Floods, droughts, then fires: Hydroclimate whiplash is speeding up globally
2025-01-09
Key takeaways
Hydroclimate whiplash – rapid swings between intensely wet and dangerously dry weather – has already increased globally due to climate change, with further large increases expected as warming continues, according to a team of researchers led by UCLA’s Daniel Swain.
The “expanding atmospheric sponge,” or the atmosphere’s ability to evaporate, absorb and release 7% more water for every degree Celsius the planet warms, is a key driver of the whiplash.
Co-management of extreme rainfall or extreme droughts, ...
Scientists fuel sustainable future with catalyst for hydrogen from ammonia
2025-01-09
Scientists have created a catalyst for hydrogen generation from ammonia that becomes more active with time, and by counting atoms revealed changes that boost the catalyst’s performance.
A research team from the University of Nottingham's School of Chemistry, in collaboration with the University of Birmingham and Cardiff University, has developed a novel material consisting of nanosized ruthenium (Ru) clusters anchored on graphitized carbon. These Ru nanoclusters react with ammonia molecules, catalysing splitting ammonia into ...
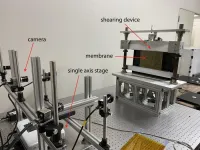
Discovering hidden wrinkles in spacecraft membrane with a single camera
2025-01-09
Exiting Earth’s gravity takes an enormous amount of fuel and power. Due to this, spacecraft strapped to rockets are limited in their carry capacity and every gram must be accounted for. To lighten the load, thin membranes are being researched as alternative materials, but their plastic wrap property causes wrinkling that can affect operational performance. For this reason, there is a need to develop measurement technology that can accurately detect deformations.
Professor Takashi Iwasa at Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Engineering led a team in developing a method for measuring the size of wrinkles ...
Women are less likely to get a lung transplant than men and they spend six weeks longer on the waiting list
2025-01-09
Women are less likely to receive a lung transplant and spend an average of six weeks longer on the waiting list, according to a study published today (Thursday) in ERJ Open Research [1]. However, women who receive a lung transplant are more likely than men to live for five years post-transplant. Based on their findings, the researchers encourage changes in regulation and clinical guidelines to address this inequality.
Lung transplantation is the only treatment for people with end-stage respiratory failure and patients on the waiting list have a high risk ...
Study sheds more light on life expectancy after a dementia diagnosis
2025-01-09
The average life expectancy of people diagnosed with dementia ranges from 9 years at age 60 to 4.5 years at age 85 for women and from 6.5 to just over 2 years, respectively, in men, finds a systematic review of the latest evidence in The BMJ today.
The results also suggest that one third of people with dementia are admitted to a nursing home within three years of diagnosis.
Nearly 10 million people worldwide receive a diagnosis of dementia every year, but survival estimates vary widely, and few ...
Tesco urged to drop an “unethical” in-store infant feeding advice service pilot
2025-01-09
UK supermarket giant Tesco is being urged to drop an “unethical” pilot of an in-store infant feeding advice service in which Danone-funded midwives are expected to wear branded uniforms and undergo training by the formula company, reveals an exclusive news report published by The BMJ today.
Critics say that the initiative, running in Tesco’s flagship store and set to be rolled out shortly, is a backward step and reminiscent of the “milk nurses” scandal of the 1970s, where formula industry salespeople dressed as nurses and promoted formula milk to parents.
One midwife hired by Danone quit ...
Unraveling the events leading to multiple sex chromosomes using an echidna genome sequence
2025-01-09
Unraveling the Events Leading to Multiple Sex Chromosomes Using an Echidna Genome Sequence
A nearly gapless genome sequence of the echidna, an egg-laying mammal with multiple sex chromosomes, helps researchers to track genomic reorganization events that gave rise to a highly unusual sex determination system.
The short-beaked echidna (Tachyglossus aculeatus) is one of Australia’s most iconic animals. Belonging to a unique group of mammals called “monotremes” (with the platypus as the other prominent member). Echidnas may at first glance be mistaken for a weird-looking hedgehog, ...
New AI platform identifies which patients are likely to benefit most from a clinical trial
2025-01-08
A new study led by Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University and Abramson Cancer Center of University of Pennsylvania researchers demonstrates that a first-of-its-kind platform using artificial intelligence (AI) could help clinicians and patients assess whether and how much an individual patient may benefit from a particular therapy being tested in a clinical trial. This AI platform can help with making informed treatment decisions, understanding the expected benefits of novel therapies and planning ...
Unique Stanford Medicine-designed AI predicts cancer prognoses, responses to treatment
2025-01-08
The melding of visual information (microscopic and X-ray images, CT and MRI scans, for example) with text (exam notes, communications between physicians of varying specialties) is a key component of cancer care. But while artificial intelligence helps doctors review images and home in on disease-associated anomalies like abnormally shaped cells, it’s been difficult to develop computerized models that can incorporate multiple types of data.
Now researchers at Stanford Medicine have developed an AI model able to incorporate visual ...
A new ultrathin conductor for nanoelectronics
2025-01-08
As computer chips continue to get smaller and more complex, the ultrathin metallic wires that carry electrical signals within these chips have become a weak link. Standard metal wires get worse at conducting electricity as they get thinner, ultimately limiting the size, efficiency, and performance of nanoscale electronics.
In a paper published Jan. 3 in Science, Stanford researchers show that niobium phosphide can conduct electricity better than copper in films that are only a few atoms thick. Moreover, these films can be created and deposited at sufficiently low temperatures to be compatible with modern computer ...
Synthetic chemicals and chemical products require a new regulatory and legal approach to safeguard children’s health
2025-01-08
Chestnut Hill, Mass (01/08/2025) – Nations must start testing and regulating chemicals and chemical products as closely as the current systems that safeguard prescription drugs or risk rising rates of chronic illnesses among children, according to a New England Journal of Medicine report by a group of experts writing as the Consortium for Children’s Environmental Health.
Global chemical inventories contain an estimated 350,000 products – such as manufactured chemicals, chemical ...
The genes that grow a healthy brain could fuel adult glioblastoma
2025-01-08
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Media Contact: Levi.Gadye@ucsf.edu, (415) 502-6397
Subscribe to UCSF News
The discovery of a new type of stem cell in the brain could usher in better treatments for the deadliest brain tumor.
UCSF scientists have discovered a stem cell in the young brain that’s capable of forming the cells found in tumors. The breakthrough could explain how adult brain cells take advantage of developmental processes to instigate the explosive growth seen in deadly brain cancers like glioblastoma.
They made the discovery while taking a broad genomic survey of human brain ...
New MSU study explains the delayed rise of plants, animals on land
2025-01-08
EAST LANSING, Mich. – If you like the smell of spring roses, the sounds of summer birdsong and the colors of fall foliage, you have the stabilization of the ozone layer to thank for it. Located in the stratosphere where it shields the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation, the ozone layer plays a key role in preserving the planet’s biodiversity.
Now, we may have a better idea of why that took more than 2 billion years to happen.
Michigan State University researcher Dalton Hardisty contributed to a new Yale University-led study finding that Earth’s early atmosphere hosted a battle royal between ...
UTA becomes one of largest natural history libraries
2025-01-08
Thanks to in-kind donations of tens of thousands of rare books, scientific journals, and articles, and reports over the past two years, The University of Texas at Arlington’s Amphibian and Reptile Diversity Research Center (ARDRC) has become one of the largest publicly accessible herpetology libraries in the world.
“Thanks to 12 independent donors, including the Joseph Rex Dinardo Jr. Herpetology and Natural History Science Research Trust in Philadelphia, Dr. Jonathan Campbell, William Lamar, Drs. Jay and Rebecca Savage, and Louis Porras, we now have thousands ...
Number of autistic individuals enrolled in Medicaid and receiving federal housing support increased by 70% from 2008-16
2025-01-08
Affordable and stable housing is critical to improving health across a person's lifespan. People with disabilities, including autism, comprise a significant share of people in need of housing assistance. However, the intersection of housing and health among individuals with autism is largely unknown because data on public housing and public health are not connected. Researchers from Drexel University’s A.J. Drexel Autism Institute examined how many autistic people in the United States received housing ...
St. Jude scientists create scalable solution for analyzing single-cell data
2025-01-08
Researchers have amassed vast single-cell gene expression databases to understand how the smallest details impact human biology. However, current analysis methods struggle with the large volume of data and, as a result, produce biased and contradictory findings. Scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital created a machine-learning algorithm capable of scaling with these single-cell data repositories to deliver more accurate results. The new method was published today in Cell Genomics.
Before single-cell analysis, bulk gene expression data ...
What is the average wait time to see a neurologist?
2025-01-08
MINNEAPOLIS – Older people wait an average of just over a month to see a neurologist for specialty care after being referred by their primary care physician or another physician, according to a study published in the January 8, 2025, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study, which looked at people who have Medicare insurance, also found some people wait more than three months to see a neurologist.
“Neurologists provide important and ongoing care for people ...
Proximity effect: Method allows advanced materials to gain new property
2025-01-08
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Ferroelectrics are special materials with polarized positive and negative charges — like a magnet has north and south poles — that can be reversed when external electricity is applied. The materials will remain in these reversed states until more power is applied, making them useful for data storage and wireless communication applications.
Now, turning a non-ferroelectric material into one may be possible simply by stacking it with another ferroelectric material, according to a team led by scientists from Penn State who demonstrated the phenomenon, called proximity ferroelectricity.
The ...
LJI researchers shed light on devastating blood diseases
2025-01-08
LA JOLLA, CA—Scientists at La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) have discovered how a mutated gene kicks off a dangerous chain of events during blood cell production.
The study, published recently in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, reveals how a mutated gene called ASXL1 is involved in a disease called clonal hematopoiesis, a precursor to malignant diseases such as myeloid malignancies and chronic monomyelocytic leukemia.
"We know that many diseases—and all cancers—are driven by mutations in the genome," says LJI Instructor Zhen Dong, ...
ISS National Lab announces up to $650,000 in funding for technology advancement in low Earth orbit
2025-01-08
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER (FL), January 7, 2025 – The International Space Station (ISSInternational Space Station) National Laboratory is soliciting flight concepts for technology advancement that utilizes the space-based environment of the orbiting laboratory. This solicitation, “Technology Advancement and Applied Research Leveraging the ISS National Lab,” is open to a broad range of technology areas, including chemical and material synthesis in space, translational medicine, in-space edge computing, and in-space servicing, assembly, and manufacturing. It also encompasses the application of space station remote sensing data to improve geospatial analytics ...
Scientists show how sleep deprived brain permits intrusive thoughts
2025-01-08
A new study has shown that sleep deprivation can inhibit the brain’s ability to suppress unwanted memories and intrusive thoughts.
Scientists at the University of York, in collaboration with the University of East Anglia, have shown that sleep deprivation interferes with the ability of the prefrontal area of the brain to restrict the retrieval of memories that would have otherwise been suppressed.
Dr Scott Cairney from the University of York said: “Memories of unpleasant experiences often intrude into our conscious ...
UC Irvine-led team discovers potential new therapeutic targets for Huntington’s disease
2025-01-08
Irvine, Calif., Jan. 8, 2025 — A University of California, Irvine-led research team has discovered intricate molecular mechanisms driving the RNA processing defects that lead to Huntington’s disease and link HD with other neurodegenerative disorders such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, frontotemporal lobar dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.
The findings may pave the way for neurodegenerative disorder researchers to collaborate and share therapeutic strategies across diseases, opening additional avenues for treatment.
While it’s known that HD is caused by an abnormal ...
Paul “Bear” Bryant Awards 2024 Coach of the Year finalists named
2025-01-08
HOUSTON, January 8, 2025 — Eight active college football coaches make up the American Heart Association’s 2024 Paul “Bear” Bryant Coach of the Year Award finalist list. The award is given each January to a college football coach for contributions that make the sport better for athletes and fans alike by demonstrating grit, integrity and a winning approach to coaching and life – both on and off the field. The Paul “Bear” Bryant Coach of the Year Award is the only college football coaching honor ...
Countering the next phase of antivaccine activism
2025-01-08
In a recent essay, pediatrician-scientist Peter Hotez proposes a focus on local data, improved benefit-risk communications, actively countering health disinformation, and state-level action to address antivaccine sentiment in the U.S.
Anti-vaccine sentiment isn’t going away any time soon. In a new opinion article published January 8 in the open-access journal PLOS Global Public Health, Prof. Peter Hotez from Baylor College of Medicine, outlines key actions to stem the momentum of anti-vaccine advocates in the U.S. over the next five years.
Anti-vaccine activities in the U.S. transformed to become a politically charged movement ...
Overcoming spasticity to help paraplegics walk again
2025-01-08
Electrical stimulation of the spinal cord is a promising strategy for reestablishing walking after spinal cord injury, recent studies show. But for patients suffering from muscle spasms, the stimulation protocols have a limited effect due to the unpredictable behaviour of involuntary muscle stiffness related to spasticity. Muscle spasticity affects almost 70% of spinal cord injured patients
Now, scientists at EPFL, Università San Raffaele and Scuola Sant’Anna have found a promising way to address and reduce muscle spasticity in patients with incomplete spinal cord injury. ...
[1] ... [736]
[737]
[738]
[739]
[740]
[741]
[742]
[743]
744
[745]
[746]
[747]
[748]
[749]
[750]
[751]
[752]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.