Wildfire surges in East, Southeast US fueled by new trees and shrubs
2024-12-18
AGU press contact:
Liza Lester, +1 (202) 777-7494, news@agu.org (UTC-5 hours)
Researcher contact:
Victoria Donovan, University of Florida, victoria.donovan@ufl.edu (UTC-5 hours)
WASHINGTON — The eastern U.S. has more trees and shrubs than three decades ago. This growth, driven by processes such as tree and understory infilling in unmanaged forests, is helping fuel wildfires, contributing to changing fire regimes in the eastern half of the country, according to a new study.
Some parts of the eastern and southeastern United States have experienced a tenfold increase ...
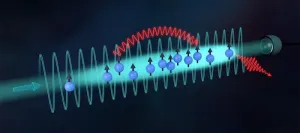
No cavity, no party: Free-space atoms give superradiant transition a pass
2024-12-18
Isolated atoms in free space radiate energy at their own individual pace. However, atoms in an optical cavity interact with the photons bouncing back and forth from the cavity mirrors, and by doing so, they coordinate their photon emission and radiate collectively, all in sync. This enhanced light emission before all the atoms reach the ground state is known as superradiance. Interestingly, if an external laser is used to excite the atoms inside the cavity moderately, the absorption of light by the atoms and the collective emission can ...
Women often told that severity of medical abortion pain no worse than period cramps
2024-12-18
Women opting for a medical abortion at home are often advised that the procedure is likely to be no more painful than period cramps, suggest the results of a survey, carried out by the British Pregnancy Advisory Service (BPAS), and published online in the journal BMJ Sexual & Reproductive Health.
This leaves many women unprepared for the intensity of the pain they experience, with some survey respondents saying they would have chosen a different option, had they known.
More realistic and patient centred information needs to be provided to enable women to make ...
Air pollution linked to increased hospital admissions for mental/physical illness
2024-12-18
Cumulative exposure to air pollution over several years is linked to a heightened risk of admission to hospital for mental/behavioural and physical illness, finds Scottish research published in the open access journal BMJ Open.
Stricter environmental restrictions are needed to curb the impact on secondary care, conclude the researchers.
Previously published research on the health effects of long term exposure to ambient air pollution has tended to emphasise deaths rather than hospital admissions, and physical, rather than mental, ill ...
Using drones, UH researchers assess the health of humpback whale mother-calf pairs across the Pacific Ocean
2024-12-17
In a groundbreaking study published this week in The Journal of Physiology, biologists at the Marine Mammal Research Program (MMRP) at the University of Hawaiʻi at Manoa Hawaiʻi Institute of Marine Biology (HIMB) used drone imagery to advance understanding of how lactating humpback whales and their calves fare as they traverse the Pacific Ocean. Recent declines in North Pacific humpback whale reproduction and survival of calves highlight an urgent need to understand how mother-calf pairs expend energy across their migratory ...
Allen Institute names Julie Harris, Ph.D., as new Vice President of The Paul G. Allen Frontiers Group
2024-12-17
SEATTLE, WASH.—December 17, 2024—The Allen Institute today announced the appointment of Julie Harris as the new Vice President of The Paul G. Allen Frontiers Group. Harris was previously Executive Vice President of Research Management at the Cure Alzheimer’s Fund where she oversaw the funding strategy and research priorities for a ~$29 million grant portfolio in support of the most promising science and scientists working to end the burden of Alzheimer’s disease.
Between 2011 and 2020 Harris worked at the Allen Institute for Brain Science as ...
Bad bacteria can trigger painful gut contractions; new research shows how
2024-12-17
Downloadable assets for media use:
https://uoregon.canto.com/b/MSHJ8
EUGENE, Ore. — Dec. 18, 2024 — After a meal of questionable seafood or a few sips of contaminated water, bad bacteria can send your digestive tract into overdrive. Your intestines spasm and contract, efficiently expelling everything in the gut — poop and bacteria alike.
A new study from the University of Oregon shows how one kind of bacteria, Vibrio cholerae, triggers those painful contractions by activating the immune system. The research also finds a more general explanation for how the gut rids itself of unwanted intruders, which could also help scientists ...
Partnership advances targeted therapies for blood cancers
2024-12-17
Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah (the U) has joined other institutions in an innovative clinical trials program designed to match patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) with a clinical trial specifically designed for the genetic signature of their disease. Sponsored by the National Cancer Institute (NCI), the myeloMATCH program aims to improve precision medicine, the use of therapies ...
How loss of urban trees affects education outcomes
2024-12-17
It’s well established that urban tree cover provides numerous environmental and psychological benefits to city dwellers. Urban trees may also bolster education outcomes and their loss could disproportionately affect students from low-income families, according to new research by University of Utah social scientists.
Economics professor Alberto Garcia looked at changes in school attendance and standardized test scores at schools in the Chicago metropolitan region over the decade after a non-native ...
New virtual reality-tested system shows promise in aiding navigation of people with blindness or low vision
2024-12-17
A new study offers hope for people who are blind or have low vision (pBLV) through an innovative navigation system that was tested using virtual reality. The system, which combines vibrational and sound feedback, aims to help users navigate complex real-world environments more safely and effectively.
The research from NYU Tandon School of Engineering, published in JMIR Rehabilitation and Assistive Technology, advances work from John-Ross Rizzo, Maurizio Porfiri and colleagues toward developing a first-of-its-kind ...
Brain cells remain healthy after a month on the International Space Station, but mature faster than brain cells on Earth
2024-12-17
LA JOLLA, CA—Microgravity is known to alter the muscles, bones, the immune system and cogni­tion, but little is known about its specific impact on the brain. To discover how brain cells respond to microgravity, Scripps Research scientists, in collaboration with the New York Stem Cell Foundation, sent tiny clumps of stem-cell derived brain cells called “organoids” to the International Space Station (ISS).
Surprisingly, the organoids were still healthy when they returned from orbit a month later, but the cells had matured faster compared ...
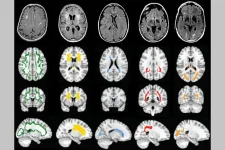
NIH grant funds study of cerebral small vessel disease
2024-12-17
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have been awarded $7.5 million from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to investigate a form of dementia caused by cerebral small vessel disease, the second-leading cause of dementia after Alzheimer’s disease.
The grant funds the Vascular Contributions to Cognitive Impairment and Dementia (VCID) Center, which is a National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke “Center Without Walls” initiative that will coordinate researchers at six sites across ...
Paranoia may be, in part, a visual problem
2024-12-17
New Haven, Conn. — Could complex beliefs like paranoia have roots in something as basic as vision? A new Yale study finds evidence that they might.
When completing a visual perception task, in which participants had to identify whether one moving dot was chasing another moving dot, those with greater tendencies toward paranoid thinking (believing others intend them harm) and teleological thinking (ascribing excessive meaning and purpose to events) performed worse than their counterparts, the study found. Those individuals more often — and confidently — claimed one dot was chasing the other when it wasn’t.
The findings, published Dec. 17 in ...
The high cost of carbon
2024-12-17
The social cost of carbon — an important figure that global policymakers use to analyze the benefits of climate and energy policies — is too low, according to a study led by the University of California, Davis.
The study, published today in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), shows that current estimates for the social cost of carbon, or SCC, fail to adequately represent important channels by which climate change could affect human welfare. When included, the SCC increases to just over $280 per ton of CO2 emitted in 2020 — more than double the ...
This mysterious plant fossil belongs to a family that no longer exists
2024-12-17
In 1969, fossilized leaves of the species Othniophyton elongatum — which translates to “alien plant” — were identified in eastern Utah. Initially, scientists theorized the extinct species may have belonged to the ginseng family (Araliaceae). However, a case once closed is now being revisited. New fossil specimens show that Othniophyton elongatum is even stranger than scientists first thought.
Steven Manchester, curator of paleobotany at the Florida Museum of Natural History, has studied 47-million-year-old fossils from Utah for several years. While visiting ...
Physicists ‘bootstrap’ validity of string theory
2024-12-17
String theory, conceptualized more than 50 years ago as a framework to explain the formation of matter, remains elusive as a “provable” phenomenon. But a team of physicists has now taken a significant step forward in validating string theory by using an innovative mathematical method that points to its “inevitability.”
String theory posits that the most basic building blocks of nature are not particles, but, rather, one-dimensional vibrating strings that move at different frequencies ...
Parents’ childhood predicts future financial support for children’s education
2024-12-17
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Childhood circumstances, such as parental divorce or growing up poor, have been shown to influence health and other outcomes later in life. But does a person’s experiences in childhood also influence their future ability to provide financial support to their children?
According to a new study from a researcher from Penn State, parents who endured difficult childhoods provided less financial support to their children’s education such as college tuition compared to parents who experienced few or no disadvantages. Regardless of current socioeconomic ...
SFU study sheds new light on what causes long-term disability after a stroke and offers new path toward possible treatment
2024-12-17
A recent study from Simon Fraser University researchers has revealed how an overlooked type of indirect brain damage contributes to ongoing disability after a stroke.
The paper, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, shows how the thalamus – a sort of central networking hub that regulates functions such as language, memory, attention and movement – is affected months or years after a person has experienced a stroke, even though it was not directly damaged itself. The findings may lead to new therapies that could reduce the burden of chronic stroke, which remains one of the leading causes of disability in the world.
“Our ...
More calories – more consumption: Individuals with and without obesity both prefer high-calories food
2024-12-17
Higher calorie foods were preferred among individuals with and without obesity despite similar taste and texture, according to a study published December 17th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Albino Oliveira-Maia from the Champalimaud Foundation, Portugal, and colleagues.
Eating sends signals to the brain with information about a food’s energy content, which can influence food preferences irrespective of flavor. People with obesity often have impairments in areas of the brain where dopamine ...
Astrophysics: Mystery of the ‘missing’ binary stars solved
2024-12-17
An international team of researchers led by PD Dr Florian Peißker has found the first binary star in the immediate vicinity of the supermassive black hole Sgr A* (Sagittarius A star) at the centre of our galaxy. Although it is known that most stars in the universe do not form alone, so far there are only five confirmed binary stars at a greater distance from the black hole. None of the systems are so close. The researchers assume that the binary star system they found, named D9, will merge into a single star in the near future. The discovery was published in Nature Communications under the title ‘A binary ...
Peptide-guided nanoparticles deliver mRNA to neurons
2024-12-17
Penn Engineers have modified lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) — the revolutionary technology behind the COVID-19 mRNA vaccines — to not only cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB) but also to target specific types of cells, including neurons. This breakthrough marks a significant step toward potential next-generation treatments for neurological diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
In a new paper in Nano Letters, the researchers demonstrate how peptides — short strings of amino ...
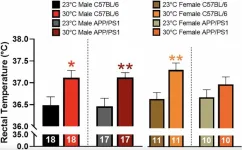
Sexual dimorphism in thermotherapy responses in APP/PS1 mice
2024-12-17
“Passive thermotherapy positively modulates multiple physiological parameters and represents a nonpharmacological approach for potential disease modifying treatment.”
BUFFALO, NY- December 17, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 21 on November 29, 2024, entitled, “Thermotherapy has sexually dimorphic responses in APP/PS1 mice.”
Researchers Samuel A. McFadden, Mackenzie R. Peck, Lindsey N. Sime, MaKayla F. Cox, Erol D. Ikiz, Caleigh A. Findley, ...
First ever binary star found near our galaxy’s supermassive black hole
2024-12-17
An international team of researchers has detected a binary star orbiting close to Sagittarius A*, the supermassive black hole at the centre of our galaxy. It is the first time a stellar pair has been found in the vicinity of a supermassive black hole. The discovery, based on data collected by the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope (ESO’s VLT), helps us understand how stars survive in environments with extreme gravity, and could pave the way for the detection of planets close to Sagittarius A*.
“Black holes are not as destructive as we thought,” says Florian Peißker, a researcher at the University of Cologne, Germany, and lead author of the ...
Training solar panels to dance with the wind
2024-12-17
WASHINGTON, Dec. 17, 2024 – Solar power is currently the fastest growing energy sector worldwide. Solar photovoltaic power plants convert sunlight into electricity and their vast potential for producing clean, renewable energy make solar power a cornerstone of the NetZero Emissions by 2050 initiative, which seeks to cut carbon dioxide emissions to zero by the year 2050.
Wind has both positive and negative effects on solar power grids. It helps maintain solar panel performance by eliminating the buildup of dirt and dust, and ...
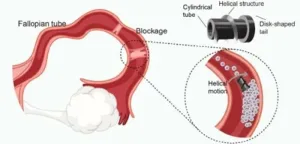
Tiny robots, big impact: Revolutionizing infertility treatment with magnetic microrobots
2024-12-17
WASHINGTON, Dec. 17, 2024 — Infertility affects an estimated 186 million people worldwide, with fallopian tube obstruction contributing to 11%-67% of female infertility cases. In AIP Advances, from AIP Publishing, researchers at the SIAT Magnetic Soft Microrobots Lab have developed an innovative solution using a magnetically driven robotic microscrew to treat fallopian tube blockages.
“This new technology offers a potentially less invasive alternative to the traditional surgical methods currently used to clear tubal obstructions, which often involve ...
[1] ... [759]
[760]
[761]
[762]
[763]
[764]
[765]
[766]
767
[768]
[769]
[770]
[771]
[772]
[773]
[774]
[775]
... [8824]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.