, sensing and more. While earlier studies identified that quantum entities called excitons are sometimes effectively confined to a single line within the material chromium sulfide bromide, the new research provides a ...
Using light to activate treatments in the right place
2025-02-19
Acting in the right place at the right time is the key to effective medical treatment with minimal side effects. However, this feat remains difficult to achieve. Biologists and chemists at the University of Geneva (UNIGE) have succeeded in developing a tool that controls the location at which a molecule is activated by a simple pulse of light lasting only a few seconds. Tested on a protein essential for cell division, this system could be applied to other molecules. The potential applications are vast, both in basic research and in improving ...
Democracy in crisis: Trust in democratic institutions declining around the world
2025-02-19
New research from the University of Southampton has found that trust in representative institutions, such as parliaments, governments and political parties, has been declining in democratic countries around the world.
The study, published in The British Journal of Political Science, presents the largest and most comprehensive analysis of trends in political trust worldwide to date. It brings together results from 3,377 surveys covering 143 countries between 1958 and 2019, representing over five million survey respondents.
Whereas trust in representative institutions is generally in decline, trust in non-representative institutions ...
Finalists announced for the 2025 UK Blavatnik Awards for Young Scientists
2025-02-19
19 February 2025 – London – The Blavatnik Family Foundation and The New York Academy of Sciences today announced the Finalists for the eighth Blavatnik Awards for Young Scientists in the United Kingdom. The Awards recognise scientific advances by UK researchers across Life Sciences, Chemical Sciences, and Physical Sciences & Engineering.
On Wednesday, 4 March, Professor Shitij Kapur, FMedSci, Vice-Chancellor & President, King’s College London, will announce the three 2025 Laureates at a gala dinner and awards ceremony. The three Laureates will each receive an unrestricted award of £100,000 (US$126,000). ...
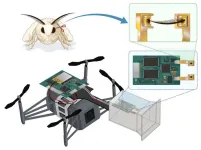
Bio-hybrid drone uses silkworm moth antennae to navigate using smell
2025-02-19
Conventional drones use visual sensors for navigation. However, environmental conditions like dampness, low light, and dust can hinder their effectiveness, limiting their use in disaster-stricken areas. Researchers from Japan have developed a novel bio-hybrid drone by combining robotic elements with odor-sensing antennae from silkworm moths. Their innovation, which integrates the agility and precision of robots with biological sensory mechanisms, can enhance the applicability of drones in navigation, gas sensing, and disaster response.
Technological advances have led to the development of drones with diverse applications, ...
Do seizures in newborns increase children’s risk of developing epilepsy?
2025-02-19
Seizures in newborns are one of the most frequent acute neurological conditions among infants admitted to neonatal care units. A study published in Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology indicates that newborns experiencing such neonatal seizures face an elevated risk of developing epilepsy.
For the study, investigators analyzed data on all children born in Denmark between 1997 and 2018, with the goal of comparing the risk of epilepsy in children with and without neonatal seizures.
Among 1,294,377 children, the researchers identified 1,998 who experienced neonatal seizures. The cumulative risk of epilepsy was 20.4% among children with neonatal seizures compared with 1.15% among children ...
Does the brain produce estrogen to control appetite?
2025-02-19
Although a woman’s ovaries produce the most estrogen, various types of estrogen are also synthesized throughout different tissues in the body, including the brain’s neurons. New research in The FEBS Journal indicates that such neuroestrogens help suppress appetite.
Knowing that the enzyme aromatase is important for the production of estrogens, investigators depleted or knocked out the gene encoding aromatase in mice, so that the animals were unable to synthesize estrogens in a systemic or body-wide manner. These mice demonstrated increased food intake and body weight compared with their aromatase-expressing counterparts. Restoring aromatase expression specifically ...
Would the prohibition of menthol cigarettes cause more harm than good?
2025-02-19
New research published in Health Economics indicates that a national prohibition of menthol cigarettes in the United States could increase the number of people who attempt to quit smoking but also support an illegal menthol cigarette market.
For the research, 639 adult menthol smokers made hypothetical choices between menthol and non-menthol cigarettes, menthol and non-menthol e-cigarettes, and attempting to quit. Participants were presented with situations where menthol cigarettes and menthol e-cigarettes were described as either legal, prohibited but available under-the-counter and online from retailers who continue ...
What are the benefits and harms of aggressive blood pressure lowering in older adults with different characteristics?
2025-02-19
Results from the Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) have supported lower blood pressure targets among community-dwelling older adults with hypertension to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and early death, but intensive blood pressure lowering can also increase risks of developing acute kidney injury and experiencing dangerously low blood pressure. A recent analysis in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society looked closely at the benefits and harms of intensive blood pressure lowering in patients with different characteristics.
The analysis found that nearly all older adults in SPRINT had a positive ...
Why is Japanese knotweed so highly invasive?
2025-02-19
Research published in New Phytologist provides insights into why the invasive plant Japanese knotweed is so successful at outcompeting native plants.
Japanese knotweed (Reynoutria japonica), which is native to eastern Asia and is a highly invasive plant species across Europe and North America, is known to damage infrastructure and ecosystems. By comparing growth and reproduction traits of introduced plants with native plants, investigators discovered that introduced plants had gained the ability to reproduce faster by clonal propagation, a method ...
How will China’s reformed standards strategy affect corporate labor employment?
2025-02-19
The Chinese government is phasing in reforms for many technical standards that shape the products and services used by consumers around the world. While China has primarily depended on unilateral government authority for developing its standard system, the reforms would also incorporate market economies. New research published in Contemporary Economic Policy examined the impact of these reforms on corporate labor employment.
The study’s findings indicate that comprehensive standardization reform facilitates an increase in corporate labor employment by reducing transaction costs, enhancing operational efficiency, and improving the financing environment. The most profound impacts ...
Make America Healthy Again agenda at risk with reduction in force across federal health agencies
2025-02-19
Staffing reductions across U.S. federal health agencies—including the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Food and Drug Administration (FDA), National Institutes of Health (NIH), and Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ)—pose a significant threat to public health, according to the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA). The dismissal of thousands of staff is a massive loss of expertise and interruption ...
Revolutionizing energy-efficient smart windows: A flexible dual-band electrochromic device with energy storage
2025-02-19
As global energy consumption continues to rise, buildings account for approximately 40% of total energy use, with nearly half of that dedicated to indoor thermal regulation (heating and cooling). Windows, being the primary pathway for energy exchange between the interior and exterior of buildings, contribute to 20-40% of energy loss. Developing energy-efficient smart windows that reduce energy consumption while maintaining natural lighting and aesthetic appeal has become a key strategy in sustainable building development.
Researchers from Nanjing University of ...
Using a data-driven approach to synthesize single-atom catalysts that can purify water
2025-02-19
All humans need clean water to live. However, purifying water can be energy-intensive, so there is great interest in improving this process. Researchers at Tohoku University have reported a strategy using data-driven predictions coupled with precise synthesis to accelerate the development of single-atom catalysts (SACs) for more robust and efficient water purification.
SACs are one of the most crucial catalysts. They play a pivotal role in enhancing efficiency in diverse applications including chemical industries, energy conversion, and environmental processes. ...
Repeated invasions shape NZ’s bird life
2025-02-19
New University of Otago – Ōtākou Whakaihu Waka research shows Aotearoa has been increasingly accepting new bird species from around the world since the start of the Ice Age, offering clues into future migration patterns.
Since the Ice Age drastically changed the Aotearoa landscape from widely forested to grass and shrubland, researchers set out to determine which of our living and recently extinct birds are a result of existing lineages that adapted to their environment tens of millions of years ago and which are the descendants of comparatively recent invaders.
Using mitogenome data from nearly all living and recently extinct New Zealand mainland bird species, researchers ...
Wild fish can recognize individual divers
2025-02-19
For years, scientific divers at a research station in the Mediterranean Sea had a problem: at some point in every field season, local fish would follow them and steal food intended as experimental rewards. Intriguingly these wild fish appeared to recognize the specific diver who had previously carried food, choosing to follow only them while ignoring other divers. To find out if that was true, a team from the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior (MPI-AB) in Germany conducted a series of experiments while wearing a range of diving gear, finding ...
New therapy reduces reoffending in male offenders with antisocial personality disorder
2025-02-19
A new psychological therapy designed by a team of UCL-led researchers has been found to reduce rates of violence and aggression among male offenders with antisocial personality disorder (ASPD).
The study, published in The Lancet Psychiatry and funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR), investigated whether aggression and antisocial behaviours could be improved by a modified form of mentalisation-based treatment (MBT).
Mentalisation-based treatment is a type of therapy that helps people to understand their own thoughts and feelings, ...
We are no longer living longer, UEA study shows
2025-02-19
The rise in human life expectancy has slowed down across Europe since 2011, according to research from the University of East Anglia and partners.
A new study, published today in The Lancet Public Health, reveals that the food we eat, physical inactivity and obesity are largely to blame, as well as the Covid pandemic.
Of all the countries studied, England experienced the biggest slowdown in life expectancy.
It means that rather than looking forward to living longer than our parents or grandparents, ...
Study on new telerehabilitation stroke therapy model led by UTHealth Houston for underserved community in the Texas Rio Grande Valley
2025-02-18
A new at-home telerehabilitation care service for stroke patients will be offered to residents of Cameron County in the Rio Grande Valley as part of a randomized clinical trial led by researchers from across UTHealth Houston.
Investigators from UTHealth Houston School of Public Health in Brownsville, UTHealth Houston Institute for Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases, and McWilliams School of Biomedical Informatics at UTHealth Houston will create and test software delivered through a website to patients who have recently ...
Study reveals genes that may help predict prostate cancer outcomes
2025-02-18
A recent study published in the Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology explored genetic predictors of prostate cancer progression to help identify its clinical outcomes. Conducted by researchers from the D’Or Institute for Research and Education (IDOR), the University of São Paulo (USP), and the São Paulo Cancer Institute (ICESP), the study focused on the role of the androgen receptor (AR), its variant AR-V7, and the p160 gene family.
Prostate cancer: a complex and deadly disease
Prostate cancer is one of the leading causes of death among ...
[1] ... [679]
[680]
[681]
[682]
[683]
[684]
[685]
[686]
687
[688]
[689]
[690]
[691]
[692]
[693]
[694]
[695]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.