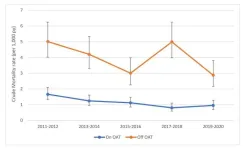
Addiction treatment decreases suicide risk among people with opioid dependence
2024-10-23
Treating opioid use disorder significantly lowers the very high rate (8 times the general population) of suicide among people with opioid dependence.
A Scottish study led by Glasgow Caledonian University of over 45,000 patients receiving methadone or buprenorphine for opioid use disorder reported this important result today in the scientific journal Addiction.
There were 575 suicides among the group of 46,453 people with opioid use disorder, accounting for 1.2% of the group. Although every member of the group received an OAT prescription at some point between 2011 and 2020, some ...
Abundant urban green space linked to lower rates of heat related illness and death
2024-10-22
Abundant green space in urban areas is linked to lower rates of heat related illness and death as well as better mental health and wellbeing, finds a systematic review of the available research, published in the open access journal BMJ Open.
Green space may help offset the adverse health effects of high temperatures, conclude the researchers.
In recognition of the detrimental heat related effects of increasing urbanisation and climate change, one of the UN Sustainable Development Goal targets stipulates the ...
Lifetime sudden cardiac death risk 4+ times higher for those with schizophrenia
2024-10-22
The lifetime risk of an unexpected and sudden death from a cardiovascular cause in the absence of pre-existing heart disease—known as sudden cardiac death—is more than 4 times higher for people with schizophrenia than it is for the general population, indicates Danish research published online in the journal Heart.
The risk is still around twice as high for those with other types of mental ill health, such as depression, whatever their age, indicate the findings, which suggest that an 18 year old can expect to live around 10 fewer years than someone of the same age without mental health issues.
The research to date indicates ...
Scurvy may be re-emerging amid cost of living crisis and rise of weight loss surgery
2024-10-22
The scourge of scurvy, which is caused by vitamin C deficiency, may be re-emerging amid the cost of living crisis and the rise in weight loss (bariatric) surgery, suggest doctors in the journal BMJ Case Reports after treating a middle-aged man with the condition.
Scurvy is eminently treatable, but because it’s a disease of the past, first associated with sailors during the Renaissance era, it may be mistaken for other conditions, especially inflamed blood vessels (vasculitis), potentially risking fatal bleeding if left untreated, highlight the authors.
Signs can appear as early as a month after a daily intake ...
Ethical framework aims to counter risks of geoengineering research
2024-10-22
WASHINGTON — As interest grows in geoengineering as a strategy for tackling global warming, the world’s largest association of Earth and space scientists today launched an ethical framework as a guide to responsible decision-making and inclusive dialogue.
The report, facilitated by the American Geophysical Union (AGU) and advised by a global panel of experts, says any research into large-scale interventions in Earth’s climate system must be grounded in sound ethical principles so society can make informed choices about whether to deploy them. It warns that the unintended consequences ...
New AI tool set to be a “game changer” in improving outcome predictions for kidney transplant patients
2024-10-22
A new advanced artificial intelligence (AI) tool, developed by renal doctors internationally, represents a significant step forward in predicting and potentially improving outcomes for UK kidney transplant patients.
For patients with late-stage renal failure, a kidney transplant can be life-changing, offering the promise of improved survival and a better quality of life compared to other treatment options. But in the UK alone, around 5,000 people are on the waiting list for a kidney transplant, ...
New VUMC hospital expansion to be named Jim Ayers Tower
2024-10-22
Vanderbilt University Medical Center will name the new expansion tower for Vanderbilt University Hospital the Jim Ayers Tower in recognition of Janet and Jim Ayers’ philanthropic legacy and abiding interest in improving the health care and quality of life for Tennesseans.
The naming of the 15-level, 470,000-square-foot tower, currently under construction between 21st Avenue South and Medical Center Drive on the Main Campus in Nashville, honors the couple’s steadfast community leadership and longtime connection to VUMC. The tower is scheduled to ...
New drug, WNTinib, delays tumor growth and improves survival in mouse models of children’s liver cancer
2024-10-22
Barcelona, Spain: A new drug called WNTinib can delay the growth of tumours and improve survival in hepatoblastoma, a type of liver cancer that occurs in young children. This effect was seen in cancer cells taken from patients and implanted into mice.
The researchers are now working on strategies to identify children who may benefit from the treatment, according to Ms Ugne Balaseviciute, a pre-doctoral researcher in the Translational Research in the Hepatic Oncology Group led by Professor Josep M, Llovet at Institut D'Investigacions Biomediques ...
Clinical study confirms tissue stiffening in breast cancer can drive metastasis
2024-10-22
TUCSON, Arizona — A study published in Clinical Cancer Research confirmed that tissue stiffening in the most common types of breast cancer, HER2-negative, can directly cause disease progression and metastasis, leading to detrimental outcomes for patients. The work was a collaboration between researchers at the University of Arizona Health Sciences and clinicians in Spain.
Researchers led by Miguel Quintela-Fandino, MD, at the Spanish National Cancer Research Center evaluated the MeCo Score™, a diagnostic test invented at ...
Medicare has a revolving door, study suggests
2024-10-22
Right now across the country, tens of millions of older adults and people with serious disabilities have a choice to make: whether to stick with their current Medicare option, or change during Open Enrollment.
One of the biggest decisions they face is whether to go with a Medicare Advantage plan offered by an insurance company, or traditional Medicare coverage offered directly by the federal government.
If they change from one to the other, a new University of Michigan study finds, they may be entering a revolving door and find themselves changing again in the future.
On average, the study shows, 3% of people with traditional Medicare switch over to ...
Floor swabbing could help prevent COVID-19 outbreaks in hospitals
2024-10-22
COVID-19 is here to stay. As restrictions and human testing have waned, new research is tackling the challenge of how we can monitor, predict, and prevent cases and outbreaks of COVID-19, especially among vulnerable groups like hospitalized patients.
One approach is environmental surveillance. The most well-known incarnation is wastewater surveillance, which rose in prominence following the advent of the COVID-19 pandemic. But the Coronavirus in the Urban Built Environment research team, also known as CUBE, is exploring an alternative—swabbing the floors.
In a recent study at two hospitals in Ontario, CUBE researchers swabbed the floors ...
Paws of polar bears sustaining ice-related injuries in a warming Arctic
2024-10-22
Polar bears in some parts of the high Arctic are developing ice buildup and related injuries to their feet, apparently due to changing sea ice conditions in a warming Arctic. While surveying the health of two polar bear populations, researchers found lacerations, hair loss, ice buildup and skin ulcerations primarily affecting the feet of adult bears as well as other parts of the body. Two bears had ice blocks up to 1 foot (30 centimeters) in diameter stuck to their foot pads, which caused deep, bleeding cuts and made it difficult for them to walk.
The study led by the University of Washington was published Oct. 22 in the journal Ecology. It’s ...
Politics may influence gift-giving choices more than personal purchases
2024-10-22
DURHAM, N.H.—(October 22, 2024)—Political affiliation may not make a difference on everyday purchases for individuals, but it can play a role when buying for friends, family and co-workers, new research from the University of New Hampshire has found. This may have implications for gift buying this holiday season and beyond.
“We performed five different studies, each looking at buying different products, and asked people to make a choice for themselves and then a gift for someone they knew really well and found that politics played a bigger role when people were purchasing gifts, because that's a case where people are making a decision based ...
Listening skills bring human-like touch to robots
2024-10-22
Note to Editors: Video clips available at: https://duke.box.com/s/wtq3ofu3kf84ayw3qr6jajxdizt0rwxc
DURHAM, N.C. – Imagine sitting in a dark movie theater wondering just how much soda is left in your oversized cup. Rather than prying off the cap and looking, you pick up and shake the cup a bit to hear how much ice is inside rattling around, giving you a decent indication of if you’ll need to get a free refill.
Setting the drink back down, you wonder absent-mindedly if the armrest is made of real wood. After ...
Acclaimed WVU doctor and researcher elected to National Academy of Medicine
2024-10-22
A world-renowned West Virginia University physician and researcher has received one of the highest honors in the fields of health and medicine.
Dr. Sally Hodder, director of the West Virginia Clinical and Translational Science Institute, associate vice president for clinical and translational science at WVU and Chancellor’s Preeminent Scholar Chair, was elected to the National Academy of Medicine for her accomplishments as an infectious diseases physician and researcher.
Hodder, the first person from WVU to be chosen for the National Academy of Medicine, is one of only 100 new members from around the world announced at the Oct. 21 NAM ...
New study reveals larger insects' critical role in decomposition in arid ecosystems
2024-10-22
New study reveals that in arid ecosystems, larger arthropods such as termites and beetles play a crucial role in decomposition, challenging the traditional view that microbial activity dominates this process in dry environments. By demonstrating that macro-decomposition can peak during the summer in arid sites and that overall decomposition rates in these regions can be similar to or even exceed those in wetter climates, the research provides new insights into how decomposition functions in drylands and its implications for global carbon ...
NASA reveals prototype telescope for gravitational wave observatory
2024-10-22
NASA has revealed the first look at a full-scale prototype for six telescopes that will enable, in the next decade, the space-based detection of gravitational waves — ripples in space-time caused by merging black holes and other cosmic sources.
The LISA (Laser Interferometer Space Antenna) mission is led by ESA (European Space Agency) in partnership with NASA to detect gravitational waves by using lasers to measure precise distances — down to picometers, or trillionths of a meter — between a trio of spacecraft distributed in a vast configuration larger than the Sun. Each side of the triangular array ...
A new kind of authoritarianism: Democracy in decline at home and abroad
2024-10-22
A majority of Americans worry this year’s general election will be tainted by fraud, according to a recent NPR/PBS News/Marist poll released earlier this month—an ominous indication of the state of democracy in the U.S.
“When citizens lose trust in the electoral process, they may question the legitimacy of elected officials and the institutions they represent, which undermines the foundational principle that government authority is derived from the will of the people,” ...
Performance in physical tests can help manage treatment for metastatic lung cancer
2024-10-22
A study of patients with metastatic lung cancer by researchers based in Brazil and the United States has found that their performance in simple physical tests such as sitting down, standing and walking can help physicians arrive at a prognosis and approach to treatment.
An article on the study is published in the European Journal of Clinical Investigation.
The findings also included identification in the volunteers’ blood plasma of two substances – serine and M22G – with the potential to become biomarkers capable of indicating which patients are most likely to respond to chemotherapy.
The study was supported by FAPESP (projects 16/20187-6 and 19/17009-7), ...
Expanding access to weight-loss drugs could save thousands of lives a year
2024-10-22
New Haven, Conn. — Expanding access to new, highly effective weight-loss medications could prevent more than 40,000 deaths a year in the United States, according to a new study led by researchers at Yale School of Public Health and the University of Florida.
The findings highlight the critical need to remove existing barriers that are hindering people’s access to effective weight loss treatments and impeding public health efforts to address the national obesity crisis, the researchers said. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, about 74% of Americans are considered overweight, with about 43% of those individuals ...
Harnessing science to tackle global crises
2024-10-22
In a paper published in PLOS Sustainability and Transformation, an international team of researchers looked at how science could play a more active role in managing crises. The paper builds on the outcomes of the international conference “What Role for Science in Crisis Times? Outlook in the Health, Environment, and Agriculture Interconnected Areas”, held in Montpellier in 2022.
To enhance science’s contribution to crisis management, the paper emphasises the need for interdisciplinarity, where science is integrated across disciplines, and transdisciplinarity, which incorporates various societal actors and stakeholders. By co-designing and co-producing ...
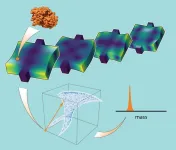
Caltech's new fingerprint mass spectrometry method paves the way to solving the proteome
2024-10-22
Caltech scientists have developed a method driven by machine learning that allows them to accurately measure the mass of individual particles and molecules using complex nanoscale devices. The new technique opens the possibility of using a variety of devices for the measurement of mass and, therefore, the identification of proteins, and could pave the way to determining the sequence of the complete proteome, the collection of all the proteins in an organism.
Proteins are the engines of living systems. Which proteins are made, ...
Invasive flathead catfish impacting Susquehanna’s food chain, researchers find
2024-10-22
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Flathead catfish — native to the Mississippi River basin — were first detected in the Susquehanna River in Pennsylvania in 2002, according to the U.S. Geological Survey. In the two decades since then, the invasive species has spread throughout the river basin. The impact of the large predator on the waterway’s food webs and ecology was unknown, but now a research team is beginning to understand what Susquehanna flatheads are eating and how their presence is affecting native aquatic species in the river.
The findings, which the team said state ...
Javadi receives DOE Early Career Award to study qubit hosts
2024-10-22
NORMAN, OKLA. – Alisa Javadi, Ph.D., professor at the University of Oklahoma School of Electrical and Computer Engineering and the Homer L. Dodge Department of Physics and Astronomy, has received funding from the U.S. Department of Energy Early Career Research Program for research that offers the potential for advancing quantum technology development.
Javadi’s research will test the use of cerium oxide as a host for quantum bits, or qubits. Qubits, the building blocks of quantum computing, need an environment free ...
Obesity Medicine Fellowship created at Pennington Biomedical
2024-10-22
Obesity Medicine Fellowship Created at Pennington Biomedical
Fellowship product of collaboration between Pennington Biomedical Research Center’s Metamor Clinic and Louisiana State University Health New Orleans School of Medicine
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Oct. 22, 2024
BATON ROUGE – A new Obesity Medicine Fellowship at Pennington Biomedical Research Center is now open for candidate applications. The one-year program is the result of a collaboration between Pennington Biomedical and Louisiana State University Health ...
[1] ... [872]
[873]
[874]
[875]
[876]
[877]
[878]
[879]
880
[881]
[882]
[883]
[884]
[885]
[886]
[887]
[888]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.