Deep learning designs proteins against deadly snake venom
2025-01-15
New proteins not found in nature have now been designed to counteract certain highly poisonous components of snake venom. The deep learning, computational methods for developing these toxin-neutralizing proteins offer hope for creating safer, more cost-effective and more readily available therapeutics than those currently in use.
Each year more than 2 million people suffer snakebites. More than 100,000 of them die, according to the World Health Organization, and 300,000 suffer severe complications and lasting disability ...
A new geometric machine learning method promises to accelerate precision drug development
2025-01-15
Proteins are the foundation of all life we currently know. With their virtually limitless diversity, they can perform a broad variety of biological functions, from delivering oxygen to cells and acting as chemical messengers to defending the body against pathogens. Furthermore, most biochemical reactions are only possible thanks to enzymes, a special type of protein catalysts.
The molecular surface of proteins is the key to their function, such as docking small molecules or other proteins or driving ...
Ancient genomes reveal an Iron Age society centred on women
2025-01-15
An international team of geneticists, led by those from Trinity College Dublin, has joined forces with archaeologists from Bournemouth University to decipher the structure of British Iron Age society, finding evidence of female political and social empowerment.
The researchers seized upon a rare opportunity to sequence DNA from many members of a single community. They retrieved over 50 ancient genomes from a set of burial grounds in Dorset, southern England, in use before and after the Roman Conquest of AD 43. The results revealed that this community was centred around bonds of female-line descent.
Dr Lara Cassidy, Assistant Professor in Trinity’s Department of Genetics, led ...
How crickets co-exist with hostile ant hosts
2025-01-15
Researchers at Nagoya University in Japan have discovered sophisticated behavioral strategies that enable parasitic crickets to survive within ant colonies. Led by Ryoya Tanaka, the team documented how these insects successfully navigate life among potentially lethal hosts through precise evasion tactics. Their findings, published in Communications Biology, reveal remarkable adaptations that allow these cricket species to thrive in a hostile environment.
Animals that live in ant colonies, known as “ant guests”, exploit their hosts’ resources. However, this ...
Tapered polymer fibers enhance light delivery for neuroscience research
2025-01-15
WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed a reliable and reproducible way to fabricate tapered polymer optical fibers that can be used to deliver light to the brain. These fibers could be used in animal studies to help scientists better understand treatments and interventions for various neurological conditions.
The tapered fibers are optimized for neuroscience research techniques, such as optogenetic experiments and fiber photometry, which rely on the interaction between genetically modified neurons and visible light delivered to and/or collected from the brain.
“Unlike standard optical fibers, which are cylindrical, the tapered fibers we developed have a conical shape, which ...
Syracuse University’s Fran Brown named Paul “Bear” Bryant Newcomer Coach of the Year Award recipient
2025-01-15
HOUSTON, January 15, 2025 — The American Heart Association has named Syracuse University’s Fran Brown as the recipient of the 2024 Paul “Bear” Bryant Newcomer Coach of the Year Award. This award celebrates the achievements of an individual who has not had any previous head coaching experience at the NCAA Division I football sub-division (FBS) level.
Coach Brown will be recognized with the honor during the 2025 Bear Bryant Awards on January 22.
After being named Syracuse’s 31st head coach on November 28, 2023, Brown immediately instilled a culture of ...
DARPA-ABC program supports Wyss Institute-led collaboration toward deeper understanding of anesthesia and safe drugs enabling anesthesia without the need for extensive monitoring
2025-01-15
By Benjamin Boettner
(BOSTON) — Currently, no anesthetic compound or cocktail can be used safely outside of a hospital facility. This is because current drugs impair the brain and central nervous system’s ability to regulate a number of vital processes, including respiration, body temperature, and heart rate in addition to creating a state of unconsciousness or sedation, making the strict monitoring of patients with the help of sophisticated instruments and highly-trained clinical personnel an absolute necessity. To reduce trauma associated with injuries and improve combat casualty outcomes, under a new DARPA-ABC contract ...
The Offshore Wind Innovation Hub 2025 call for innovators opens today
2025-01-15
The Offshore Wind Innovation Hub today announced the opening of its 2025 application process, designed to identify and support entrepreneurial and innovative companies that will help unleash the potential of the dynamic emerging offshore wind industry.
Winners take on a six-month mentoring and business development program residency designed to prepare them for strategic partnerships with major offshore wind developers and to be part of the larger offshore wind value chain. The program aims to enable innovators to overcome barriers ...
Aligning Science Across Parkinson’s (ASAP) launches a new funding opportunity to join the Collaborative Research Network
2025-01-15
The Aligning Science Across Parkinson’s (ASAP) initiative opened applications for members of the research community to apply to join the Collaborative Research Network (CRN) 2025 Scientific Track. The new Scientific Track grants will support collaborative research teams focused on dissecting the mechanisms that contribute to Parkinson’s disease (PD) heterogeneity across one of six focus areas listed below, offering funding of up to $3 million per year over three years.
Examining PD in the context of aging
Understanding how co-pathologies can influence PD pathogenesis and progression
Dissecting ...
State-of-the-art fusion simulation leads three scientists to the 2024 Kaul Foundation Prize
2025-01-15
Three scientists were awarded the 2024 Kaul Foundation Prize for Excellence in Plasma Physics Research and Technology Development based on their decades of groundbreaking research about how plasma behaves in fusion reactors.
Choongseok (CS) Chang, Seung-Hoe Ku and Robert Hager of the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) were recognized “for experimentally validated simulations of turbulence-broadened divertor heat flux widths using the X-Point Included Gyrokinetic Code (XGC),” following decades of research developing comprehensive simulations to model the fusion plasma edge.
Recently, ...
Davos Alzheimer's Collaborative launches innovative brain health navigator program for intuitive coordination between patients and providers
2025-01-15
The Davos Alzheimer’s Collaborative (DAC), a pioneering worldwide initiative seeking to cure Alzheimer’s disease and improve brain health, today announced the launch of its Brain Health Navigator program. The initiative led by the DAC Healthcare System Preparedness (DAC-SP) team will provide resources for patients and providers at six sites across the U.S.
Despite Alzheimer’s status as a growing worldwide epidemic, pathways for accurate diagnosis and evidence based interventions including new therapies are either underdeveloped or non-existent. ...
Media registration now open: ATS 2025 in San Francisco
2025-01-15
New York, NY – Jan. 15, 2025 –We are excited to welcome you to San Francisco for the ATS 2025 International Conference! Journalists will have access to leaders, as well as emerging scientists and clinicians, who are at the forefront of medical breakthroughs and clinical innovation in pulmonary, critical care and sleep medicine.
Join us beginning Sunday, May 18* through Wednesday, May 21. Register now and check out our Program at a Glance.
As always, you are welcome to contact the ATS communications and marketing director about scientific sessions and expert interviews whether you are joining us in person or from your (home) office. Registered ...
New study shows that corn-soybean crop rotation benefits are extremely sensitive to climate
2025-01-15
MINNEAPOLIS / ST. PAUL (01/15/2024) — A study by researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities offers new insights into how alternating corn and soybean crops can help increase crop yield in a changing climate.
The research is published in the peer-reviewed scientific journal Global Change Biology.
Rising temperatures and weather extremes are threatening global food security, making it crucial to understand how sustainable practices like crop rotation can help improve agricultural yields and resilience.
The study found that the benefits to corn-soybean rotation, compared to continuous corn year after year, are extremely sensitive to ...
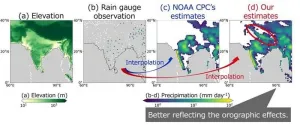
From drops to data: Advancing global precipitation estimates with the LETKF algorithm
2025-01-15
With the increase in climate change, global precipitation estimates have become a necessity for predicting water-related disasters like floods and droughts, as well as for managing water resources. The most accurate data that can be used for these predictions are ground rain gauge observations, but it is often challenging due to limited locations and sparse rain gauge data. To solve this problem, Assistant Professor Yuka Muto from the Center for Environmental Remote Sensing, Japan, and Professor Shunji Kotsuki of the Institute for Advanced Academic Research, Center for Environmental Remote Sensing, ...
SeoulTech researchers propose a novel method to shed light on PFOS-induced neurotoxicity
2025-01-15
The term “omics” refers to the study of entirety of molecular mechanisms that happen inside an organism. With the advent of omics technologies like transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and lipidomics, our understanding of molecular pathways of toxic environmental pollutants has deepened. But most environmental toxicology studies are still dependent on a single-omics analyses, leading to gaps in our understanding of integrated toxicity pathways of pollutants. Researchers from all over the world have ...
Large-scale TMIST breast cancer screening trial achieves enrollment goal, paving the way for data that provides a precision approach to screeninge
2025-01-15
The Tomosynthesis Mammographic Imaging Screening Trial (TMIST) has reached its enrollment goal of 108,508 women, as announced today by the ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (ECOG-ACRIN). The study, funded by the National Cancer Institute (NCI), one of the National Institutes of Health, will now proceed with the completion of regularly scheduled mammograms and follow-up on all participants through 2027. Key in this follow-up is the collection of biospecimens and data that will help researchers learn how to personalize breast cancer screening for women.
Participants in TMIST were randomly ...
Study published in NEJM Catalyst finds patients cared for by MedStar Health’s Safe Babies Safe Moms program have better outcomes in pregnancy, delivery, and postpartum
2025-01-15
WASHINGTON - Women who were cared for by the MedStar Health D.C. Safe Babies Safe Moms program (SBSM) have better outcomes in pregnancy, delivery, and postpartum, according to a study published today in NEJM Catalyst Innovations in Care Delivery. Additionally, the study showed that Black patients cared for by SBSM were also less likely to have low or very low birthweight babies or preterm birth than Black or White patients who received prenatal care elsewhere.
Compared to patients who received prenatal care elsewhere, patients cared for under Safe ...
Octopus arms have segmented nervous systems to power extraordinary movements
2025-01-15
Octopus arms move with incredible dexterity, bending, twisting, and curling with nearly infinite degrees of freedom. New research from the University of Chicago revealed that the nervous system circuitry that controls arm movement in octopuses is segmented, giving these extraordinary creatures precise control across all eight arms and hundreds of suckers to explore their environment, grasp objects, and capture prey.
“If you're going to have a nervous system that's controlling such dynamic movement, that's a good way to set it up,” said Clifton Ragsdale, PhD, Professor of Neurobiology at UChicago and senior author ...
Protein shapes can help untangle life’s ancient history
2025-01-15
The three-dimensional shape of a protein can be used to resolve deep, ancient evolutionary relationships in the tree of life, according to a study in Nature Communications.
It is the first time researchers use data from protein shapes and combine it with data from genomic sequences to improve the reliability of evolutionary trees, a critical resource used by the scientific community for understanding the history of life, monitor the spread of pathogens or create new treatments for disease.
Crucially, the approach works even with the ...
Memory systems in the brain drive food cravings that could influence body weight
2025-01-15
PHILADELPHIA, PA (January 15, 2025) - Can memory influence what and how much we eat? A groundbreaking Monell Chemical Senses Center study, which links food memory to overeating, answered that question with a resounding “Yes.” Led by Monell Associate Member Guillaume de Lartigue, PhD, the research team identified, for the first time, the brain’s food-specific memory system and its direct role in overeating and diet-induced obesity.
Published in Nature Metabolism, they describe a specific population of neurons in the mouse brain that encode memories for sugar and fat, profoundly impacting food intake and body ...
Indigenous students face cumbersome barriers to attaining post-secondary education
2025-01-15
Indigenous students identified inadequate funding as a major barrier to completing post-secondary education according to a new study published in AlterNative: An International Journal of Indigenous Peoples.
The study surveyed Indigenous university students at Algoma University. The students, who identified as either First Nations or Métis, reported that they required multiple sources of funding, including government student loans and personal savings, to afford their post-secondary education. About two-thirds (69%) of students received funding for their education from First Nations sources, including funding from federal programs for Indigenous students.
“This ...
Not all Hot Jupiters orbit solo
2025-01-15
Hot Jupiters are giant planets initially known to orbit alone close to their star. During their migration towards their star, these planets were thought to accrete or eject any other planets present. However, this paradigm has been overturned by recent observations, and the final blow could come from a new study led by the University of Geneva (UNIGE). A team including the National Centre of Competence in Research (NCCR) PlanetS, the Universities of Bern (UNIBE) and Zurich (UZH) and several foreign universities has just announced the existence of a planetary system, WASP-132, ...
Study shows connection between childhood maltreatment and disease in later life
2025-01-15
University of Birmingham venture Dexter has demonstrated the power of its Dexter software platform in a study showing that people whose childhoods featured abuse, neglect or domestic abuse carry a significantly increased risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis or psoriasis in later life.
The starting point for the recently published study was a database of over 16 million Electronic Health Records, from which the Dexter software defined a cohort, one arm that was exposed to childhood maltreatment, and one arm that was not.
The software then checked the records over a 26-year period ...
Discovery of two planets sheds new light on the formation of planetary systems
2025-01-15
The discovery of two new planets beyond our solar system by a team of astronomers from The University of Warwick and the University of Geneva (UNIGE), is challenging scientific understanding of how planetary systems form.
The existence of these two exoplanets - an inner super-Earth and an outer icy giant planet - within the WASP-132 system is overturning accepted paradigms of how ‘hot Jupiter’ planetary systems form and evolve.
Hot Jupiters are planets with masses similar to those of Jupiter, but which orbit closer to their star than Mercury orbits the Sun. There is not enough gas and dust for these giant planets to form ...
New West Health-Gallup survey finds incoming Trump administration faces high public skepticism over plans to lower healthcare costs
2025-01-15
WASHINGTON, D.C. — Weddnesday, Jan. 15, 2025 — Nearly half of Americans (46%) think the country is headed in the wrong direction when it comes to the incoming president’s policies to lower healthcare costs, while 31% say it’s on the right track, according to the latest West Health-Gallup survey released today.
When viewed through a political lens, only Republicans are more positive than negative about the future of healthcare costs under the Trump administration; nearly three-quarters (73%) think the incoming administration’s healthcare policies are headed in the right direction. In contrast, 24% of independents and 3% of Democrats say the same. Democrats ...
[1] ... [734]
[735]
[736]
[737]
[738]
[739]
[740]
[741]
742
[743]
[744]
[745]
[746]
[747]
[748]
[749]
[750]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.