New findings may help researchers develop a grapefruit devoid of compounds that affect medication levels
2025-01-08
Grapefruit and pummelo contain compounds called furanocoumarins that may affect the blood levels of more than 100 prescription drugs, so that people taking these medications are advised to remove these fruits from their diets. Research published in New Phytologist reveals genetic information about the synthesis of furanocoumarins in different citrus plant tissues and species and provides new insights that could be used to develop grapefruit and pummelo that lack furanocoumarins.
The research indicates that the production of furanocoumarins in citrus ...
Advanced wearable robot eases heavy lifting and other injury-causing tasks for workers
2025-01-08
In research published in Advanced Intelligence Systems, scientists have developed an innovative, soft, wearable robot to help workers avoid job-related injuries while lifting, lowering, and carrying objects.
While many available wearable robots are limited to supporting a single degree of freedom of the body (meaning the body can only move in one direction at a given joint), the new robot, called WeaRo, operates through multiple degrees of freedom, allowing for complex movements.
In tests, WeaRo effectively reduced the muscle activation levels of lumbar, biceps, and triceps muscles by a maximum of 18.2%, 29.1%, and ...
Does job strain compromise long-term sleep quality?
2025-01-08
In a recent study published in the American Journal of Industrial Medicine, middle aged workers in the U.S. who reported high job strain at the start of the study experienced significantly more sleep disturbances over an average follow-up of nine years.
The study analyzed data from 1,721 workers, with an average age of 51 years, who participated in the Midlife in the United States (MIDUS) study. Sleep disturbances were assessed with an established scale, based on four sleep-related symptoms: trouble falling asleep, waking up during ...
Artificial intelligence–based method assesses depression in business leaders
2025-01-08
Researchers have developed a novel method to assess depression in CEOs by using machine learning models (a type of artificial intelligence) to analyze vocal acoustic features from conference call recordings. This innovative approach, detailed in an article published in the Journal of Accounting Research, provides insights into a mental health issue that often remains hidden in high-pressure executive roles.
The researchers examined how CEO depression is related to career outcomes, compensation, and incentives. Their findings suggest ...
Study assesses the benefits of alfalfa-almond intercropping
2025-01-08
The practice of growing different but complementary plants within a given area, also known as intercropping, has numerous positive effects such as reduced soil erosion, weed suppression, nitrogen fixation (the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen to nitrogen compounds that can be used by plants and other organisms), and pollinator benefits. New research published in Agrosystems, Geosciences & Environment reveals the increased land use efficiency and environmental benefits in an alfalfa–almond intercropped ecosystem ...
Mediterranean sharks continue to decline despite conservation progress
2025-01-08
Overfishing, illegal fishing and increasing marketing of shark meat pose significant threats to the more than 80 species of sharks and rays that inhabit the Mediterranean Sea, according to a new study.
The research examined current levels of legislation in place to protect elasmobranch populations (which include sharks, rays and skates) within each of the 22 coastal states of the Mediterranean region.
Across those countries – stretching from Spain and Morocco in the west to Israel, Lebanon and Syria in the east – the researchers identified more than 200 measures that concern elasmobranchs in some ...
New treatment option for severe hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in children shows promise
2025-01-08
Trametinib, a mitogen-activated protein kinase (MEK) inhibitor, reduces mortality and morbidity in children with severe hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) caused by pathogenic variants in the RAS/MAPK pathway, according to a study published today in JACC: Basic to Translational Science. The study provides strong evidence for personalized treatment targeting the underlying genetic causes of RASopathies, a group of rare disorders that often lead to life-threatening cardiac complications.
“Our findings represent a breakthrough in the treatment of HCM in children, particularly those suffering from severe forms of the disease due to genetic variants in the RAS/MAPK ...
Repairing a domestication mutation in tomato leads to an earlier yield
2025-01-08
Genome editing with CRISPR-Cas is often associated with the induction of mutations. However, a team of researchers from the Swiss University of Lausanne now shows that it can also be used to repair natural mutations.
All living organisms mutate, which is a major driver of biodiversity and evolution. Humans have been domesticating plants for thousands of years, by selecting mutations that lead to favorable characteristics such as larger or more numerous fruits. However, this process often caused the ...
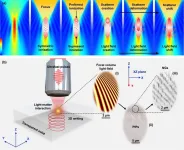
Focal volume optics for composite structuring in transparent solids
2025-01-08
For a long time, an ultrafast laser has been applied as a point-typed energy source to trigger various material modifications, and the profile of light intensity is mainly considered a Gaussian type. Therefore, the actual morphology and evolution of the light field in the focal volume have been overlooked.
In International Journal of Extreme Manufacturing, researchers indicates that the 3D spatial distribution of the light field at the focus can possess finer structures and is tunable, which offers a novel strategy for highly controllable micro-nano fabrication with more degrees of freedom beyond conventional point-by-point optical modification.
It is proposed and experimentally demonstrated ...
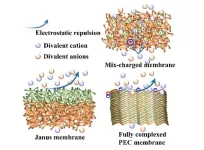
Novel mix-charged nanofiltration membrane developed for high-salinity wastewater treatment
2025-01-08
A research team led by Prof. WAN Yinhua at the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has recently developed an innovative mix-charged nanofiltration (NF) membrane featuring horizontal charge distribution, designed specifically for wastewater treatment. This novel membrane exhibits remarkable salt permeation and organic matter retention capabilities as well as antifouling properties, making it particularly effective for treating high-salinity organic wastewater.
The findings ...
Fishy business: Male medaka mating limits revealed
2025-01-08
Working out the kinks of mating in the animal kingdom helps to gain insights into the survival of species. Among animals that have multiple partners who deposit eggs outside their body, such as most fish, the males release sperm several times a day, but producing these gametes requires energy and time.
Osaka Metropolitan University experts on fish behavior have recently uncovered a daily mating capacity for medaka. In findings published in Royal Society Open Science, Graduate School of Science Specially Appointed Dr. Yuki Kondo, Specially Appointed Professor Masanori Kohda, and Professor Satoshi Awata detailed the effects of continuous mating by medaka ...
Morning coffee may protect the heart better than all-day coffee drinking
2025-01-08
People who drink coffee in the morning have a lower risk of dying from cardiovascular disease and a lower overall mortality risk compared to all-day coffee drinkers, according to research published in the European Heart Journal [1] today (Wednesday).
The research was led by Dr Lu Qi, HCA Regents Distinguished Chair and Professor at the Celia Scott Weatherhead School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine at Tulane University, New Orleans, USA. He said: “Research so far suggests that drinking coffee doesn’t raise the risk of cardiovascular disease, and it ...
For many low-income single moms, government aid serves as their paid family leave, study shows
2025-01-08
CORVALLIS, Ore. – The majority of low-income single mothers in Oregon who rely on federal cash assistance around the time of childbirth are in the program for less than a year, suggesting they’re using it as a form of paid family leave, Oregon State University research shows.
The first-of-its-kind study has important implications in the state, which in 2023 established a taxpayer-funded paid family leave program, and throughout the United States as poverty has a particularly high incidence among young children.
“Understanding how mothers ...
Tumor-secreted protein may hold the key to better treatments for deadly brain tumor, study finds
2025-01-08
A study co-led by UCLA scientists has found targeting a protein called endocan and its related signaling pathway could be a promising new approach for treating glioblastoma, an aggressive and lethal type of brain cancer.
The team of researchers discovered that endocan, which is produced by endothelial cells lining blood vessels in the tumor, activates PDGFRA, a receptor on glioblastoma cells that drives tumor growth and makes the cancer resistant to standard therapies such as radiation.
The discovery, published in Nature Communications, suggests a path toward the development of therapies that specifically inhibit ...
Ready to quit vaping in the new year? A new study uncovers the best ways
2025-01-08
A new study, co-led by a University of Massachusetts Amherst researcher, set out to identify the most effective strategies for helping people quit vaping. The findings, published today in the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, suggest that varenicline, a prescription medication often used to help people stop smoking, and text message-based interventions can help people quit.
“This is an area of research that is in its infancy, but is growing rapidly and organically from people who vape asking about help to quit vaping,” says senior author Jamie Hartmann-Boyce, assistant professor of health policy and management in the School ...
Regular physical activity before cancer diagnosis may lower progression and death risks
2025-01-08
Regular physical activity before a cancer diagnosis may lower the risks of both disease progression and death, suggests research published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
And even relatively low levels of physical activity may be advantageous, the findings indicate.
There is compelling evidence that physical activity has a key part to play in lowering the risk of death from cancer, but the evidence isn’t as conclusive for its role in disease progression, explain the researchers.
To explore this further, they analysed anonymised data from the Discovery Health Medical Scheme (DHMS), linked to the Vitality health promotion programme. The DHMS is the ...
Basking too long in a sauna without adequate hydration may risk heat stroke, doctors warn
2025-01-08
Basking too long in a sauna may put bathers at risk of heat stroke, particularly if they haven’t drunk enough water beforehand, warn doctors in the journal BMJ Case Reports, after treating a woman whose condition required admission to hospital.
Although relatively rare, heat stroke can be life threatening, even in the absence of various underlying risk factors, such as heart, lung, or neurological disease, and heavy drinking or taking a cocktail of prescription meds, they point out.
Heat stroke is defined as a sharp increase in core body temperature above ...
DNA adds new chapter to Indonesia’s layered human history
2025-01-08
A new study from the University of Adelaide and The Australian National University (ANU) has outlined the first genomic evidence of early migration from New Guinea into the Wallacea, an archipelago containing Timor-Leste and hundreds of inhabited eastern Indonesian islands.
The study, published in PNAS, addresses major gaps in the human genetic history of the Wallacean Archipelago and West Papuan regions of Indonesia – a region with abundant genetic and linguistic diversity that is comparable to the Eurasian ...
Many children and young people with diagnosable mental health disorders are not receiving timely help, says new research
2025-01-08
Children and young people with high levels of mental health needs are struggling to receive the help they need, or to have their difficulties recognised, according to a new study.
The STADIA trial, which is published in the Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, was led by experts from the School of Medicine at the University of Nottingham, and was funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR).
The large study, which spans different parts of England, involved 1,225 children and young people with emotional difficulties who had been referred to Child and Adolescent Mental Health Services (CAMHS) for help, and followed them up over 18 months to see ...
Dinosaurs roamed the northern hemisphere millions of years earlier than previously thought, according to new analysis of the oldest North American fossils
2025-01-08
MADISON — How and when did dinosaurs first emerge and spread across the planet more than 200 million years ago? That question has for decades been a source of debate among paleontologists faced with fragmented fossil records. The mainstream view has held that the reptiles emerged on the southern portion of the ancient supercontinent Pangea called Gondwana millions of years before spreading to the northern half named Laurasia.
But now, a newly described dinosaur whose fossils were uncovered by University of Wisconsin–Madison paleontologists is challenging ...
Breakthrough Durham University research offers new insights into quenching electrical waves in the heart
2025-01-08
-With images-
Scientists at Durham University have developed a theoretical framework to predict the efficacy of quenching of electrical pulses in excitable media, such as those found in the human heart.
This breakthrough could significantly accelerate the development of more efficient defibrillation techniques for treating cardiac arrhythmias.
The study, published in Physical Review E, addresses a longstanding challenge in understanding how stable excitation waves in systems like cardiac tissue can be effectively neutralised through small changes.
These electrical waves, when irregular, are thought to underly serious conditions such as fibrillation, ...
SLAC will play a key role in DOE’s new research centers for advancing next-generation microelectronics
2025-01-07
Around the globe day and night, the microelectronics behind much of modern technology help run computers, medical devices and state-of-the-art instruments that power scientific discoveries. But all of that technology consumes energy, and adding artificial intelligence to the mix increases our energy needs dramatically. Some experts caution that this pace of energy usage is unsustainable.
To tackle this challenge, the Department of Energy (DOE) has announced funding $179 million for three Microelectronics ...
Market researchers and online advertisers, are A-B tests leading you astray? A new study says they could be
2025-01-07
Researchers from Southern Methodist University and University of Michigan published a new Journal of Marketing study that examines platforms’ A-B testing of online ads and uncovers significant limitations that can create misleading conclusions about ad performance.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Where A-B Testing Goes Wrong: How Divergent Delivery Affects What Online Experiments Cannot (and Can) Tell You About How Customers Respond to Advertising” and is authored by Michael Braun and Eric M. Schwartz.
Consider a landscaping company whose designs focus ...
Research alert: Ketamine use on the rise in U.S. adults; new trends emerge
2025-01-07
A recent study analyzing data from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) found that past-year recreational ketamine use among adults has increased dramatically since 2015, including significant shifts in associations with depression and sociodemographic characteristics such as race, age and education status. Ketamine use has shown promise in clinical trials therapy for several mental illnesses, including treatment-resistant depression, and the new research suggests that ongoing monitoring of recreational use trends is crucial to balancing these ...
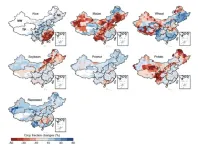
Crop switching for climate change in China
2025-01-07
A study of Chinese agriculture recommends planting areas currently growing maize and rapeseed with alternative crops to reduce environmental costs while maximizing food production as the climate changes.
Chinese food production has nearly doubled since the 1980s, mainly thanks to intensified nutrient usage and irrigation. Given that China’s demand for food is forecast to increase further, Qi Guan and colleagues modeled the country’s agricultural system under varying climate change scenarios in the 21st century, using a dynamic global vegetation model. The authors created scenarios ...
[1] ... [751]
[752]
[753]
[754]
[755]
[756]
[757]
[758]
759
[760]
[761]
[762]
[763]
[764]
[765]
[766]
[767]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.