University of Iowa study traces Ebola's route to the skin surface
2025-01-01
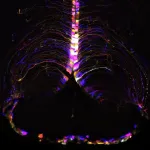
Ebola is a deadly hemorrhagic disease caused by a virus that is endemic in parts of East-Central and West Africa. Most people are aware that a primary route for person-to-person transmission is through contact with bodily fluids from an infected person. But more recent outbreaks, including the 2013-2016 Ebola epidemic in West Africa, demonstrated that infectious Ebola virus (EBOV) is also found on the skin’s surface of those who have succumbed to infection or at late times during infection. Although evidence suggests that EBOV can be passed on from skin contact with a person in the later stages of the disease, very little is known about how the virus makes its way out ...
Study finds smoking linked to increased risk of chronic kidney disease in later stages
2025-01-01
A recent study published in Health Data Science led by Zhilong Zhang from the Institute of Medical Technology at Peking University Health Science Center and Professor Luxia Zhang from the National Institute of Health Data Science at Peking University has shed light on the complex relationship between smoking behavior and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Using data from over 500,000 participants in the UK Biobank cohort, the researchers conducted both traditional observational studies and advanced Mendelian randomization (MR) analyses to explore whether smoking behavior ...
System to auto-detect new variants will inform better response to future infectious disease outbreaks
2025-01-01
Researchers have come up with a new way to identify more infectious variants of viruses or bacteria that start spreading in humans - including those causing flu, COVID, whooping cough and tuberculosis.
The new approach uses samples from infected humans to allow real-time monitoring of pathogens circulating in human populations, and enable vaccine-evading bugs to be quickly and automatically identified. This could inform the development of vaccines that are more effective in preventing disease.
The approach can also quickly detect ...
Key players in brain aging: New research identifies age-related damage on a cellular level
2025-01-01
SEATTLE, WASH.—January 1, 2025—Scientists at the Allen Institute have identified specific cell types in the brain of mice that undergo major changes as they age, along with a specific hot spot where many of those changes occur. The discoveries, published in the journal Nature, could pave the way for future therapies to slow or manage the aging process in the brain.
Key findings
Sensitive cells: Scientists discovered dozens of specific cell types, mostly glial cells, known as brain support cells, that underwent significant gene expression changes with age. Those strongly affected included microglia and border-associated ...
Pupil size in sleep reveals how memories are sorted, preserved
2025-01-01
ITHACA, N.Y. – Cornell University researchers have found the pupil is key to understanding how, and when, the brain forms strong, long-lasting memories.
By studying mice equipped with brain electrodes and tiny eye-tracking cameras, the researchers determined that new memories are being replayed and consolidated when the pupil is contracted during a substage of non-REM sleep. When the pupil is dilated, the process repeats for older memories. The brain’s ability to separate these two substages of sleep with a previously unknown micro-structure is what ...
Revealing a key mechanism of rapid centromere evolution
2025-01-01
A joint research group team led by Sayuri Tsukahara and Tetsuji Kakutani of the University of Tokyo has clarified a mechanism of how retrotransposons, genetic elements that can “jump around” chromosomes and are known drivers of evolution, preferentially insert in the centromere. The findings were published in the journal Nature.
The centromere is the thinnest part of the chromosome that divides it into a long and short arm, much like how the waist separates the upper and lower body. Its role in transmitting information via cell division has been preserved ...
A tour de force: Columbia engineers discover new “all-optical” nanoscale sensors of force
2025-01-01
New York, NY—January 1, 2025—Mechanical force is an essential feature for many physical and biological processes. Remote measurement of mechanical signals with high sensitivity and spatial resolution is needed for a wide range of applications, from robotics to cellular biophysics and medicine and even to space travel. Nanoscale luminescent force sensors excel at measuring piconewton forces, while larger sensors have proven powerful in probing micronewton forces. However, large gaps remain in the force magnitudes that can be probed remotely from subsurface ...
Ancient DNA unlocks new understanding of migrations in the first millennium AD
2025-01-01
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 16:00 GMT Wednesday 1 January 2025
Peer reviewed
Observational study
Ancient people
Ancient DNA unlocks new understanding of migrations in the first millennium AD
Waves of human migration across Europe during the first millennium AD have been revealed using a more precise method of analysing ancestry with ancient DNA, in research led by the Francis Crick Institute.
Researchers can bring together a picture of how people moved across the world by looking at changes in their DNA, but this becomes a lot harder when historical ...
MIT scientists pin down the origins of a fast radio burst
2025-01-01
Fast radio bursts are brief and brilliant explosions of radio waves emitted by extremely compact objects such as neutron stars and possibly black holes. These fleeting fireworks last for just a thousandth of a second and can carry an enormous amount of energy — enough to briefly outshine entire galaxies.
Since the first fast radio burst (FRB) was discovered in 2007, astronomers have detected thousands of FRBs, whose locations range from within our own galaxy to as far as 8 billion light-years away. Exactly how ...
Researchers reveal why the lung is a frequent site of cancer metastasis
2025-01-01
Leuven, 2 January 2024 – Researchers from the lab of Prof. Sarah-Maria Fendt (VIB-KU Leuven) and colleagues have uncovered that the availability of the amino acid aspartate is one reason why the lung is a frequent organ of metastasis. Their work appears in Nature and improves our understanding of cancer biology while providing the foundation for new therapeutic interventions in metastatic diseases.
A role for aspartate
More than half of cancer patients in whom the cancer spreads beyond the primary site have lung metastases. What makes the lungs such a ...
Aging may change some brain cells more than others
2025-01-01
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE: Jan. 1, 2025, 11 a.m. ET
CONTACT:
NIAPressTeam@mail.nih.gov, 301-496-1752
Aging may change some brain cells more than others
NIH-funded mouse study provides roadmap for how aging may alter brain cell genetic activity
Based on new brain mapping research funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), scientists have discovered that not all cell types in the brain age in the same way. They found that some cells, such as a small group of hormone-controlling cells, may undergo more age-related changes in genetic activity than others. The results, published ...
Special issue of APA’s official journal focuses on psychedelic medication
2025-01-01
WASHINGTON, D.C., Jan. 1, 2025—As the body of research grows around the potential promise of psychedelic medications in psychiatry, many questions and challenges remain. The January issue of the American Journal of Psychiatry features a series of articles, including new research, reviews and commentaries, on the use of these treatments.
The issue addresses many of the ongoing challenges and looming questions in the field of psychiatric psychedelic research and treatment. These include issues relevant to basic ...
Geneticist unlocks mysteries of childhood psychiatric disorders through innovative research
2024-12-31
TORONTO, Ontario, Canada, 31 December 2024 - In a comprehensive Genomic Press Interview, leading geneticist Dr. Cathy Barr unveils crucial discoveries about the complex interplay between genes and childhood psychiatric disorders. As a Senior Scientist at both the Hospital for Sick Children and Krembil Research Institute, Dr. Barr's research illuminates the genetic foundations of conditions including depression, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, reading disabilities, and Tourette syndrome.
"After decades of searching ...
New study uncovers key insights into protein interactions in Duchenne muscular dystrophy, paving way for more targeted therapies
2024-12-31
AURORA, Colo. (Dec. 31, 2024) – A groundbreaking study has shed light on the complex interactions between dystrophin, a protein critical to muscle stability, and its partner protein, dystrobrevin, offering new pathways for understanding and treating Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD).
Published in the December issue of the Journal of Biological Chemistry, researchers characterize the mysterious C-terminal (CT) domain of dystrophin and its role in stabilizing cellular membranes across various tissues.
DMD, a severe genetic disorder that causes muscle weakness and shortens lifespans, arises from mutations in the gene encoding ...
Revolutionizing fragrance design using deep neural networks (DNNs) scent profiles from chemical data
2024-12-31
Scientific research explores the potential of DNNs in transforming fragrance design. By analyzing the sensing data of 180 essential oils, the DNN was trained using the odor descriptor data from 94 essential oils to generate fragrance profiles, validated through sensory evaluations to align with human olfactory perceptions. The study underscores the technological ability to streamline fragrance creation, reduce costs, and foster innovation, opening up exciting possibilities for personalized and scalable scent development.
Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) have become an essential driver of innovation across various industries, ...
Custom-fit bone grafts: the future of craniomaxillofacial surgery
2024-12-31
A recent review is transforming the landscape of craniomaxillofacial bone regeneration with the introduction of personalized bioceramic grafts. This pioneering research explores the fabrication and clinical potential of synthetic grafts created through additive manufacturing (AM), addressing key limitations of traditional autogenous grafts. By focusing on 3D-printed bioceramics tailored to meet individual patient needs, the study marks a significant advancement in both precision medicine and patient-specific care, offering new hope for those requiring bone reconstruction.
Craniofacial bone defects, resulting from trauma, congenital conditions, or surgical ...
A new ‘molecular lantern’ detects brain metastasis in mice by inserting a probe thinner than a hair into the brain
2024-12-31
Monitoring the changes caused in the brain at the molecular level by cancer and other neurological pathologies in a non-invasive way is one of the great challenges of biomedical research. A new technique, still in the experimental stage, achieves this by introducing light into the brains of mice using a very thin probe. The innovation, which is published today in the journal Nature Methods, is ledby an international team including groups from the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) and the Spanish National Cancer Research ...
McGill scientist reveals how early life experiences reshape our genes and brain health
2024-12-31
MONTREAL, Quebec, Canada, 31 December 2024 - In a comprehensive Genomic Press Interview, renowned neuroscientist Dr. Michael Meaney reveals pivotal discoveries about the intricate relationship between genes and environment in shaping brain health. As a James McGill Professor Emeritus and former Director of the Translational Neuroscience program at ASTAR Singapore, Dr. Meaney's research has fundamentally altered our understanding of how early-life experiences influence genetic expression and brain development.
"I have always been genuinely fascinated ...
Renowned scientist reveals vital link between inflammation and depression through groundbreaking research
2024-12-31
JERUSALEM, Israel, 31 December 2024 - In a comprehensive Genomic Press Interview, distinguished neuroscientist Professor Raz Yirmiya unveils transformative insights into the relationship between inflammation and depression. As head of the Laboratory for Psychoneuroimmunology at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Professor Yirmiya's work has fundamentally changed our understanding of depression's biological underpinnings.
"Most depressed patients do not have any overt inflammatory disease. However, we and others found that exposure to stress, which is the most significant trigger of depression in humans and animals, also ...
Medical researcher explores economic impact of psychedelic therapy implementation
2024-12-31
ATLANTA, Georgia, USA, 31 December 2024 - In a comprehensive Genomic Press Interview, Emory University MD candidate Fayzan Rab shares insights into his pioneering research on the economic and public health implications of psychedelic therapy implementation. Rab's work at the Emory Center for Psychedelics and Spirituality bridges the gap between clinical research and real-world healthcare delivery systems.
"It would be a fool's errand to say that psychedelic therapies alone would change that," says Rab, discussing mental healthcare challenges. "Treating mental illness will require changes within clinical practice but also investments into social safety ...
Improving immunotherapies for kidney cancer
2024-12-30
A Medical University of South Carolina Hollings Cancer Center researcher is exploring new ways to improve treatment options for kidney cancer patients. With funding from a Department of Defense (DOD) Academy of Kidney Cancer Investigators Early Career Scholar Award, Aguirre de Cubas, Ph.D., will investigate how the immune system can be boosted to detect and kill kidney tumors. Congress established the award in 2017 to support research with high potential impact and exceptional scientific merit. De Cubas’ approach focuses on reactivating the immune system to recognize and target cancer cells better, offering new possibilities for improving existing ...
Billing patients for portal messages could decrease message volume and ease physician workload
2024-12-30
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 30 December 2024
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, ...
Study of Sherpas highlights key role of kidneys in acclimatization to high altitudes
2024-12-30
(Calgary) — A study from a Mount Royal University physiologist and his team demonstrates the key role of the kidneys in acclimatization to high altitude, and illustrates another way that Sherpas are better adapted to high altitude ascent.
Results from the study were recently published in in the prestigious international science journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The paper, “Comparing integrative ventilatory and renal acid-base acclimatization in lowlanders and Tibetan highlanders during ascent to 4,300 m”, describes findings ...
Smartphone app can help reduce opioid use and keep patients in treatment, UT Health San Antonio study shows
2024-12-30
SAN ANTONIO, Dec. 30, 2024 – Patients with opioid use disorder can reduce their days of opioid use and stay in treatment longer when using a smartphone app as supportive therapy in combination with medication, a new study by The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio) shows.
The cohort study of 600 underserved patients found that those who chose to use the app – which combines contingency management behavioral therapy and recovery support from peers – and alongside medication, reduced their days of opioid use by 35% compared with ...
Improved health care value cannot be achieved by hospital mergers and acquisitions alone
2024-12-30
Key Takeaways
A new study finds little evidence that hospital mergers and acquisitions reduce costs or improve quality of care.
More strategic quality improvement efforts are needed for patients to benefit from health care integration.
CHICAGO (December 30, 2024) — Mergers and acquisitions of U.S. hospitals and health systems rarely improve the quality of care delivered or result in lower health care costs and prices, according to a study published in the Journal of the American College of Surgeons (JACS).
The study, a systematic review of hundreds of published ...
[1] ... [755]
[756]
[757]
[758]
[759]
[760]
[761]
[762]
763
[764]
[765]
[766]
[767]
[768]
[769]
[770]
[771]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.