A model for the decline of trends, fads, and information sharing
2024-10-22
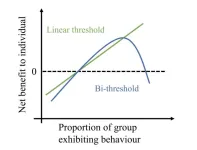
A model of human behavior finds that people will share information if enough—but not too many—of their contacts do so. Humans are social creatures, and many behaviors and beliefs can spread from person to person. Understanding the dynamics of behavioral diffusion can help encourage healthy or sustainable behaviors or stop the spread of misinformation. Linear threshold models assume that people will adopt a behavior when the number of their social contacts that have done so passes a threshold. Pouria Ramazi and colleagues propose an addition to the model, ...
Plastic mulch is contaminating agricultural fields
2024-10-22
Using plastic sheets for weed control, even under current best management practices, pollutes soil with macro- and micro-plastics and negatively affect critical soil functions, according to a study. The United Nations considers soil plastic contamination an environmental health and food security threat. Around the world, over 25 million acres of farmland is seasonally covered with opaque plastic films used as “mulch” to prevent weeds, retain moisture, and warm soil—a practice known ...
Scientists discover how fungi interact with soil actinomycetes
2024-10-22
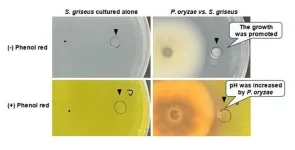
In the world of agriculture, rice is a staple food for more than half of the global population, making its cultivation crucial for food security. However, the rice blast fungus Pyricularia oryzae (syn. Magnaporthe oryzae) poses a significant threat to rice crops, causing extensive damage and leading to substantial yield losses. Traditional methods of controlling this pathogen often rely on chemical fungicides, which can have detrimental environmental impacts and contribute to the development of resistant strains. Therefore, researchers are increasingly exploring alternative strategies that leverage natural ...
Beyond longevity: The critical role of mental health in Japan’s well-being
2024-10-22
The Japanese population is known for its longest life expectancy (LE) at birth. Extensive studies have been conducted on the physical health of the Japanese population, mainly on mortality outcomes. However, research on mental health is limited due to the social stigma against mental illnesses. This is alarming since mental health problems such as anxiety, substance use disorders, and suicide rates have largely increased over the years.
Additionally, previous studies have examined the physical and mental health of the Japanese population separately, which makes it harder to understand the relationship between them.
Against this backdrop, Associate Professor Yuka Minagawa ...
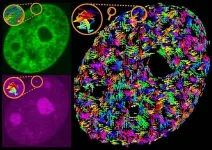
Stirred, not shaken — Scientists uncover how transcription drives motion within the genome
2024-10-22
A team of scientists has discovered surprising connections among gene activity, genome packing, and genome-wide motions, revealing aspects of the genome’s organization that directly affect gene regulation and expression.
The findings, reported in the journal Nature Communications, bolster our understanding of the mechanics behind transcription-dependent motions of single genes—the dysfunction of which may lead to neurological and cardiovascular disorders as well as to cancer.
“The genome is ‘stirred’ by transcription-driven ...
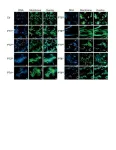
Engineering creates molecules that target cancer-causing proteins
2024-10-22
For some proteins, a single mutation, or change in its DNA instructions, is all it takes to tip the balance between functioning normally and causing cancer. But despite causing major disease, these slightly mutated proteins can resemble their normal versions so closely that treatments designed to target mutants could also harm healthy cells.
Led by researchers at NYU Langone Health and its Perlmutter Cancer Center, a new study describes the development of a biologic, a drug derived from natural biological systems, that targets a mutant cancer protein called HER2 (human epidermal growth factor receptor 2) without attacking ...
Wearable cameras allow AI to detect medication errors
2024-10-22
A team of researchers says it has developed the first wearable camera system that, with the help of artificial intelligence, detects potential errors in medication delivery.
In a test whose results were published today, the video system recognized and identified, with high proficiency, which medications were being drawn in busy clinical settings. The AI achieved 99.6% sensitivity and 98.8% specificity at detecting vial-swap errors.
The findings are reported Oct. 22 in npj Digital Medicine.
The system could ...
New bacterial toxins discovered: A key to fighting infections
2024-10-22
Researchers have discovered a new group of bacterial toxins that can kill harmful bacteria and fungi, opening the door to potential new treatments for infections. These toxins, found in over 100,000 microbial genomes, can destroy the cells of bacteria and fungi without harming other organisms. The study revealed how some bacteria use these toxins to compete with other microbes, and the findings could lead to new ways to fight infections, especially as antibiotic resistance becomes a growing concern.
A new ...
AI eye to eye with ophthalmologists in diagnosing corneal infections, study finds
2024-10-22
Eye care specialists could see artificial intelligence help in diagnosing infectious keratitis (IK), a leading cause of corneal blindness worldwide, as a new study finds that deep learning models showed similar levels of accuracy in identifying infection.
In a meta-analysis study published in eClinicalMedicine, Dr Darren Ting from the University of Birmingham conducted a review with a global team of researchers analysing 35 studies that utilised Deep Learning (DL) models to diagnose infectious keratitis.
AI models ...
Virginia Tech researcher works to preserve the white shark in the Mediterranean Sea
2024-10-22
The Mediterranean Sea is a paradise.
Pristine waters and an incredible coastline spanning multiple continents that are renowned the world over.
Below those picturesque, and sometimes crowded, waters swim a legendary creature facing a treacherous and uncertain future: the white shark.
Francesco Ferretti, an assistant professor in the College of Natural Resources and Environment, is working to save one of the most endangered white shark populations on the planet. The research team located signs of the remaining white sharks ...
How the coronavirus defeats the innate immune response
2024-10-22
The novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 has an enzyme that can counteract a cell’s innate defense mechanism against viruses, explaining why it is more infectious than the previous SARS and MERS-causing viruses. The Kobe University discovery may point the way to the development of more effective drugs against this and possibly similar, future diseases.
When a virus attacks, the body’s immune response has two basic layers of defense: the innate and the adaptive immune systems. While the adaptive immune system grows stronger against a specific pathogen as the body ...
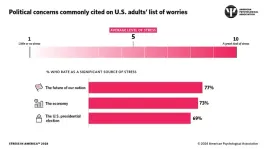
APA Poll: Future of nation, economy and presidential election top U.S. stressors
2024-10-22
WASHINGTON — More than 7 in 10 adults said the future of the nation (77%) is a significant source of stress in their lives, with the economy (73%) and the 2024 U.S. presidential election (69%) following closely behind, according to the latest Stress in America™ survey released today by the American Psychological Association.
At the same time, the poll found many common stressors among people with different political party affiliations. The survey was conducted by The Harris Poll on behalf of APA among more ...
Towards better solar cells: Exploring an anomalous phenomenon of electricity generation
2024-10-22
The bulk photovoltaic (BPV) effect is an uncommon phenomenon that may enable certain materials to outperform the conventional p–n junctions used in solar cells. In a recent study, researchers from Japan have experimentally demonstrated the BPV effect in alpha-phase indium selenide (α-In2Se3) for the first time along the out-of-plane direction, validating previous theoretical predictions. The remarkable conversion efficiency recorded in their α-In2Se3 device signals a promising advancement for future solar cell technologies and photosensors.
A firm understanding ...
KERI’s innovation in anode materials for solid-state batteries selected as a cover article
2024-10-22
The KERI's research on anode materials for solid-state batteries (SSBs), conducted in collaboration with Kumoh National Institute of Technology and Inha University, has been selected as the cover article of a world-leading journal in the energy field.
The SSBs have replaced the combustible liquid electrolyte that transfers ions between the anode and cathode with a solid electrolyte, significantly reducing the risk of fire or explosion. However, SSBs, due to their 'solid' nature, require much advanced technology, such as ensuring electro-chemo-mechanical stability during the charging and discharging processes. In particular, since the anode has a ...
A visit from the stork brings genomic hope for this endangered species
2024-10-22
A Visit from the Stork Brings Genomic Hope for this Endangered Species
A new genomic study of the endangered Oriental Stork reveals that the population's genetic health is still surprisingly strong, with high genetic diversity and low levels of inbreeding. This is an uncommon finding in most endangered species populations, which makes it more difficult to rescue those species from extinction. Thus, despite the human-caused decline in the Oriental stork numbers, the findings in this study provide hope for the species' long-term ...
Study uncovers the true burden of asthma in African pupils, highlighting need for better access to asthma diagnosis and care
2024-10-21
Peer reviewed | Observational study | People
Rapid urbanisation and population growth in sub-Saharan Africa has increased the incidence of asthma in young people, but the lack of diagnosis and care means that many young people are suffering from untreated symptoms of asthma, according to research from Queen Mary University of London.
The team who led the study, whose pioneering research on the impact of pollution on lung health was instrumental in introducing the Ultra Low-Emission Zone (ULEZ) in London, are calling for better access to asthma diagnosis and care in areas of ...
A remote-controlled car for cancer immunotherapy
2024-10-21
OCTOBER 21, 2024, NEW YORK – Ludwig Cancer Research scientists have devised new types of chimeric antigen-receptor (CAR) T cells—a type of cancer immunotherapy—that can be switched on to varying degrees of intensity and then switched off on demand with existing drugs. The design and preclinical evaluation of the CAR-T cells, led by Melita Irving and Greta Maria Paola Giordano Attianese of the Lausanne Branch of the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research, is detailed in this week’s issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“CAR-T cells are already used today to treat a number of blood cancers, but ...
New ice core data provides insight into climate ‘tipping points’ during the last Ice Age
2024-10-21
CORVALLIS, Ore. – A changing climate triggers a sudden shift in ocean circulation, creating weather havoc and plunging Earth into an abrupt new Ice Age.
It sounds like the basis for a Hollywood blockbuster - the 2004 science fiction disaster film “The Day After Tomorrow,” has similar plot lines – but it’s actually a scenario that played out multiple times during the last Ice Age, which ended more than 11,000 years ago.
Just published research from multiple ice cores collected across Greenland with data spanning up to 120,000 years provides new understanding of these abrupt events, how they unfold and what that might ...
Being part of a ‘civilization’ only reduces violence if you’re a woman in ancient Andes populations
2024-10-21
The extent to which “civilization” heightens or lessens the likelihood of violent conflict throughout human history has remained one of the most enduring questions among anthropologists. But a new collaborative study of archaeological groups from the Andes region of South America suggests that being part of a centrally organized state society is only part of the equation.
“Our findings suggest that being in a ‘civilization’ may reduce violence, but only for women, and only slightly then,” ...
Gladstone to present 2024 Ogawa-Yamanaka Stem Cell Prize to Neuroscientist Rusty Gage
2024-10-21
SAN FRANCISCO—Neuroscientist Rusty Gage, PhD, will be the recipient of the 2024 Ogawa-Yamanaka Stem Cell Prize, awarded by Gladstone Institutes. He was selected for pioneering stem cell biology of the central nervous system and the use of reprogrammed cells to study age-related neurodegenerative disease and psychiatric disorders.
Gage is a professor in the Laboratory of Genetics at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies, where he also serves as the Vi and John Adler Chair for Research on Age-Related Neurodegenerative Disease. He was president of the Salk Institute from 2018 to 2023.
Over the course of his scientific career, Gage has made several paradigm-shifting ...
A blueprint for mapping melting ice sheets
2024-10-21
Researchers in the Stanford Radio Glaciology lab use radio waves to understand rapidly changing ice sheets and their contributions to global sea-level rise. This technique has revealed groundwater beneath Greenland, the long-term impacts of extreme melt, a process that could accelerate ice sheet mass loss in Antarctica, the potential instability of an ice sheet that could raise sea levels by 10 feet, and more.
Now, PhD students within the group have created an open-source tool that others can use to make ice-penetrating radar systems, core instruments ...
People hate stories they think were written by AI. Even if they were written by people
2024-10-21
Stories written by the latest version of ChatGPT were nearly as good as those written by human authors, according to new research on the narrative skills of artificial intelligence.
But when people were told a story was written by AI — whether the true author was an algorithm or a person — they rated the story poorly, a sign that people distrust and dislike AI-generated art.
“People don’t like when they think a story is written by AI, whether it was or not,” said Haoran “Chris” Chu, Ph.D., a professor of public relations at the University of Florida and co-author of the new study. “AI is good at writing something that is consistent, ...
From Houston to Scotland: Seed grants boosting shared energy solutions and innovations
2024-10-21
HOUSTON, Oct. 21, 2024 – The University of Houston and Scotland’s Heriot-Watt University have awarded seed grants to six innovative energy projects as part of their transatlantic research collaboration. The projects, which bring together researchers from both universities, focus on cutting-edge solutions ranging from advanced hydrogen sensing technology to converting waste into sustainable products.
“This partnership is rooted in a shared commitment to advancing research that supports a just energy ...
AI-assisted colonoscopy increases polyp and adenoma detection in routine screening
2024-10-21
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 21 October 2024
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, ...
Younger adults respond to colorectal cancer screening outreach
2024-10-21
The updated national colorectal cancer screening guidelines that recommend screening begin at age 45 — rather than 50 — can benefit younger adults, a new Kaiser Permanente study found.
The study, published October 22 in Annals of Internal Medicine, included more than 267,000 Kaiser Permanente members in Northern California, Washington, and Colorado ages 45 to 50 who received their first invitation for colorectal cancer screening along with a fecal immunochemical test (FIT) kit between January and September 2022.
“The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force lowered the age to start screening in response to studies showing an increased rate of colorectal cancer in ...
[1] ... [870]
[871]
[872]
[873]
[874]
[875]
[876]
[877]
878
[879]
[880]
[881]
[882]
[883]
[884]
[885]
[886]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.