RealtyMX Enters the Mobile App World With Taap.it Mobile Marketplace
2011-09-16
Taap.it Mobile Marketplace solidifies itself as the go-to app for real estate in NYC through a strategic partnership with RealtyMX, the complete marketing management system for real estate brokers and agents looking to successfully grow their online marketing efforts. The partnership provides a tool for RealtyMX and its clients to saturate the rapidly growing mobile commerce market. "RealtyMX identified mCommerce as a growing force in the real estate industry and we can provide the platform they need to leverage that space. It is growing at an exponential rate." ...
Genomic catastrophe causes developmental delay, cognitive disorders
2011-09-16
HOUSTON -- (Sept. 16, 2011) – Using a diversity of DNA sequencing and human genome analytic techniques, researchers led by Baylor College of Medicine have identified some cases of developmental delay or cognitive disorders associated with a sudden chromosomal catastrophe that occurred early in development, perhaps during cell division when DNA is replicated.
In a report in the journal Cell, Dr. Weimin Bi, assistant professor of molecular and human genetics, Dr. James R.Lupski, vice chair of molecular and human genetics, both at BCM, first author Pengfei Liu, a graduate ...
Mom, dad and kids undergo novel genome analyses for medical risks in new Stanford study
2011-09-16
STANFORD, Calif. — Stanford University School of Medicine researchers have predicted the inherited health risks of a four-person family by analyzing their whole genome sequences. With the DNA sequences of both parents and children, the team was able to better check for sequencing errors and more accurately predict how individual genetic variants affect each family member's risk for disease.
The project improved computational tools that provide medical interpretation of genomes, which includes disease-risk prediction and how an individual would respond to common medications. ...
agoda.com Partners with Channel Manager Hotel Net Solutions
2011-09-16
agoda.com, Asia's global hotel booking site and part of Nasdaq-listed Priceline Group (Nasdaq: PCLN), today announced a partnership with European channel manager Hotel Net Solutions.
Germany-based company Hotel Net Solutions provides online inventory management tools to more than 250 hotel clients across Europe. As a result of the partnership, these properties can quickly and easily connect to agoda.com and distribute their inventory worldwide in 37 languages.
A trusted brand within Asia, agoda.com connects hotels with hard-to-reach non-English-speaking demographics. ...
Chronic drinking leads to reduced cortical thickness in frontal and temporal brain regions
2011-09-16
Contact: Catherine Brawn Fortier, Ph.D.
catherine_fortier@hms.harvard.edu
857.364.4361
Harvard Medical School
Terence M. Keane, Ph.D.
terry.keane@va.gov
857.364.4551
VA Boston Healthcare System & Harvard Medical School
Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research
Chronic drinking leads to reduced cortical thickness in frontal and temporal brain regions
Researchers already know that chronic misuse of alcohol can cause widespread damage to the brain. While previous studies examined cortical atrophy in individuals with alcoholism, none examined alcohol-associated ...
AsiaRooms.com - Witness Natural Wonder of Naga Fireballs in Thailand
2011-09-16
The Nong Khai region of Thailand will see the occurrence of a mysterious phenomenon known as the Naga Fireballs next month.
Expected to take place between October 11th and 12th this year, the unusual natural event sees a series of ruby-coloured orbs of light emerging from the Mekong River, floating silently into the air before disappearing into the night sky.
Usually occurring between 18:00 and 21:00 local time, as many as 19 fireballs at a time can linger in the air for up to eight seconds, with almost 3,500 globes having been counted in 1999.
Debate rages ...
Alcohol metabolism causes DNA damage and triggers a breast cancer-related DNA damage response
2011-09-16
Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research
Alcohol metabolism causes DNA damage and triggers a breast cancer-related DNA damage response
Alcohol is known to be carcinogenic to humans in the upper aerodigestive tract, liver, colorectum, and the female breast. Evidence suggests that acetaldehyde, the primary metabolite of alcohol, plays a major role in alcohol-related esophageal cancer. A new study using human cells has established linkages between alcohol metabolism and acetaldehyde-DNA damage that may have implications for breast and liver cancers.
Results will ...
People born after World War II are more likely to binge drink, develop alcohol disorders
2011-09-16
Contact: Katherine M. Keyes, Ph.D.
kmk2104@columbia.edu
212-543-5002
Columbia University
Richard A. Grucza, Ph. D., M.P.E.
rick@wustl.edu
314-362-6535
Washington University School of Medicine
Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research
People born after World War II are more likely to binge drink, develop alcohol disorders
Drinking can be influenced by both personal and societal factors, the latter leading to “drinking cultures.”
Researchers have completed a review of 31 studies on birth-cohort and gender differences in drinking.
Analysis shows that people ...
AsiaRooms.com - Malaysia to Host Cat City International Cat Show 2011
2011-09-16
Cat fanciers visiting Malaysia may wish to get involved in the excitement of the Cat City International Cat Show 2011, which is being held in Sarawak next month.
The fourth edition of the annual event is organised by the Sarawak Cat Club and will be taking place at the Kuching Civic Centre on October 15th this year, providing an opportunity for pedigree and household felines to show off their credentials.
Pets will be judged in accordance with Cat Fanciers' Association rules, meaning participating cats can expect to be evaluated based on their uniqueness, unusual ...
Damaged gait and balance can recover with long-term abstinence from alcohol
2011-09-16
Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research
Damaged gait and balance can recover with long-term abstinence from alcohol
Chronic alcoholism is often associated with a disturbed gait and balance, likely caused by alcohol damage to neural systems. While some studies have suggested that abstinence can lead to partial recovery of gait and balance functions, questions remain about duration of abstinence and sample size. This study of both short- and long-term abstinence has found that alcoholics' gait and balance can continue to recover with long-term abstinence from alcohol ...
Heavy drinkers may die needlessly in house fires
2011-09-16
PISCATAWAY, NJ – People who drink heavily may increase their risk of dying in house fires that should otherwise have been escapable, a new study suggests.
The findings, reported in the September issue of the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, highlight one of the less-recognized dangers of downing too much alcohol -- especially in combination with smoking.
Looking at coroners' records for 95 fire victims, Australian researchers found that 58% had positive results on blood alcohol tests, often with very high alcohol levels. And those intoxicated victims ...
AsiaRooms.com - Owl City to Perform in Seoul in October
2011-09-16
Popular US music act Owl City, otherwise known as Adam Young, will be performing to audiences in Seoul as part of his global tour next month.
The singer-songwriter and multi-instrumental performer will be playing to crowds at the AX Hall venue on October 24th, beginning at 20:30 local time.
A native of Minnesota, Young has been performing as Owl City for a number of years, but only hit the big time in 2009 with the release of his major label debut album Ocean Eyes.
The record spawned the quadruple-platinum single Fireflies, which topped the charts in 24 countries, ...
In rapidly warming seas, some fish lose while others gain
2011-09-16
Rising temperatures in the northeast Atlantic Ocean have already led to major shifts in the abundance of commercially important fish stocks. That's according to a report published online on September 15 in Current Biology, a Cell Press publication, that is the first to consider the absolute abundance of species as opposed to their presence or absence alone.
"We see many more southerly, warm-water species faring well on the European shelf than more northerly, cold-adapted species," said Stephen Simpson of the University of Bristol. "This means more small-bodied, faster-growing ...
New insight into immune tolerance furthers understanding of autoimmune disease
2011-09-16
It is no easy task to preserve the delicate balance that allows us to maintain a strong immune system that can defend us from harmful pathogens, but that is sensitive enough to correctly identify and spare our own cells. Therefore, it is not surprising that the mechanisms that underlie immune activation and tolerance are not completely understood. Now, a new research study published by Cell Press in the journal Immunity and available online on September 15th provides intriguing insight into the complex immune regulatory mechanisms that underlie immune tolerance.
Cells ...
LateRooms.com - Bob Dylan and Mark Knopfler to Perform in Paris
2011-09-16
Veteran singer-songwriters Mark Knopfler and Bob Dylan are heading to Paris next month for a show at the city's Bercy venue.
Former Dire Straits frontman Knopfler is supporting Dylan on his current European tour, which is due to call at the French capital on Monday October 17th.
The two performers are set to play at cities across the continent during the run of gigs, which will get underway in Dublin on Sunday October 6th and finish in Zurich on Wednesday November 16th.
Dylan is widely considered to be one of the most influential figures in popular music and ...
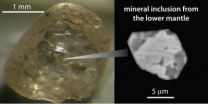
Journey to the lower mantle and back
2011-09-16
The theory of plate tectonics is at the centre of our understanding of how the Earth works. It has been known for decades that new crust is formed at mid-ocean ridges and that this crust is subducted as plates dive underneath other plates in regions such as the Pacific Ring of Fire and descend into the Earth's mantle. What is not so well known is the fate of these subducted plates.
In this week's edition of the journal Science, scientists from the University of Bristol (Prof. M. Walter, Dr. S. Kohn, Dr. G. Bulanova, Mr. C. Smith), Universidade de Brasilia (Prof. D. Araujo), ...
Diamonds show depth extent of Earth's carbon cycle
2011-09-16
Washington, D.C.—Scientists have speculated for some time that the Earth's carbon cycle extends deep into the planet's interior, but until now there has been no direct evidence. The mantle–Earth's thickest layer –is largely inaccessible. A team of researchers analyzed diamonds that originated from the lower mantle at depths of 435 miles (700 kilometers) or more, and erupted to the surface in volcanic rocks called kimberlites. The diamonds contain what are impurities to the gemologist, but are known as mineral inclusions to the geologist. Analysis shows compositions consistent ...
Carbon cycle reaches Earth's lower mantle, Science study reports
2011-09-16
The carbon cycle, upon which most living things depend, reaches much deeper into the Earth than generally supposed—all the way to the lower mantle, researchers report.
The findings, which are based on the chemistry of an unusual set of Brazilian diamonds, will be published online by the journal Science, at the Science Express Web site, on 15 September. Science is published by AAAS, the non-profit, international science society.
"This study shows the extent of Earth's carbon cycle on the scale of the entire planet, connecting the chemical and biological processes that ...
LateRooms.com - See Dennis Taylor at A Question of Sport Live in Glasgow
2011-09-16
Snooker, rugby, football and cricket fans will be well served by the upcoming A Question of Sport Live show in Glasgow.
Quizmaster Sue Barker and captains Phil Tufnell and Matt Dawson are set to be joined onstage at the event by special guests Dennis Taylor, Chris Cusiter and Anthony Stokes.
Former World Snooker champion Taylor spent two decades in the top 16 of the rankings and was also a huge hit with fans of the sport. Since retiring, he has become an important part of the BBC commentary team for live snooker coverage.
Celtic striker Stokes, who began his ...
LateRooms.com - British Rockers Mogwai to Play in Barcelona Next Month
2011-09-16
Fans of the British rock group Mogwai will be descending on Barcelona next month to see the band perform as part of their global tour.
The Scottish musicians will be putting on a show at the Casino L'Alianca Del Poblenou on October 28th, with proceedings to get underway at 20:00 local time.
Mogwai have been playing together since the mid-1990s and are a five-piece act fronted by Stuart Braithwaite, with the band having won acclaim for their innovative musical stylings.
Having recorded six previous studio albums and worked on the soundtrack for Darren Aronofsky's ...
Scripps Research team discovers treatable mechanism responsible for often deadly response to flu
2011-09-16
VIDEO:
Scripps Research Institute Professors Hugh Rosen and Michael Oldstone discuss their recent findings pinpointing the cells that orchestrate a dangerous immune reaction called "cytokine storms, " opening up entirely new possibilities...
Click here for more information.
LA JOLLA, CA – September 15, 2011 – Researchers at The Scripps Research Institute have found a novel mechanism by which certain viruses such as influenza trigger a type of immune reaction that ...
LateRooms.com - Enjoy Memorable Sights at Berlin Festival of Lights
2011-09-16
Visitors to Berlin next month will be able to enjoy a colourful spectacle when the seventh annual Festival of Lights commences in the German capital next month.
Taking place between October 12th and 23rd 2011, the event will see more than 50 of the city's most famous landmarks and public spaces brightened up with illuminations and projections.
Among the locations that will be lit up are the Brandenburg Gate, Berlin Cathedral and the radio tower, while the Europa-Center and Kaiser Wilhelm Memorial Church will also be involved for the first time.
The festival ...
CycleHarmony.com Announces Release of Mood, PMS Symptom & Lifestyle Tracker
2011-09-16
Most people know that unhealthy lifestyles are the cause of many of their personal challenges in life, from being overweight to chronic fatigue to PMS/PMDD symptoms, just to name a few - challenges which can determine the very quality of their lives.
Yet few succeed in breaking free of these unhealthy lifestyles. Why?
According to Jing Jin, the founder of cycleharmony.com, "It's because they've taken on an impossible task. An unhealthy lifestyle is almost impossible to break because it takes vigilance and an energy that few of us have. Think about the chocoholic ...
Black-white marriages increased rapidly since 1980, study finds
2011-09-16
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new study of interracial marriages in the United States since the 1980s suggests that the racial boundary between blacks and whites continues to break down – but is not yet close to disappearing.
Marriages between African Americans and whites increased rapidly between 1980 and 2008, outpacing the rate of unions between whites and other ethnic and racial groups, including Latinos, Asian Americans and American Indians.
Still, the total number of marriages between blacks and whites continues to be much smaller than those between whites and other racial ...
Avoiding fatal responses to flu infection
2011-09-16
Most of the time, being ill with the flu is little more than a nuisance. Other times, it can spark an exaggerated immune response and turn deadly. Researchers reporting in the September 16th issue of the journal Cell, a Cell Press publication, have now traced the origins of this severe immune response -- called a cytokine storm -- to its source.
Cytokines are the chemical signals that drive inflammation, and cytokine storms are thought to be the cause of many of the deaths attributed to the 1918 worldwide influenza pandemic and to the more recent outbreaks of swine ...
[1] ... [6929]
[6930]
[6931]
[6932]
[6933]
[6934]
[6935]
[6936]
6937
[6938]
[6939]
[6940]
[6941]
[6942]
[6943]
[6944]
[6945]
... [8798]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.