FAU names Lewis S. Nelson, M.D., Dean of the Schmidt College of Medicine
2025-01-07
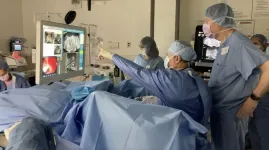
Florida Atlantic University has named Lewis S. Nelson, M.D., as the new dean of the Charles E. Schmidt College of Medicine. Nelson previously served as professor and inaugural chair of the Department of Emergency Medicine and chief of the Division of Medical Toxicology and Addiction Medicine at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School in Newark, and chief of the Emergency Department at University Hospital of Newark, a public safety net hospital. He assumed his role as dean on Jan. 6.
Nelson has more than 30 years of academic and clinical leadership experience with a proven record of fostering innovation, research, and clinical excellence. During his eight-year tenure ...
UC Irvine-led study challenges traditional risk factors for brain health in the oldest-old
2025-01-07
Irvine, Calif., Jan. 7, 2025 – A study led by the University of California, Irvine has found cardiovascular conditions such as high blood pressure and diabetes, which are known to contribute to brain blood vessel damage in younger populations, not to be associated with an increased risk of such harm in individuals 90 and older.
The work, published online today in the journal Alzheimer’s & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association, suggests that the relationship among blood pressure, vascular health and brain aging is more complex than previously thought.
“For decades, we’ve known that factors like high blood ...
Study shows head trauma may activate latent viruses, leading to neurodegeneration
2025-01-07
Concussions and repetitive head trauma in sports like football and boxing, once accepted as an unpleasant consequence of intense athletic competition, are now recognized as serious health threats. Of particular concern is the connection between head injuries and neurodegenerative diseases such as chronic traumatic encephalopathy, Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease, prompting sports governing bodies to adjust protective equipment and rules of play to minimize the risk.
Researchers at Tufts University and Oxford University have now uncovered mechanisms that may ...
Advancements in neural implant research enhance durability
2025-01-07
Crucial research on brain diseases
Neural implants are crucial in order to study the brain and develop treatments for patients with diseases like Parkinson's or clinical depression. Neural implants electrically stimulate, block, or record signals from neurons or neural networks in the brain. For study and treatment, and specifically for chronic use, these neural implants must be durable.
"Miniaturized neural implants have enormous potential to transform healthcare, but their long-term stability in the body ...
SwRI models Pluto-Charon formation scenario that mimics Earth-Moon system
2025-01-07
SAN ANTONIO — January 7, 2025 —A NASA postdoctoral researcher at Southwest Research Institute has used advanced models that indicate that the formation of Pluto and Charon may parallel that of the Earth-Moon system. Both systems include a moon that is a large fraction of the size of the main body, unlike other moons in the solar system. The scenario also could support Pluto’s active geology and possible subsurface ocean, despite its location at the frozen edge of the solar system.
“We ...
Researchers identify public policies that work to prevent suicide
2025-01-07
An analysis led by New York University researchers determines which public policies effectively prevent suicide deaths in the United States. But it’s not just policies that limit firearms and expand access to health care—many economic and social policies that are not explicitly focused on mental health can also prevent suicide, according to their article published in the Annual Review of Public Health.
“Most of the policies that demonstrate evidence do not mention suicide and were not passed to prevent ...
Korea University College of Medicine and Yale Univeristy co-host forum on Advancing Healthcare through Data and AI Innovations
2025-01-07
Korea University College of Medicine and Yale Univeristy Co-Host Forum
on Advancing Healthcare through Data and AI Innovations
On October 2nd (Wednesday), Korea University College of Medicine (Dean: Pyun Sung-Bom) hosted a forum titled “Advancing Healthcare through Innovations in Data and AI in Clinical Informatics and Natural Language Processing” in the 6th-floor lecture hall of the First Medical Building.
As part of Korea University’s 120th-anniversary celebration, this annual joint forum with Yale University has been held since 2023. This year’s ...
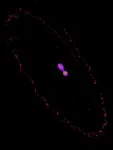
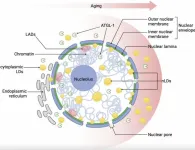
Nuclear lipid droplets: Key regulators of aging and nuclear homeostasis
2025-01-07
“A consistent feature of aging across diverse species is the progressive accumulation of lipid droplets (nLDs) within the nuclear compartment, which disrupts nuclear architecture and functionality.”
BUFFALO, NY- January 7, 2025 – A new research perspective was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 22 on December 9, 2024, entitled “Nuclear lipid droplets: a novel regulator of nuclear homeostasis ...
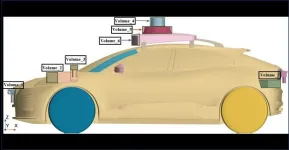
Driving autonomous vehicles to a more efficient future
2025-01-07
WASHINGTON, Jan. 7, 2025 – Thanks to the rapid progress of information technology and artificial intelligence, autonomous vehicles (AVs) have been taking off. In fact, AV technology is now advanced enough that the vehicles are being used for logistics delivery and low-speed public transportation.
While most research has focused on control algorithms to heighten safety, less attention has been directed at improving aerodynamic performance, which is essential for lowering energy consumption and extending driving range. As a result, aerodynamic drag issues have ...
Severe maternal morbidity among pregnant people with opioid use disorder enrolled in Medicaid
2025-01-07
About The Study: This cross-sectional study of pregnant people enrolled in Medicaid found that the rate of opioid use disorder among this group was more than twice as high as previous estimates. Pregnant people with opioid use disorder face a disproportionately high risk of severe maternal morbidity, particularly those who enroll in Medicaid later in pregnancy. Targeted interventions that facilitate early Medicaid enrollment and coverage continuity may be needed to reduce the burden of adverse outcomes in this group.
Corresponding ...
Macronutrients in human milk exposed to antidepressant and anti-inflammatory medications
2025-01-07
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study, some maternal medications were associated with lower levels of protein and fat in milk, which could impose health risks for breastfed infants. Other factors that could influence macronutrient levels need to be clarified before the clinical implications of these findings can be confirmed.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Essi Whaites Heinonen, MD, PhD, email essi.heinonen@ki.se.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.53332)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
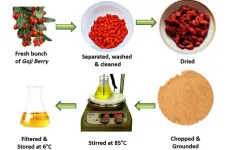
Exploring the eco-friendly future of antibiotic particles
2025-01-07
WASHINGTON, Jan. 7, 2025 – As the search for sustainability permeates all fields, researchers are turning to a unique organic source for creating antibacterial silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) – the humble goji berry.
Goji berries are a ubiquitous superfood known for a multitude of health benefits, including their antibiotic properties. In research published in AIP Advances, by AIP Publishing, researcher Kamran Alam from Sapienza University of Rome along with others from NED University of Engineering and Technology and King Saud University found an effective way to harvest ...
Can you steam away prostate cancer?
2025-01-07
LOS ANGELES — Steam eliminates wrinkles and germs, but can it destroy cancer cells too?
Keck Medicine of USC is participating in a national, multisite clinical trial examining if a water vapor system that uses small, targeted amounts of steam to kill cancer cells is a safe and effective treatment for prostate cancer.
Researchers hope that steam may offer patients a less invasive way of controlling or curing cancer than currently exists.
“The most common therapies for prostate cancer often cause life-altering side effects, and we are investigating if this new treatment may not only treat the cancer, ...
The CTAO becomes a European Research Infrastructure Consortium
2025-01-07
Bologna, Italy, 7 January 2025 – On January 7, 2025, the European Commission established the Cherenkov Telescope Array Observatory (CTAO) as a European Research Infrastructure Consortium (ERIC), furthering its mission to become the world’s largest and most powerful observatory for gamma-ray astronomy. The creation of the CTAO ERIC will enable the Observatory's construction to advance rapidly and provide a framework for distributing its data worldwide, significantly accelerating its progress toward scientific discovery.
“The ERIC will streamline the construction and operation ...
Introduction to science journalism guide published in Albanian
2025-01-07
A new guide aimed at helping aspiring science journalists in Albania to cover scientific topics has been published.
The guide has information about science journalism efforts in the country, and provides ideas for specific topics and how to approach them from a scientific and journalistic perspective. It also has links to relevant international sources for further study and advice.
The guide was written by Altin Raxhimi, an experienced journalist from Albania who has reported for print, digital media and television on topics ranging from war to food ...
Official launch of Global Heat Health Information Network Southeast Asia Hub at NUS Medicine
2025-01-07
The Heat Resilience & Performance Centre (HRPC) at the Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore (NUS Medicine) has been officially designated as the Global Heat Health Information Network (GHHIN) Southeast Asia Hub, a recognition that underscores its leading role in advancing heat resilience. This designation highlights the Centre's expertise in addressing the growing challenges of heat-related health risks in the region. With this appointment, the Centre is poised to play a pivotal role in working with the region to shape strategies, research, and policies aimed at mitigating ...
Childhood smoking increases a person’s risk of developing COPD
2025-01-07
Miami (January 7, 2025) – Childhood smoking before age 15 increases a person’s risk of developing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), according to a new study. The study is published in the November 2024 issue of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation, a peer-reviewed, open-access journal.
COPD is an inflammatory lung disease, comprising several conditions, including chronic bronchitis and emphysema, and can be caused by genetics and irritants like smoke or pollution. The disease affects more than 30 million Americans and is the ...
MD Anderson and Myriad Genetics form strategic alliance to evaluate clinical utility of Myriad’s molecular residual disease assay
2025-01-07
HOUSTON and SALT LAKE CITY ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and Myriad Genetics, Inc. today announced a five-year strategic alliance to accelerate the clinical evaluation and development of Myriad’s molecular residual disease (MRD) assay.
This strategic alliance brings together the longstanding oncology diagnostic experience of Myriad Genetics and the clinical and translational research expertise of MD Anderson to create a portfolio of studies to evaluate the clinical validity and utility of Myriad’s Precise MRD.
“We look forward to working ...
Method can detect harmful salts forming in nuclear waste melters
2025-01-07
PULLMAN, Wash. – A new way to identify salts in nuclear waste melters could help improve clean-up technology, including at the Hanford Site, one of the largest, most complex nuclear waste clean-up sites in the world.
Reporting in the journal Measurement, Washington State University researchers used two detectors to find thin layers of sulfate, chloride and fluoride salts during vitrification, a nuclear waste storage process that involves converting the waste into glass. The formation of salts can be problematic for waste processing and storage.
“We were able to demonstrate a technique ...
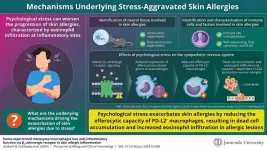
Researchers reveal how psychological stress may aggravate skin allergies
2025-01-07
Psychological stress is known to exacerbate skin allergies, but the underlying molecular mechanisms remain poorly understood. Recent studies using a mouse model of immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated cutaneous allergic inflammation (IgE-CAI) suggest that stress may disrupt immune functions, thereby worsening allergic symptoms by interfering with the body's inflammatory responses. IgE-CAI is characterized by swelling and infiltration of eosinophils, a type of immune cell involved in allergic inflammation, at the affected site.
In a recent study, a research group led by Associate Professor Soichiro Yoshikawa, Professor Kenji Takamori, and Professor Sachiko Miyake ...
International partnership aims to provide first-class osteopathy training
2025-01-07
The University of Plymouth and International Osteopathic Education (IOE) have formed a new partnership that will offer first-class training to aspiring osteopaths from across the world.
The organisations – both renowned internationally for quality healthcare training – have developed a rigorous and comprehensive Master of Osteopathic Medicine (MOstM) programme.
Those enrolling on the programme, which is being validated and awarded by the University of Plymouth, will engage in five years of flexible study.
They will benefit from clinical teaching in the IOE educational clinic in Bordeaux, ...
Reducing irrigation for livestock feed crops is needed to save Great Salt Lake, study argues
2025-01-07
CORVALLIS, Ore. – The Great Salt Lake has lost more than 15 billion cubic yards of water over the past three decades, is getting shallower at the rate of 4 inches a year, and an analysis of its water budget suggests reducing irrigation is necessary for saving it.
The study published today in Environmental Challenges shows that 62% of the river water bound for the lake is diverted for human uses, with agricultural activities responsible for nearly three-quarters of that percentage.
“The research highlights the alarming role of water consumption for feeding livestock in driving the lake’s rapid depletion,” said co-author ...
Clean energy tax credit safeguards could save taxpayers $1 trillion
2025-01-07
A new study published today in IOP Publishing’s journal Environmental Research: Energy shows why new safeguards adopted by the U.S. Treasury Department are necessary to avoid substantial climate impacts and wasted taxpayer resources from a generous hydrogen production tax credit.
The new study illustrates how, absent safeguards, hydrogen producers could potentially claim the highest level of tax credits ($3 per kilogram) for producing "gray" hydrogen from fossil natural gas, by blending in small amounts of biomethane or waste methane. ...
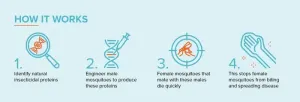
New genetic biocontrol breakthrough offers hope against disease-carrying mosquitoes and agricultural pests
2025-01-07
A revolutionary new biological pest control method that targets the lifespan of female insects could significantly reduce the threat of insect pests such as disease-carrying mosquitoes by offering faster and more effective results than current methods.
Described today in Nature Communications, the technique developed by researchers in Applied BioSciences and the ARC Centre of Excellence in Synthetic Biology at Macquarie University is a new approach called the Toxic Male Technique (TMT).
It works by genetically engineering male insects to produce insect-specific venom ...
Sex differences in brain structure present at birth
2025-01-07
Sex differences in brain structure are present from birth, research from the Autism Research Centre at the University of Cambridge has shown.
While male brains tended to be greater in volume than female brains, when adjusted for total brain volume, female infants on average had significantly more grey matter, while male infants on average had significantly more white matter in their brains.
Grey matter is made up of neuron cell bodies and dendrites and is responsible for processing and interpreting information, ...
[1] ... [740]
[741]
[742]
[743]
[744]
[745]
[746]
[747]
748
[749]
[750]
[751]
[752]
[753]
[754]
[755]
[756]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.