Robert McKeown recognized for a half century of distinguished service
2025-01-02
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – For nearly half a century, Robert D. “Bob” McKeown has probed nuclear particles and educated rising generations of physicists. Now, the former deputy director for science at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility is being honored for his outstanding career contributions with the 2024 American Physical Society’s Division of Nuclear Physics (DNP) Distinguished Service Award.
McKeown is recognized for his work in experimental physics and his extensive leadership in the broader ...
University of Maryland awarded $7.8 million to revolutionize renewable energy for ocean monitoring devices
2025-01-02
University of Maryland researcher Stephanie Lansing received a Phase 1 $7.8M award from Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) to develop and test a biologically fueled energy source to power research and sensing devices throughout the world’s oceans.
There is a vast array of ocean sensing devices that provide critical information for understanding marine environments, monitoring climate change and maintaining national security. Many of these sensors are currently powered by long underwater cables or lithium-ion batteries.
Lansing is leading a large, collaborative effort that will overcome the need for batteries and ship-based or shore-based ...
Update: T cells may offer some protection in an H5N1 ‘spillover’ scenario
2025-01-02
Update: This LJI study was previously shared on bioRxiv in September 2024. Since then, health officials have reported a rise in H5N1 “bird flu” infections in humans, including the first severe H5N1 human case requiring hospitalization. Officials have also reported increased cases in feline species, including an outbreak among big cats at a wildlife sanctuary. In California, the recent spread of H5N1 to dairy herds in Southern California prompted Gov. Gavin Newsom to declare a “State of Emergency” on Dec. 18, 2024.
LA JOLLA, CA—New research led by scientists at La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) ...
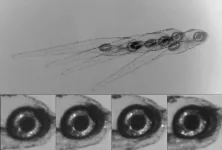
Newborn brain circuit stabilizes gaze
2025-01-02
An ancient brain circuit, which enables the eyes to reflexively rotate up as the body tilts down, tunes itself early in life as an animal develops, a new study finds.
Led by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, the study revolves around how vertebrates, which includes humans and animals spanning evolution from primitive fish to mammals, stabilize their gaze as they move. To do so they use a brain circuit that turns any shifts in orientation sensed by the balance (vestibular) system in their ears into an instant counter-movement by their eyes.
Called ...
Bats surf storm fronts during continental migration
2025-01-02
Birds are the undisputed champions of epic travel—but they are not the only long-haul fliers. A handful of bats are known to travel thousands of kilometers in continental migrations across North America, Europe, and Africa. The behavior is rare and difficult to observe, which is why long-distance bat migration has remained an enigma. Now, scientists from the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior (MPI-AB) have studied 71 common noctule bats on their spring migration across the European continent, providing a leap in understanding this mysterious behavior. Ultra-lightweight, intelligent sensors attached ...
Canadian forests are more prone to severe wildfires in recent decades
2025-01-02
Climate change is driving more intense wildfires in Canada, according to a new modeling study, with fuel aridity and rising temperatures amplifying burn severity, particularly over the last several decades. The findings underscore the growing impact of climate change on wildfire behavior, with the most severe effects concentrated in Canada’s northern forests. Fueled by ongoing climate change, Canada – one of the most forested and fire-prone regions in the Northern Hemisphere – is grappling with increasingly severe and prolonged wildfire seasons. ...
Secrets of migratory bats: They “surf” storm front winds to save energy
2025-01-02
A species of migrating bat “surfs” the warm winds of incoming storm fronts to conserve energy, according to a study that used tags to track the tiny animals on their long journeys across central Europe. The findings offer new insights into how weather, physiology, and environmental factors shape bats’ seasonal migration patterns. While bird migration is well-documented and studied, this is not the case for seasonal migration of bats – particularly the few long-distance, migratory species. These nocturnal travelers face substantial challenges, ...
Early life “luck” among competitive male mice leads to competitive advantage overall
2025-01-02
Early life "luck" plays a pivotal role in shaping individuality and success, particularly for males, according to a new study in mice. In male animals, competitive social dynamics amplified small initial differences into lifelong disparities in fitness. The findings highlight parallels between biological competition and societal inequalities and they demonstrate how chance events can drive divergent outcomes even among genetically identical individuals. Contingency (colloquially, “luck”) refers to the role of chance in shaping outcomes. It is a critical factor in both biological and social sciences, ...
A closer look at the role of rare germline structural variants in pediatric solid tumors
2025-01-02
Largescale changes in the genome inherited from parents are significant risk factors for pediatric solid tumors, such as Ewing sarcoma, neuroblastoma, and osteosarcoma, according to a new study. The findings, which highlight the role of germline structural variants (SVs) in early genome instability, provide new insights into the genetic underpinnings of pediatric cancers and open doors for improved diagnostic and treatment strategies. Unlike adult cancers, which often result from environmental factors or DNA damage built up over time, ...
Genetics of alternating sexes in walnuts
2025-01-02
The genetics behind the alternating sexes of walnut trees has been revealed by biologists at the University of California, Davis. The research, published Jan. 3 in Science, reveals a mechanism that has been stable in walnuts and their ancestors going back 40 million years — and which has some parallels to sex determination in humans and other animals.
Flowering plants have many ways to avoid pollinating themselves. Some do this by structuring flowers to make self-pollination difficult; some species have separate “male” and “female” plants. ...
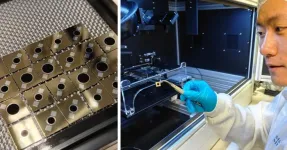
Building better infrared sensors
2025-01-02
Detecting infrared light is critical in an enormous range of technologies, from remote controls to autofocus systems to self-driving cars and virtual reality headsets. That means there would be major benefits from improving the efficiency of infrared sensors, such as photodiodes.
Researchers at Aalto University have developed a new type of infrared photodiode that is 35% more responsive at 1.55 µm, the key wavelength for telecommunications, compared to other germanium-based components. Importantly, this new device can be manufactured using current production techniques, making it highly practical for adoption.
‘It ...
Increased wildfire activity may be a feature of past periods of abrupt climate change, study finds
2025-01-02
CORVALLIS, Ore. – A new study investigating ancient methane trapped in Antarctic ice suggests that global increases in wildfire activity likely occurred during periods of abrupt climate change throughout the last Ice Age.
The study, just published in the journal Nature, reveals increased wildfire activity as a potential feature of these periods of abrupt climate change, which also saw significant shifts in tropical rainfall patterns and temperature fluctuations around the world.
“This study showed that the planet experienced these short, ...
Dogs trained to sniff out spotted lanternflies could help reduce spread
2025-01-02
Media note: Video of the Labrador retriever, Dia, in action is available for download, along with photos of the dogs and egg masses, here.
ITHACA, N.Y. - Growers and conservationists have a new weapon to detect invasive spotted lanternflies early and limit their spread: dogs trained to sniff out egg masses that overwinter in vineyards and forests.
A Cornell University study found that trained dogs – a Labrador retriever and a Belgian Malinois – were better than humans at detecting egg masses in forested areas near vineyards, while people spotted them better than the dogs in vineyards.
The spotted lanternfly, which was first ...
New resource available to help scientists better classify cancer subtypes
2025-01-02
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (Jan. 2, 2025) — A multi-institutional team of scientists has developed a free, publicly accessible resource to aid in classification of patient tumor samples based on distinct molecular features identified by The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) Network.
The resource comprises classifier models that can accelerate the design of cancer subtype-specific test kits for use in clinical trials and cancer diagnosis. This is an important advance because tumors belonging to different subtypes may vary in their response to cancer therapies.
The resource is the first of its kind to bridge the gap between TCGA’s immense data library ...
What happens when some cells are more like Dad than Mom
2025-01-02
NEW YORK, NY--New work by Columbia researchers has turned a textbook principle of genetics on its head and revealed why some people who carry disease-causing genes experience no symptoms.
Every biology student learns that each cell in our body (except sperm and eggs) contains two copies of each gene, one from each parent, and each copy plays an equal part in the cell.
The new study shows that some cells are often biased when it comes to some genes and inactivate one parent’s copy. The phenomenon was discovered about a decade ago, but ...
CAR-T cells hold memories of past encounters
2025-01-02
AURORA, Colo. (Jan. 2, 2025) - Researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus have discovered that some CAR-T cells engineered to fight cancer and other conditions carry the memory of past encounters with bacteria, viruses and other antigens within them, a finding that may allow scientists to manufacture the cells in more precise and targeted ways.
The study, published today in the journal Nature Immunology, focused on chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cells, an effective therapy against ...
Quantity over quality? Different bees are attracted to different floral traits
2025-01-02
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — When it comes to deciding where they’re going to get their next meal, different species of bees may be attracted to different flower traits, according to a study led by researchers at Penn State and published in PNAS Nexus.
The study focused on two species of solitary bees: the horned-face bee, which helps pollinate crops like apples and blueberries, and the alfalfa leafcutting bee, which pollinates alfalfa.
The researchers found that the horned-face bees tended to prefer plants with a large number of flowers — for them, quantity was most important. ...
Cancer-preventing topical immunotherapy trains the immune system to fight precancers
2025-01-02
A new study by investigators from Mass General Brigham uncovers how a novel immunotherapy prevents squamous cell carcinoma, with benefits lasting five years after treatment. This therapy is the first to activate specific components of the adaptive immune system, particularly CD4+ T helper cells, which are not known to be involved in traditional cancer treatments. This work highlights the potential for similar immunotherapies to prevent other cancers throughout the body. Results are published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
“One of the unique challenges with squamous cell carcinoma is that individuals who develop it are at an increased risk of developing multiple new ...
Blood test can predict how long vaccine immunity will last, Stanford Medicine-led study shows
2025-01-02
When children receive their second measles-mumps-rubella vaccine, around the time they start kindergarten, they gain protection against all three viruses for all or most of their lives. Yet the effectiveness of an influenza vaccine given in October starts to wane by the following spring.
Scientists have long been stymied by why some vaccines can coax the body to produce antibodies for decades, while others last mere months. Now, a study led by researchers at Stanford Medicine has shown that variation in vaccine durability can, in part, be pinned on a surprising type ...
The nose knows: Nasal swab detects asthma type in kids
2025-01-02
Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh have developed a nasal swab test for kids that diagnoses specific asthma subtype, or endotype. This non-invasive approach could help clinicians prescribe medications more precisely and pave the way for research toward better treatments for lesser-studied asthma types, which have been difficult to diagnose accurately until now.
Published today in JAMA, the findings are based on data from three independent U.S.-based studies that focused on Puerto Rican and African American youths, who have higher rates of asthma and are more likely to die from the disease than their non-Hispanic white counterparts.
“Asthma ...
Knowledge and worry following review of standard vs patient-centered pathology reports
2025-01-02
About The Study: Most study participants could not extract basic information—including whether they have cancer—from standard prostate cancer pathology reports but were able to understand this diagnostic information from the patient-centered pathology reports (PCPRs). Also, they discriminated between risk levels (i.e., lower levels of perceived worry in the low-risk condition) with PCPRs compared with standard reports. Hospital systems should consider including PCPRs with standard pathology reports to improve patient understanding.
Corresponding ...
Cardiovascular disease and breast cancer stage at diagnosis
2025-01-02
About The Study: This case-control study found that individuals with more advanced breast cancer at diagnosis were more likely to have prevalent cardiovascular disease. This finding may be specific to hormone receptor–positive and ERBB2-negative (formerly HER2) disease. Future studies are needed to confirm these findings and investigate interventions to improve patient outcomes, including personalized cancer screening.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Kevin T. Nead, MD, MPhil, email ktnead@mdanderson.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.52890)
Editor’s ...
Herpes virus might drive Alzheimer's pathology, study suggests
2025-01-02
PITTSBURGH, Jan. 2, 2025 – University of Pittsburgh researchers uncovered a surprising link between Alzheimer’s disease and herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1), suggesting that viral infections may play a role in the disease. The study results are published today in Cell Reports.
The study also revealed how tau protein, often viewed as harmful in Alzheimer’s, might initially protect the brain from the virus but contribute to brain damage later. These findings could lead to new treatments targeting infections and the brain’s immune response.
“Our study challenges ...
Patients with heart disease may be at increased risk for advanced breast cancer
2025-01-02
HOUSTON ― Cardiovascular disease (CVD) and cancer are the two leading causes of death in the U.S. According to researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, patients diagnosed with late-stage or metastatic breast cancer have a statistically significant increased risk of pre-diagnosis CVD compared to those with early-stage cancer at diagnosis.
The study, published today in JAMA Network Open, found those with advanced breast cancer at diagnosis were 10% more likely to have had pre-existing ...
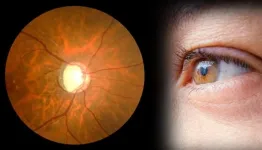
Chinese Medical Journal study reveals potential use of artificial intelligence (AI) in finding new glaucoma drugs
2025-01-02
Glaucoma is a progressive eye disorder characterized by fluid buildup inside the eye, causing ocular hypertension. By 2040, it is estimated that 111.8 million people worldwide will be affected by glaucoma, potentially leading to blindness if left untreated. Currently, there are treatments available to manage ocular hypertension, but a cure for glaucoma remains elusive.
Retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) are crucial for transmitting visual signals from the eyes to the brain, and their degeneration leads to optic nerve damage, which is a hallmark of glaucoma. In recent years, scientists ...
[1] ... [745]
[746]
[747]
[748]
[749]
[750]
[751]
[752]
753
[754]
[755]
[756]
[757]
[758]
[759]
[760]
[761]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.