New software tool helps evaluate natural cooling options for buildings
2011-05-26
A new, free software tool from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) could prove to be a breath of fresh air for architects and designers of ventilation systems for "green" commercial buildings.
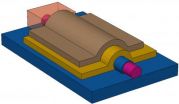
With the Climate Suitability Tool,* building design teams can evaluate whether the local climate is suitable for cooling a prospective building with natural ventilation or requires a hybrid system that supplies supplemental cooling capacity. The tool is based on a model of the heat-related characteristics of a building configured to take full advantage of ambient ...
NIST 'nanowire' measurements could improve computer memory
2011-05-26
A recent study* at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) may have revealed the optimal characteristics for a new type of computer memory now under development. The work, performed in collaboration with researchers from George Mason University (GMU), aims to optimize nanowire-based charge-trapping memory devices, potentially illuminating the path to creating portable computers and cell phones that can operate for days between charging sessions.
The nascent technology is based on silicon formed into tiny wires, approximately 20 nanometers in diameter. ...
Fish species discovered by LSU researcher makes 2011 top 10 list
2011-05-26
BATON ROUGE – The International Institute for Species Exploration at Arizona State University and a committee of taxonomists from around the world announced their picks for the top 10 new species described in 2010. Among their top picks is Halieutichthys intermedius, a pancake batfish recently discovered by Prosanta Chakrabarty, curator of fishes at LSU's Museum of Natural Science, and colleagues.
Halieutichthys intermedius, more commonly referred to as the Louisiana pancake batfish, gained some notoriety during the spring and summer of 2010, when the Deepwater Horizon ...
Public universities place greater focus on internal research services than public ones do
2011-05-26
Research expenditure has increased in Spain, as has the focus on research performance. However, the internal services that universities provide to support research, both in terms of infrastructure and staff, have not improved, according to a study published in the journal The Service Industries Journal, which also shows that public universities outperform private ones in this respect.
"The Ministry of Science and Innovation provides Spanish universities with access to databases. However, we have seen that in many cases there are no research support staff to explain how ...
New study provides global analysis of seagrass extinction risk
2011-05-26
A team of 21 researchers from 11 nations, including professor Robert "JJ" Orth of the Virginia Institute of Marine Science, has completed the first-ever study of the risk of extinction for individual seagrass species around the world.
The 4-year study, requested by the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN), shows that 10 of the 72 known seagrass species (14%) are at an elevated risk of extinction, while 3 species qualify as endangered.
The authors caution that loss of seagrass species and seagrass biodiversity will seriously impact marine ecosystems ...
Improved prognosis for esophageal cancer
2011-05-26
In recent years, the number of cases of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus (or gullet) has been on the rise. At the same time, however, new ways of treatment are improving the outlook for patients. In the current issue of Deutsches Ärzteblatt International (Dtsch Artzebl Int 2011; 108[18]: 313𔃇), Angelika Behrens and her working group report on innovations in diagnosis and treatment.
The main cause of this cancer is reflux of gastric acid from the stomach, with heartburn as the main symptom. Other risk factors are being male, being overweight, and having relatives ...
New bandwidth management techniques boost operating efficiency in multi-core chips
2011-05-26
Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed two new techniques to help maximize the performance of multi-core computer chips by allowing them to retrieve data more efficiently, which boosts chip performance by 10 to 40 percent.
To do this, the new techniques allow multi-core chips to deal with two things more efficiently: allocating bandwidth and "prefetching" data.
Multi-core chips are supposed to make our computers run faster. Each core on a chip is its own central processing unit, or computer brain. However, there are things that can slow these ...
Global warming may affect the capacity of trees to store carbon, MBL study finds
2011-05-26
MBL, WOODS HOLE, MASS.—One helpful action anyone can take in response to global warming is to plant trees and preserve forests. Trees and plants capture carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, thereby removing the most abundant greenhouse gas from the atmosphere and storing some of it in their woody tissue.
Yet global warming may affect the capacity of trees to store carbon by altering forest nitrogen cycling, concludes a study led by Jerry Melillo, Distinguished Scientist at the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) Ecosystems Center, and published this week in Proceedings ...
New Canadian blood pressure education program a powerful tool in fight to reduce stroke
2011-05-26
(Toronto, May 25, 2011): High blood pressure – the silent killer – is taking a hit from a new, ground-breaking treatment program from the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Ontario.
Last Sunday, in New York City, Dr. Sheldon Tobe, Chair of the Canadian Hypertension Education Program (CHEP) and a long-standing Heart and Stroke Foundation researcher, unveiled a new and powerful tool in the management of hypertension at the American Society of Hypertension (ASH) Scientific Meeting —The Heart&Stroke Hypertension Management Program.
"Diagnosing high blood pressure (hypertension) ...
2020 vision of vaccines for malaria, TB and HIV/AIDS
2011-05-26
SEATTLE, WA, May 25, 2011 – Collectively, malaria, TB & HIV/AIDS cause more than five million deaths per year – nearly the entire population of the state of Washington – and represent one of the world's major public health challenges as we move into the second decade of the 21st century. In the May 26, 2011, edition of the premier scientific journal Nature, Seattle BioMed Director Alan Aderem, Ph.D., along with Rino Rappuoli, Ph.D., Global Head of Vaccines Research for Novartis Vaccines & Diagnostics, discuss recent advances in vaccine development, along with new tools ...
Can we get there from here? Translating stem cell research into therapies
2011-05-26
A new article published by Cell Press in the May 26 issue of the journal Neuron provides comprehensive insight into the current status of neural stem cell research and the sometimes labyrinthine pathways leading to stem cell-based therapies. The perspective on translating neural stem cell research into clinical therapeutics is part of a special issue of Neuron devoted to neural stem cells and neurogenesis and is published in collaboration with the May issue of Cell Stem Cell, which also has a selection of reviews on this topic.
Neurological disease and injury are a major ...
Endangered gourmet sea snail could be doomed by increasing ocean acidity
2011-05-26
Increasing levels of ocean acidity could spell doom for British Columbia's already beleaguered northern abalone, according to the first study to provide direct experimental evidence that changing sea water chemistry is negatively affecting an endangered species.
The northern abalone--prized as a gourmet delicacy--has a range that extents along the North American west coast from Baja California to Alaska. Even though British Columbia's northern abalone commercial fisheries where closed in 1990 to protect dwindling populations, the species has continued to struggle, largely ...
Japan earthquake appears to increase quake risk elsewhere in the country
2011-05-26
Japan's recent magnitude 9.0 earthquake, which triggered a devastating tsunami, relieved stress along part of the quake fault but also has contributed to the build up of stress in other areas, putting some of the country at risk for up to years of sizeable aftershocks and perhaps new main shocks, scientists say.
After studying data from Japan's extensive seismic network, researchers from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), Kyoto University and the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) have identified several areas at risk from the quake, Japan's largest ever, which ...
Syracuse University scientists discover new hitch to link nerve cell motors to their cargo
2011-05-26
With every bodily movement—from the blink of an eye to running a marathon—nerve cells transmit signals to muscle cells. To do that, nerve cells rely on tiny molecular motors to transport chemical messengers (neurotransmitters) that excite muscles cells into action. It's a complex process, which scientists are still trying to understand. A new study by Syracuse University researchers has uncovered an important piece of the puzzle.
The study, published in the April 22 issue of the Journal of Biological Chemistry (JBC), describes the discovery of a protein that is involved ...
Rethinking extinction
2011-05-26
For more than 40 years, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has published the Red List of Threatened Species describing the conservation status of various species of animals. They are now also including plants in their lists and the picture they present is dramatic. According to recent estimates, around 20 per cent of flowering plants are currently at risk of extinction – though the exact number is unknown since such a small proportion of plant species has even been measured.
Now, however, research conducted in South Africa and the U.K. by an international ...
Study shows elderly drivers support competency tests
2011-05-26
AURORA, Colo. (May 25, 2011) – Researchers studying driving habits and accident rates among the elderly found a majority surveyed supported mandatory retesting of drivers based on age while saying they would hand over the keys if a doctor or loved one said they were no longer fit to drive.
"We are now exploring the idea of an advance directive for driving where someone would be designated to take away your keys at some point," said Emmy Betz, MD, MPH, at the University of Colorado School of Medicine who led the study and presented it in May before the American Society ...
Study details path to sustainable aviation biofuels industry in Northwest
2011-05-26
SEATTLE–The Pacific Northwest has the diverse feedstocks, fuel-delivery infrastructure and political will needed to create a viable biofuels industry capable of reducing greenhouse gases and meeting the future fuel demands of the aviation industry. Creating an aviation biofuels industry, however, will depend upon securing early government policy support to prioritize the aviation industry in U.S. biofuel development.
That's the conclusion announced today in a 10-month study by Sustainable Aviation Fuels Northwest (SAFN), the nation's first regional stakeholder effort to ...
Most labor unions unlikely to follow decertification path of NFL players
2011-05-26
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — With legislation to diminish private- and public-sector collective bargaining rights already in the books in Wisconsin and Ohio, should more labor unions steal a page from the playbook of the NFL Players Association and decertify? Although there are parallels between the pros and regular Joes (and Janes), union decertification is not a viable strategy for ordinary workers to use when bargaining for better wages and working conditions, says a University of Illinois law and labor expert.
Whether it's a teacher in Wisconsin or a construction worker in Indiana, ...
Autism changes molecular structure of the brain, UCLA study finds
2011-05-26
For decades, autism researchers have faced a baffling riddle: how to unravel a disorder that leaves no known physical trace as it develops in the brain.
Now a UCLA study is the first to reveal how the disorder makes its mark at the molecular level, resulting in an autistic brain that differs dramatically in structure from a healthy one. Published May 25 in the advance online edition of Nature, the findings provide new insight into how genes and proteins go awry in autism to alter the mind.
The discovery also identifies a new line of attack for researchers, who ...
Caltech-led team debunks theory on end of 'Snowball Earth' ice age
2011-05-26
PASADENA, Calif.—There's a theory about how the Marinoan ice age—also known as the "Snowball Earth" ice age because of its extreme low temperatures—came to an abrupt end some 600 million years ago. It has to do with large amounts of methane, a strong greenhouse gas, bubbling up through ocean sediments and from beneath the permafrost and heating the atmosphere.
The main physical evidence behind this theory has been samples of cap dolostone from south China, which were known to have a lot less of the carbon-13 isotope than is normally found in these types of carbonate rocks. ...
Pitt team recreates brain cell networks with new view of activity behind memory formation
2011-05-26
PITTSBURGH—University of Pittsburgh researchers have reproduced the brain's complex electrical impulses onto models made of living brain cells that provide an unprecedented view of the neuron activity behind memory formation.
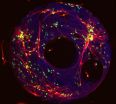
The team fashioned ring-shaped networks of brain cells that were not only capable of transmitting an electrical impulse, but also remained in a state of persistent activity associated with memory formation, said lead researcher Henry Zeringue [zuh-rang], a bioengineering professor in Pitt's Swanson School of Engineering. Magnetic resonance images ...
Violent video games reduce brain response to violence and increase aggressive behavior
2011-05-26
VIDEO:
Scientists have known for years that playing violent video games causes players to become more aggressive. The findings of a new University of Missouri study provide one explanation for...
Click here for more information.
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Scientists have known for years that playing violent video games causes players to become more aggressive. The findings of a new University of Missouri (MU) study provide one explanation for why this occurs: the brains of violent ...
Many patients fail to properly take oral chemo, leading to complications
2011-05-26
EAST LANSING, Mich. — As the use of oral chemotherapy continues to rise, researchers from Michigan State University have discovered many patients fail to properly take the cancer-fighting medication, a significant clinical problem that can result in complications and premature death.
That lack of adherence needs to be addressed by the health care community, said College of Nursing researcher Barbara Given, who led the study that is published in the May edition of Seminars in Oncology Nursing.
"Given the increasing use of oral chemotherapy in treating cancer, patient ...
Big bucks for MLB megastars mean big team profits, but fewer wins
2011-05-26
ANN ARBOR, Mich.---Spending top dollar for megastar players like Miguel Cabrera and Alex Rodriguez helps Major League Baseball teams attract fans and earn higher profits, but clubs that spend the bulk of their player payroll on a couple of superstars ultimately win fewer games, a University of Michigan study shows.
"Superstars who are paid more could bring more to the team in terms of profits," said Jason Winfree, an associate professor of sport management at the U-M School of Kinesiology. "The flip side of that is that a more equitable pay scale among all players results ...
Protein drinks after exercise help maintain aging muscles
2011-05-26
Bethesda, MD—A new research report appearing online in the FASEB Journal (http://www.fasebj.org) shows that what someone drinks after exercise plays a critical role in maximizing the effects of exercise. Specifically, the report shows that protein drinks after aerobic activity increases the training effect after six weeks, when compared to carbohydrate drinks. Additionally, this study suggests that this effect can be seen using as little as 20 grams of protein.
"It is not a mystery that exercise and nutrition help slow the aging process," said Benjamin F. Miller, Ph.D., ...
[1] ... [7306]
[7307]
[7308]
[7309]
[7310]
[7311]
[7312]
[7313]
7314
[7315]
[7316]
[7317]
[7318]
[7319]
[7320]
[7321]
[7322]
... [8804]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.