Ready to quit vaping in the new year? A new study uncovers the best ways
2025-01-08
A new study, co-led by a University of Massachusetts Amherst researcher, set out to identify the most effective strategies for helping people quit vaping. The findings, published today in the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, suggest that varenicline, a prescription medication often used to help people stop smoking, and text message-based interventions can help people quit.
“This is an area of research that is in its infancy, but is growing rapidly and organically from people who vape asking about help to quit vaping,” says senior author Jamie Hartmann-Boyce, assistant professor of health policy and management in the School ...
Regular physical activity before cancer diagnosis may lower progression and death risks
2025-01-08
Regular physical activity before a cancer diagnosis may lower the risks of both disease progression and death, suggests research published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
And even relatively low levels of physical activity may be advantageous, the findings indicate.
There is compelling evidence that physical activity has a key part to play in lowering the risk of death from cancer, but the evidence isn’t as conclusive for its role in disease progression, explain the researchers.
To explore this further, they analysed anonymised data from the Discovery Health Medical Scheme (DHMS), linked to the Vitality health promotion programme. The DHMS is the ...
Basking too long in a sauna without adequate hydration may risk heat stroke, doctors warn
2025-01-08
Basking too long in a sauna may put bathers at risk of heat stroke, particularly if they haven’t drunk enough water beforehand, warn doctors in the journal BMJ Case Reports, after treating a woman whose condition required admission to hospital.
Although relatively rare, heat stroke can be life threatening, even in the absence of various underlying risk factors, such as heart, lung, or neurological disease, and heavy drinking or taking a cocktail of prescription meds, they point out.
Heat stroke is defined as a sharp increase in core body temperature above ...
DNA adds new chapter to Indonesia’s layered human history
2025-01-08
A new study from the University of Adelaide and The Australian National University (ANU) has outlined the first genomic evidence of early migration from New Guinea into the Wallacea, an archipelago containing Timor-Leste and hundreds of inhabited eastern Indonesian islands.
The study, published in PNAS, addresses major gaps in the human genetic history of the Wallacean Archipelago and West Papuan regions of Indonesia – a region with abundant genetic and linguistic diversity that is comparable to the Eurasian ...
Many children and young people with diagnosable mental health disorders are not receiving timely help, says new research
2025-01-08
Children and young people with high levels of mental health needs are struggling to receive the help they need, or to have their difficulties recognised, according to a new study.
The STADIA trial, which is published in the Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, was led by experts from the School of Medicine at the University of Nottingham, and was funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR).
The large study, which spans different parts of England, involved 1,225 children and young people with emotional difficulties who had been referred to Child and Adolescent Mental Health Services (CAMHS) for help, and followed them up over 18 months to see ...
Dinosaurs roamed the northern hemisphere millions of years earlier than previously thought, according to new analysis of the oldest North American fossils
2025-01-08
MADISON — How and when did dinosaurs first emerge and spread across the planet more than 200 million years ago? That question has for decades been a source of debate among paleontologists faced with fragmented fossil records. The mainstream view has held that the reptiles emerged on the southern portion of the ancient supercontinent Pangea called Gondwana millions of years before spreading to the northern half named Laurasia.
But now, a newly described dinosaur whose fossils were uncovered by University of Wisconsin–Madison paleontologists is challenging ...
Breakthrough Durham University research offers new insights into quenching electrical waves in the heart
2025-01-08
-With images-
Scientists at Durham University have developed a theoretical framework to predict the efficacy of quenching of electrical pulses in excitable media, such as those found in the human heart.
This breakthrough could significantly accelerate the development of more efficient defibrillation techniques for treating cardiac arrhythmias.
The study, published in Physical Review E, addresses a longstanding challenge in understanding how stable excitation waves in systems like cardiac tissue can be effectively neutralised through small changes.
These electrical waves, when irregular, are thought to underly serious conditions such as fibrillation, ...
SLAC will play a key role in DOE’s new research centers for advancing next-generation microelectronics
2025-01-07
Around the globe day and night, the microelectronics behind much of modern technology help run computers, medical devices and state-of-the-art instruments that power scientific discoveries. But all of that technology consumes energy, and adding artificial intelligence to the mix increases our energy needs dramatically. Some experts caution that this pace of energy usage is unsustainable.
To tackle this challenge, the Department of Energy (DOE) has announced funding $179 million for three Microelectronics ...
Market researchers and online advertisers, are A-B tests leading you astray? A new study says they could be
2025-01-07
Researchers from Southern Methodist University and University of Michigan published a new Journal of Marketing study that examines platforms’ A-B testing of online ads and uncovers significant limitations that can create misleading conclusions about ad performance.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Where A-B Testing Goes Wrong: How Divergent Delivery Affects What Online Experiments Cannot (and Can) Tell You About How Customers Respond to Advertising” and is authored by Michael Braun and Eric M. Schwartz.
Consider a landscaping company whose designs focus ...
Research alert: Ketamine use on the rise in U.S. adults; new trends emerge
2025-01-07
A recent study analyzing data from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) found that past-year recreational ketamine use among adults has increased dramatically since 2015, including significant shifts in associations with depression and sociodemographic characteristics such as race, age and education status. Ketamine use has shown promise in clinical trials therapy for several mental illnesses, including treatment-resistant depression, and the new research suggests that ongoing monitoring of recreational use trends is crucial to balancing these ...
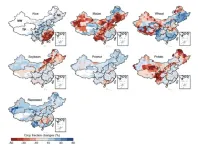
Crop switching for climate change in China
2025-01-07
A study of Chinese agriculture recommends planting areas currently growing maize and rapeseed with alternative crops to reduce environmental costs while maximizing food production as the climate changes.
Chinese food production has nearly doubled since the 1980s, mainly thanks to intensified nutrient usage and irrigation. Given that China’s demand for food is forecast to increase further, Qi Guan and colleagues modeled the country’s agricultural system under varying climate change scenarios in the 21st century, using a dynamic global vegetation model. The authors created scenarios ...
Cell-based therapy improves outcomes in a pig model of heart attacks
2025-01-07
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – In a large-animal model study, researchers have found that heart attack recovery is aided by injection of heart muscle cell spheroids derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells, or hiPSCs, that overexpress cyclin D2 and are knocked out for human leukocyte antigen classes I and II. This research, published in the journal Circulation Research, used a pig model of heart attacks. Pig hearts more closely resemble the human heart in size and physiology, and thus have a higher clinical relevance to human disease, compared to studies in mice.
University of Alabama at Birmingham researchers, led by Jianyi “Jay” ...
Researchers have a better understanding of how our cells dispose of waste while developing ways to control it
2025-01-07
Recycling takes place in our cells at all times: in a process called autophagy, cell components that are no longer needed are enclosed by membranes and broken down into their basic building blocks. This vital process prevents the formation of harmful aggregates and makes nutrients available again. A research team co-led by Prof. Dr. Claudine Kraft from the CIBSS Cluster of Excellence at the University of Freiburg and Dr. Florian Wilfling from the Max Planck Institute of Biophysics in Frankfurt has now discovered the conditions necessary for autophagy to start. They were also able ...
Earth’s air war: Explaining the delayed rise of plants, animals on land
2025-01-07
New Haven, Conn. — If you like the smell of spring roses, the sounds of summer birdsong, and the colors of fall foliage, you have the stabilization of the ozone layer to thank for it. Located in the stratosphere, where it shields the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation, the ozone layer plays a key role in preserving the planet’s biodiversity.
And now we may have a better idea of why that took so long — more than 2 billion years — to happen.
According to a new, Yale-led study, ...
More than half of college students report alcohol-related harms from others
2025-01-07
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Tuesday, January 7, 2025
Contact:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
##
More than half of US college students experienced alcohol-related harms caused by others, according to the first national probability-based survey of such harms conducted in 20 years. The findings, published in the journal Drug and Alcohol Review in December, shed light on how others’ drinking affects students’ health, academics, and safety.
“Our research ...
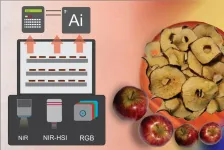
Smart food drying techniques with AI enhance product quality and efficiency
2025-01-07
URBANA, Ill.– Food drying is a common process for preserving many types of food, including fruits and meat; however, drying can alter the food’s quality and nutritional value. In recent years, researchers have developed precision techniques that use optical sensors and AI to facilitate more efficient drying. A new study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign discusses three emerging smart drying techniques, providing practical information for the food industry.
“With traditional drying systems, you need to remove samples to monitor the process. But with smart drying, or precision drying, you can continuously ...
Typical cost of developing new pharmaceuticals is skewed by high-cost outliers
2025-01-07
The typical cost of developing new medications may not be as high as generally believed, with a few ultra-costly medications skewing public discussions about the cost of pharmaceutical research and development, according to a new RAND study.
Using a novel method to assess spending on research and development for 38 drugs that were recently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, researchers found that the mean, or average, cost of developing a new drug was much higher than the mid-point (median) cost of development.
Researchers estimated a median direct research and development cost of $150 million compared to a mean of $369 million.
Costs ...
Predicting the progression of autoimmune disease with AI
2025-01-07
HERSHEY, Pa. — Autoimmune diseases, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own healthy cells and tissues, often have a preclinical stage before diagnosis that’s characterized by mild symptoms or certain antibodies in the blood. However, in some people, these symptoms may resolve before culminating in the full disease stage.
Knowing who may progress along the disease pathway is critical for early diagnosis and intervention, improved treatment and better disease management, according to a team led by researchers from the ...
Unlocking Romance: UCLA offers dating program for autistic adults
2025-01-07
Love doesn’t come with an instruction manual, but for autistic adults seeking to navigate the complexities of romance, a UCLA Health program offers a roadmap to finding and sustaining meaningful relationships through the launch of a new research study, called PEERS for Dating.
Led by the UCLA Program for the Education and Enrichment of Relationship Skills (PEERS) Clinic, the new 20-week program aims to demystify the often complex social rules surrounding dating and help participants gain a deeper understanding of relationship dynamics
“Romantic relationships can be transformative, but for many autistic adults, the path to connection can feel uncertain,” ...
Research Spotlight: Researchers reveal the influences behind timing of sleep spindle production
2025-01-07
How would you summarize your study for a lay audience?
Our research focuses on sleep spindles—short bursts of brain activity during sleep that are crucial for stabilizing sleep and supporting memory.
Sleep spindles are of great interest because changes in spindle activity have been linked to many neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease and autism.
While many factors influence when and how these spindles occur, such as sleep stages or brain rhythms, we discovered that short-term patterns, like a musical rhythm spanning just a few seconds, play the most ...
New research reveals groundwater pathways across continent
2025-01-07
Researchers from Princeton University and the University of Arizona have created a simulation that maps underground water on a continental scale. The result of three years’ work studying groundwater from coast to coast, the findings plot the unseen path that each raindrop or melted snowflake takes before reemerging in freshwater streams, following water from land surface to depths far below and back up again, emerging up to 100 miles away, after spending from 10 to 100,000 years underground.
The simulation, published Jan. 6 in the journal Nature Water, shows that rainfall and snowmelt ...
Students and faculty to join research teams this spring at Department of Energy National Laboratories and a fusion facility
2025-01-07
WASHINGTON, D.C. - A diverse group of 164 undergraduate students and six faculty will participate in unique workforce development programs at 11 of the nation’s national laboratories and a fusion facility during Spring 2025.
This opportunity is part of a continuing effort by the Department of Energy (DOE) to ensure the nation has a strong, sustained workforce trained in the skills needed to address the energy, environment, and national security challenges of today and tomorrow.
“The ...
SETI Forward recognizes tomorrow’s cosmic pioneers
2025-01-07
January 7, 2025, Mountain View, CA -- The SETI Institute announces the 2024 SETI Forward Award recipients: Gabriella Rizzo and Pritvik Sinhadc. This year's recipients worked on research projects to understand extremophiles in deep-sea hydrothermal vents and to analyze gravitational wave signals for potential extraterrestrial technosignatures. Established by Lew Levy, SETI Forward committee founder and member of the SETI Institute’s Council of Advisors, this award is a beacon for promising young scientists. The goal is to connect students with opportunities that foster their ...
Top mental health research achievements of 2024 from the Brain & Behavior Research Foundation
2025-01-07
The Brain & Behavior Research Foundation (BBRF) has announced the 2024 Leading Research Achievements by BBRF grantees, prizewinners, and scientific council members. It includes important studies of suicide, childhood anxiety, depression, eating disorders, cocaine addiction, and other aspects of brain and behavior illness.
The 2024 Leading Research Achievements are:
Suicide Risk Fluctuates Across the Menstrual Cycle, Affecting Different Women Differently
Tory Anne Eisenlohr-Moul, Ph.D., University of Illinois, Chicago
Preliminary Trial of Psychoactive ...
FAU names Lewis S. Nelson, M.D., Dean of the Schmidt College of Medicine
2025-01-07
Florida Atlantic University has named Lewis S. Nelson, M.D., as the new dean of the Charles E. Schmidt College of Medicine. Nelson previously served as professor and inaugural chair of the Department of Emergency Medicine and chief of the Division of Medical Toxicology and Addiction Medicine at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School in Newark, and chief of the Emergency Department at University Hospital of Newark, a public safety net hospital. He assumed his role as dean on Jan. 6.
Nelson has more than 30 years of academic and clinical leadership experience with a proven record of fostering innovation, research, and clinical excellence. During his eight-year tenure ...
[1] ... [739]
[740]
[741]
[742]
[743]
[744]
[745]
[746]
747
[748]
[749]
[750]
[751]
[752]
[753]
[754]
[755]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.