New study uncovers key mechanism behind learning and memory
2025-01-21
AURORA, Colo. (Jan. 22, 2025) – A breakthrough study published today in the Journal of Neuroscience sheds new light on how brain cells relay critical information from their extremities to their nucleus, leading to the activation of genes essential for learning and memory.
Researchers have identified a key pathway that links how neurons send signals to each other, or synaptic activity, to the expression of genes necessary for long-term changes in the brain, providing crucial insights into the molecular processes underlying memory formation.
“These findings illuminate ...
Seeing the unseen: New method reveals ’hyperaccessible’ window in freshly replicated DNA
2025-01-21
San Francisco—January 21, 2025—DNA replication is happening continuously throughout the body, as many as trillions of times per day. Whenever a cell divides—whether to repair damaged tissue, replace old cells, or simply to help the body grow—DNA is copied to ensure the new cells carry the same genetic instructions.
But this fundamental aspect of human biology has been poorly understood, chiefly because scientists lack the ability to closely observe the intricate process of replication. Attempts to do so have relied on chemicals that damage the DNA structure or strategies ...
Extreme climate pushed thousands of lakes in West Greenland ‘across a tipping point,’ study finds
2025-01-21
West Greenland is home to tens of thousands of blue lakes that provide residents drinking water and sequester carbon from the atmosphere. Yet after two months of record heat and precipitation in fall 2022, an estimated 7,500 lakes turned brown, began emitting carbon and decreased in water quality, according to a new study.
Led by Fulbright Distinguished Arctic Scholar and University of Maine Climate Change Institute Associate Director Jasmine Saros, a team of researchers found that the combination of extreme climate events in fall 2022 caused ecological change that ...
Illuminating an asymmetric gap in a topological antiferromagnet
2025-01-21
Topological insulators (TIs) are among the hottest topics in condensed matter physics today. They’re a bit strange: their surfaces conduct electricity, yet their interiors do not, instead acting as insulators. Physicists consider TIs the materials of the future because they host fascinating new quantum phases of matter and have promising technological applications in electronics and quantum computing. Scientists are just now beginning to uncover connections between TIs and magnetism that could unlock new uses for these exotic materials.
A ...
Global public health collaboration benefits Americans, SHEA urges continued support of the World Health Organization
2025-01-21
The Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA) wants to emphasize the importance of global partnerships in addressing health threats that impact all of us, as Americans and global citizens. We urge President Trump to reconsider the decision to terminate the U.S. relationship with the World Health Organization (WHO). The most effective way to address emerging health threats is through collaborative efforts with international partners. Eliminating U.S. involvement in the WHO would leave our country—and the world—more vulnerable to infectious diseases and less prepared to manage pandemics, fight emerging health threats, ...
Astronomers thought they understood fast radio bursts. A recent one calls that into question.
2025-01-21
Astronomer Calvin Leung was excited last summer to crunch data from a newly commissioned radio telescope to precisely pinpoint the origin of repeated bursts of intense radio waves — so-called fast radio bursts (FRBs) — emanating from somewhere in the northern constellation Ursa Minor.
Leung, a Miller Postdoctoral Fellowship recipient at the University of California, Berkeley, hopes eventually to understand the origins of these mysterious bursts and use them as probes to trace the large-scale structure of the universe, a key to its origin and evolution. He had written most of the computer code that allowed ...
AAAS announces addition of Journal of EMDR Practice and Research to Science Partner Journal program
2025-01-21
Journal of EMDR Practice and Research (JEMDR), launched in 2007, is devoted to integrative, state-of-the-art papers about EMDR therapy. It is a broadly conceived interdisciplinary journal that stimulates and communicates research and theory about EMDR therapy and its application to clinical practice. The journal publishes articles on all aspects of EMDR therapy and Adaptive Information Processing (AIP) theory. JEMDR is co-lead by Jenny Ann Rydberg, MA, PhdD cand. (University of Lorraine, Nancy, France) and Derek Farrell, PhD, MBE (Northumbria, Newcastle-upon-Tyne, UK).
As a member of the Science Partner Journal program, JEMDR will publish on a continuous basis under ...
Study of deadly dog cancer reveals new clues for improved treatment
2025-01-21
Researchers at the University of Florida College of Veterinary Medicine and the UF Health Cancer Center have identified a crucial link between a gene mutation and immune system signaling in canine hemangiosarcoma, a discovery that could lead to better treatments for both dogs and humans with similar cancers.
The research focuses on hemangiosarcoma, an aggressive cancer that forms malignant blood vessels in dogs. This life-threatening condition is difficult to diagnose early, as tumors can grow silently before rupturing without warning, leading to emergencies. ...
Skin-penetrating nematodes have a love-hate relationship with carbon dioxide
2025-01-21
Key takeaways
Globally, over 600 million people are infected with the skin-penetrating threadworm, Strongyloides stercoralis, mostly in tropical and subtropical regions with poor sanitation infrastructure.
Infections are treated with ivermectin, but some nematodes are starting to develop resistance to this first-line drug.
UCLA biologists have discovered that the nematodes respond differently to carbon dioxide at different stages in their life cycle, which could help scientists find ways to prevent or cure infections by targeting ...
Fewer than 1% of U.S. clinical drug trials enroll pregnant participants, study finds
2025-01-21
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — A new study by researchers from the Brown University School of Public Health found that pregnant women are regularly excluded from clinical drug trials that test for safety, raising concerns for the efficacy of these medications for maternal and child health.
The study, published in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, analyzed 90,860 drug trials involving women ages 18 to 45 from the past 15 years and found that only 0.8% included pregnant participants. ...
A global majority trusts scientists, wants them to have greater role in policymaking, study finds
2025-01-21
In what is considered the most comprehensive post-pandemic survey of trust in scientists, researchers have found a majority of people around the world carry widespread trust in scientists — believing them to be honest, competent, qualified and concerned with public well-being.
Researchers surveyed more than 72,000 individuals across 68 countries on perceptions of scientists’ trustworthiness, competence, openness and research priorities.
The results, published in the journal Nature Human Behavior, also showed the general public’s desire ...
Transforming China’s food system: Healthy diets lead the way
2025-01-21
According to the study published in Nature Food, China’s current trajectory is misaligned with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The researchers assessed potential pathways for achieving the SDGs in China by transforming its food system, focusing on dietary changes, climate change mitigation, ecological conservation, and socio-economic development. “Action across all areas of the food system is required to achieve a sustainable food system and efficiently address the wide range of social and environmental ...
Time to boost cancer vaccine work, declare UK researchers
2025-01-21
UK oncology researchers have come together to write the first ever national thought leadership strategy report into cancer vaccine advances and the opportunities these present for those affected by cancer. The strategy report has been published in Cambridge University Press journal Cambridge Prisms: Precision Medicine.
Cancer vaccines hold the potential to revolutionise cancer treatment. These vaccines leverage neoantigens to activate the immune system against tumours, offering a personalised approach to combat cancer. This transformative potential is particularly significant in light of recent advancements in oncology, including ...
Colorado State receives $326M from DOE/EPA to improve oil and gas operations and reduce methane emissions
2025-01-21
The Department of Energy and Environmental Protection Agency have awarded $326 million to three Colorado State University research projects that aim to improve U.S. oil and gas operations and reduce methane emissions nationwide.
The EPA’s Methane Emissions Reduction Program is providing the funding to the CSU Energy Institute and faculty working across multiple departments in the Walter Scott, Jr. College of Engineering, with the goal of helping oil and gas operators improve operational efficiency and manage emissions. The efforts will also support activity to build an inventory of methane emissions, ...
Research assesses how infertility treatments can affect family and work relationships
2025-01-21
Infertility is a problem that affects between 8% and 12% of couples of reproductive age worldwide – for some of them, the problem interrupts a life project, which is the desire to have children and build a family. Advances in technology and medicine have made assisted reproductive treatments possible, but they can be physically and psychologically draining for the couples involved, especially because of expectations of results that may not be achieved.
The emotional impact of treatment is well documented in the scientific literature. ...
New findings shed light on cell health: Key insights into the recycling process inside cells
2025-01-21
A recent study from Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Mumbai, India has revealed new details about how our cells clean up and recycle waste. This process, known as autophagy, is like a self-cleaning mechanism for cells, helping the cells stay healthy by getting rid of damaged parts and recycling useful components. The process involves formation of a vesicle called autophagosome, which encapsulates the cellular waste. The autophagosome then fuses with another type of vesicle called lysosome. ...
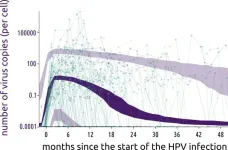
Human papillomavirus infection kinetics revealed in new longitudinal study
2025-01-21
Non-persistent human papillomavirus (HPV) infections are characterized by a sharp increase in viral load followed by a long plateau, according to a study published January 21st in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Samuel Alizon of the National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS), France, and colleagues.
Chronic HPV infection is responsible for more than 600,000 new cancers each year, including nearly all cervical cancers. Infection among young women is common, impacting nearly 20% of women 25 years of age. Fortunately, the vast majority of these infections ...
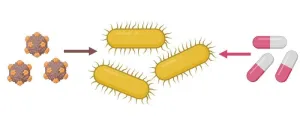
Antibiotics modulate E. coli’s resistance to phages
2025-01-21
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002952
Article title: Chloramphenicol and gentamicin reduce the evolution of resistance to phage ΦX174 by suppressing a subset of E. coli LPS mutants
Author countries: Germany
Funding: This work was generously supported by funds from the Max Planck Society (L.P.-F.B.). L.P. was supported by the International Max Planck Research ...
Building sentence structure may be language-specific
2025-01-21
Do speakers of different languages build sentence structure in the same way? In a neuroimaging study published in PLOS Biology, scientists from the Max Planck institute for Psycholinguistics, Donders Institute and Radboud University in Nijmegen recorded the brain activity of participants listening to Dutch stories. In contrast to English, sentence processing in Dutch was based on a strategy for predicting what comes next rather than a ‘wait-and-see’ approach, showing that strategies may differ across languages.
While listening to spoken language, people need to link ‘abstract’ knowledge of grammar to ...
Biotin may shield brain from manganese-induced damage, study finds
2025-01-21
While manganese is an essential mineral involved in many bodily functions, both deficiency and excessive exposure can cause health issues. Maintaining a balanced diet typically provides sufficient manganese for most individuals; however, high levels of exposure can be toxic, particularly to the central nervous system. Chronic manganese exposure may result in a condition known as manganism, characterized by symptoms resembling Parkinson's disease, including tremors, muscle stiffness, and cognitive disturbances.
New research published in Science Signaling employs model systems and human nerve cells to show the mechanisms by which manganese inflicts damage ...
Treatment for children with obesity has lasting effect
2025-01-21
When children with obesity undergo weight-loss treatment, the effects have repercussions later in life and the risk of serious health problems and premature death is lower as they reach young adulthood. However, this is not the case for depression and anxiety, a study from Karolinska Institutet published in JAMA Pediatrics reports.
The study shows that children and adolescents who respond well to obesity treatment are less likely to develop obesity-related diseases, such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension and dyslipidaemia (abnormally high levels of fat in the blood) as young adults.
The treatment studied ...
Spotted hyena found in Egypt for the first time in 5,000 years
2025-01-21
A spotted hyena (Crocuta crocuta) has been found in South Eastern Egypt: the first recorded instance of the creature in this region for thousands of years.
The lone individual was caught and killed by people around 30km from the border with Sudan, a paper in De Gruyter’s Mammalia reports.
“My first reaction was disbelief until I checked the photos and videos of the remains,” said the study’s lead author, Dr. Adbullah Nagy from Al-Azhar University, Egypt. “Seeing the evidence, I was completely taken aback. It was beyond anything we had expected to find in Egypt.”
The sighting took place some 500km north of the known range of spotted ...
SignGPT – Project awarded £8.45m to build a sign language AI model for the Deaf community
2025-01-21
A large-language model (LLM) built to meet the needs of the Deaf community, translating between signed and spoken language, is the aim of a new project led by the University of Surrey.
SignGPT: Building Generative Predictive Transformers for Sign Language has been awarded £8.45m from the UK Engineering & Physical Sciences Research Council. The five-year project will build tools to allow spoken language to be automatically translated into photo-realistic sign language and video of sign language to be translated into spoken language – a complex translation problem that is yet to be solved.
Surrey ...
Garden ponds: Hidden gems of urban biodiversity conservation
2025-01-21
Urbanisation is rapidly transforming landscapes worldwide, becoming a key driver of global biodiversity loss. It often impacts biodiversity negatively by creating selective environments that limit species diversity in urban compared to natural habitats. Amidst this challenge, understanding and enhancing urban blue-green infrastructure is critical. Garden ponds are small yet significant water features that are increasingly common in urban areas. They offer numerous ecosystem services, like aesthetic purposes, microclimate regulation, and habitats for ornamental species. However, their role in supporting ...
Epigenetic aging and DNA-methylation as tumor markers for breast cancer
2025-01-21
“Our study contributes to the development of a DNAm biomarker that integrates conventional BC risk factors to better reflect the risk for BC subtypes, promoting epigenetically targeted preventive interventions tailored to aged individuals with high risk.”
BUFFALO, NY- January 21, 2025 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) on December 5, 2024, Volume 16, ...
[1] ... [722]
[723]
[724]
[725]
[726]
[727]
[728]
[729]
730
[731]
[732]
[733]
[734]
[735]
[736]
[737]
[738]
... [8829]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.