Why we need to expand the search for climate-friendly microalgae
2025-02-12
New research has highlighted microalgae’s capacity as a solution in the fight against climate change, but researchers warn that “smart microalgal bioprospecting” is needed to unlock its full potential.
The study highlights the vast, largely unexplored capacity of microalgae to mitigate CO2 emissions while driving sustainable industry.
“Microalgae have remarkable properties that make them an ideal tool for tackling climate change,” said lead author, PhD candidate Joan Labara Tirado from the University of Technology Sydney (UTS).
The review paper, The need for smart microalgal bioprospecting was ...
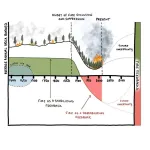
Fewer forest fires burn in North America today than in the past—and that's a bad thing
2025-02-12
Fewer wildfires burn in North American forests today than in previous centuries, increasing the risk of more severe wildfires, according to research published this week in Nature Communications. The findings may seem counterintuitive, but frequent low-lying surface fires often maintain balance in forests by reducing fuel sources across large areas.
The new study led by the Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences (CIRES) at the University of Colorado Boulder and the U.S. Forest Service’s Rocky Mountain Research Station ...
Older people in England are happier now than before the COVID pandemic, new national study suggests
2025-02-12
Older people have greater general happiness, life satisfaction and sense of purpose than they did before the Covid-19 pandemic.
That’s according to a new study which tracked 3,999 over 50s in England for 11 years, published today in the peer-reviewed journal, Aging and Mental Health.
Analysing data to understand positive psychological well-being and depression within this group, an expert team from UCL (University College London), funded by the National Institute of Ageing, a consortium of UK government departments coordinated by the National Institute ...
Texas A&M chemist wins NSF CAREER Award
2025-02-11
Dr. Alison Altman, an assistant professor in the Texas A&M Chemistry Department, has received a National Science Foundation (NSF) CAREER Award, which supports early-career faculty in research and education. The award recognizes her work on underexplored elements of the periodic table and her dedication to teaching. For Altman, it’s a launchpad for future discoveries.
“It’s an honor to receive this award, as it acknowledges not just my research program but also my teaching efforts,” ...
Micro-nano plastics make other pollutants more dangerous to plants and intestinal cells
2025-02-11
Micro- and nanoscale plastic particles in soil and water can significantly increase how much toxic chemicals plants and human intestinal cells absorb, according to two new studies from Rutgers Health that raise fresh concerns about food safety from plastic pollution.
The first study in NanoImpact found that lettuce exposed to both nanoscale plastic particles and common environmental pollutants such as arsenic took up substantially more of the toxic substances than plants exposed to the pollutants, alone confirming the risks of polycontamination of our food chain. A companion study in Microplastics journal showed ...
Study of female genital tract reveals key findings
2025-02-11
Seeking to understand what constitutes a healthy vaginal microbiome, a global research collaboration that includes a Rutgers-New Brunswick scientist has reported a series of findings, including identifying which bacteria thwart vaginal disease and determining that microbiomes vary significantly across human populations.
Authors of the study, published in Trends in Microbiology, are part of a Belgium-based initiative called the Isala Sisterhood. Members of the group aim to inspire research on microbiomes worldwide by creating a “reference map” of vaginal microbiota. Launched in 2020 at the University of Antwerp, the project has expanded to include more than 3,000 ...
Pitt Engineering Professor Fang Peng elected to National Academy of Engineering
2025-02-11
The National Academy of Engineering (NAE) today announced that University of Pittsburgh Professor Fang Peng, an internationally acclaimed power electronics researcher, is among the newest cohort elected to the academy. The NAE is recognizing Peng for “contributions to the development of high-powered electronic technologies for advanced power grid and energy conversion.”
Peng, the RK Mellon Endowed Chair Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering and Director of the Energy GRID Institute at Pitt’s Swanson School of Engineering, ...
Short-course radiation therapy effective for endometrial cancer patients
2025-02-11
In a randomized clinical trial, researchers from Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah (the U) have found that short-course, higher dose vaginal brachytherapy for endometrial cancer had similar effectiveness to more frequent, lower dose sessions.
Gita Suneja, MD, MS, physician-scientist at Huntsman Cancer Institute and professor of radiation oncology at the U, is the first author of the SAVE trial report—which stands for, Short-Course Adjuvant Vaginal Cuff Brachytherapy in Early Endometrial Cancer Compared with Standard of Care.
“There ...
Breast cancer treatment advances with light-activated ‘smart bomb’
2025-02-11
Scientists have developed new light-sensitive chemicals that can radically improve the treatment of aggressive cancers with minimal side effects. In mouse tests, the new therapy completely eradicated metastatic breast cancer tumors.
The novel chemicals, called cyanine-carborane salts, and their role in the next-generation of cancer treatments, are described in a new article published in Angewandte Chemie, a journal of the German Chemical Society.
Photodynamic therapy, or PDT, has been used for decades to treat forms of skin and bladder cancers. It works by flooding a patient’s body with light-sensitive chemicals that accumulate in cancer cells. ...
JSCAI article at THT 2025 sets the standard for training pathways in interventional heart failure
2025-02-11
WASHINGTON–Interventional heart failure (IHF) has rapidly evolved as a critical subspecialty within cardiology at the crossroads of advanced heart failure and interventional cardiology. The increasing complexity of patient care—spanning both pharmacological treatments and an expanding array of device-based therapies—has underscored the urgent need for a standardized approach to training and career development in this field.
That’s the message from experts in a comprehensive review, “Charting the Course for Careers in Interventional Heart ...
Engineering biological reaction crucibles to rapidly produce proteins
2025-02-11
Biomedical engineers at Duke University have demonstrated a new synthetic approach that turbocharges bacteria into producing more of a specific protein, even proteins that would normally destroy them, such as antibiotics.
The technique directs bacteria to produce synthetic disordered proteins that bunch together to form compartments called biological condensates. When these compartments trap mRNA carrying instructions for specific proteins together with the machinery needed to implement them, they can greatly enhance the rate of protein production.
The technique could be a boon to industries that use bacteria to produce a wide range of products such as pharmaceuticals, ...
Minecraft: a gamechanger for children’s learning
2025-02-11
It’s the globally popular video game that’s captured the attention of more than 141 million active players, but Minecraft can also play a significant role in shaping children’s development, social interactions, and cognitive learning, say researchers at the University of South Australia.
Published in the new book Children’s online learning and interaction, the study found that when children engage in collaborative Minecraft play, they foster teamwork, communication, and social skills as players exchange ideas and problem-solve ...
Presidential awards spotlight naval research excellence
2025-02-11
WASHINGTON, D.C. – An alternative energy mechanical engineer, two aerospace engineers, and a corrosion research engineer received the highest honor bestowed to early career U.S. government scientists and engineers.
These four U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) researchers each received a Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers (PECASE) for their research on next generation energy storage solutions, solid fuel combustion for use in high-speed propulsion devices, solving large-scale ...
SETI Institute names first Frank Drake Postdoctoral Fellow
2025-02-11
February 11, 2025, Mountain View, CA -- The SETI Institute awarded the first Frank Drake Postdoctoral Fellowship to Dr. Anastasia Yanchilina. Yanchilina will focus on distinguishing biosignatures from false positives across space and time. Her research combines experimental and analytical research to refine biosignature detection techniques. She will conduct lab experiments to generate key mineral analogs and study Earth’s extreme environments to understand what potential signs of life to look for on other planets.
“It has long been my scientific dream to explore whether life exists ...
From photons to protons: Argonne team makes breakthrough in high-energy particle detection
2025-02-11
Particle detectors play a crucial role in our understanding of the fundamental building blocks of the universe. They allow scientists to study the behavior and properties of the particles produced in high-energy collisions. Such particles are boosted to near the speed of light in large accelerators and then smashed into targets or other particles where they are then analyzed with detectors. Traditional detectors, however, lack the needed sensitivity and precision for certain types of research.
Researchers at the U.S. Department of ...
Cancer’s ripple effect may promote blood clot formation in the lungs
2025-02-11
Blood clots form in response to signals from the lungs of cancer patients—not from other organ sites, as previously thought—according to a preclinical study by Weill Cornell Medicine, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center and University of California San Diego Health. Clots are the second-leading cause of death among cancer patients with advanced disease or aggressive tumors.
While blood clots usually form to stop a wound from bleeding, cancer patients can form clots without injury, plugging up vessels and cutting off circulation to organs. The study, published Feb. 11 in Cell, shows that tumors drive clot formation (thrombosis) by releasing ...
New UVA clinical trial explores AI-powered insulin delivery for better diabetes care
2025-02-11
For people living with Type 1 Diabetes (T1D), keeping blood sugar levels in check is a constant challenge. A new clinical trial at UVA is aiming to simplify diabetes management by testing an innovative AI-powered device designed to improve automated insulin delivery.
The trial is co-led by several School of Data Science faculty, including Assistant Professor of Data Science Heman Shakeri; Boris Kovatchev, founding director of the UVA Center for Diabetes Technology, a professor at the School of Medicine and professor ...
New technology could quash QR code phishing attacks
2025-02-11
The ubiquitous QR (“quick response”) codes that appear on everything from parking pay stations to soda cans and promotional flyers have become an increasingly popular target for cybercriminals to exploit through QR code–based phishing attacks, also known as “quishing.” Bad actors will place phony QR codes that direct smartphone users to enter their sensitive private information in fake websites masquerading as bank websites, parking enforcement offices, or other seemingly ...
Study reveals direct gut-brain communication via vagus nerve
2025-02-11
A new study in an animal model provides direct evidence for the role of the vagus nerve in gut microbiome-brain communication, addressing a critical gap in the field.
The research, led by Kelly G. Jameson while a PhD student in the Hsiao Lab at UCLA, demonstrates a clear causal relationship between gut microbiota and vagal nerve activity.
While the vagus nerve has long been thought to facilitate communication between the gut microbiome—the community of microorganisms living in the intestines—and the brain, direct evidence for this process ...
MSU expert: Using light to hear biology
2025-02-11
Images
Elad Harel is used to shining a light on the mysteries of the natural world.
Working at the cutting-edge of ultrafast spectroscopy — the application of short laser pulses to analyze the dynamics of molecules — the Michigan State University associate professor’s research aims to reveal how microscopic phenomena impact large complex systems.
One promising frontier Harel has been working on is the development of new methods of microscopy that will allow researchers to observe molecular and atomic landscapes in motion rather than through static imagery. Such work has earned Harel MSU’s 2023 ...
“I can’t hear you, I’m too stressed”: Repeated stress in mice reduces sound perception
2025-02-11
After a week of stress, mice show changes in how their brains process sound, reducing how well they perceive loud noises, according to a study published February 11th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology led by Ghattas Bisharat, from the Ben-Gurion University of the Negev in Israel, and colleagues.
Repeated stress has negative impacts on mental health that can go beyond psychiatric disorders. They can also cause changes in how we perceive the world, making us jump at loud noises, or become easily irritated by scratchy sweaters or offensive odors. To understand how repeated stress can impact how the brain processes sensory information, the authors ...
Chronic stress affects how brain processes sound in mice
2025-02-11
BEER-SHEVA, Israel, February 11, 2025 – Chronic stress changes the way our brain processes sounds, according to new research conducted on mice at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev. For instance, sounds need to be louder during chronic stress to trigger similar responses.
Chronic stress is known to impact learning and decision-making, but could it also affect how we hear? Dr. Jennifer Resnik from Ben-Gurion University’s Department of Life Sciences set out to find whether stress influences basic brain functions, ...
Insilico Medicine announces developmental candidate benchmarks and timelines for novel therapeutics discovered using generative AI
2025-02-11
Cambridge, MA – Insilico Medicine ( “Insilico”) , a clinical stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven biotechnology company today announced a set of preclinical drug discovery benchmarks from the 22 developmental candidate nominations achieved by its platform from 2021 to 2024. These benchmarks underscore the platform's efficiency and represent a potential new standard for the drug discovery industry by significantly reducing developmental times, cost, and by allowing resources to be redirected toward further ...
A wealth of evidence: PIK compiles 85,000 individual studies about climate policy
2025-02-11
“Rather than directly providing answers to questions about the effects of climate policies, this study displays an overview of what has actually been scientifically studied so far,” explains Max Callaghan, PIK researcher and lead author of the study. “On the one hand, this informs existing gaps and thus directions for primary research, including through funding. On the other hand, this overview facilitates evidence synthesis work, i.e. the summarisation of the state of knowledge for governments, for example in the IPCC Assessment Reports.”
The study shows, among other ...
New fish species with ‘face paint’ named after Studio Ghibli character
2025-02-11
Researchers in China have named a newly discovered fish species after the Studio Ghibli character San from Princess Mononoke based on its similar facial markings.
Published in the open-access journal ZooKeys, Branchiostegus sanae is a deepwater tilefish belonging to the family Branchiostegidae. It was discovered when scientists noticed unique cheek pattern on some deepwater tilefish individuals in online seafood markets.
The research team used genetic analysis to confirm the new-species status of the fish, and were inspired by its facial stripes to name it after the female protagonist, San, from Hayao Miyazaki’s animated film Princess Mononoke, choosing “sanae” ...
[1] ... [678]
[679]
[680]
[681]
[682]
[683]
[684]
[685]
686
[687]
[688]
[689]
[690]
[691]
[692]
[693]
[694]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.