New study links obesity to elevated hypertension risk among young middle eastern women
2024-10-15
Obesity is a widespread public health challenge in the Middle East, maintaining prevalence in 54.2% of women and 31.4% of men in this region. Overweight and obese women have a higher risk of hypertension and cardiovascular risk factors than women with a standard BMI, according to an analysis of the ANCORS-YW STUDY presented at ACC Middle East 2024. The findings highlight the urgent need for targeted interventions that address socioeconomic determinants of health to reduce the cardiovascular risk ...
How ‘vaccinating’ plants could reduce pesticide use and secure global food supplies
2024-10-15
In a growing and changing world, we need to find ways of putting food on everyone’s table. Pesticides have enabled mass cultivation on an incredible scale, but they can have harmful secondary effects on humans and wildlife, and pests are rapidly evolving to overcome them. To overcome this challenge and develop the sustainable and resilient agriculture of the future, scientists writing in Frontiers in Science explore the potential of induced resistance. Like a vaccination for plants, it deliberately triggers a plant’s immune system, so that when the plant encounters a similar ...
Seven new frog species discovered in Madagascar: sounds like something from Star Trek
2024-10-15
Seven New Frog Species Discovered in Madagascar: Sounds Like Something from Star Trek
An international team of researchers have discovered seven new species of tree frogs that make otherworldly calls in the rainforests of Madagascar. Their strange, high-pitched whistling calls sound more like sound effects from the sci-fi series Star Trek. As a result, the researchers have named the new species after seven of the series' most iconic
If you think all frogs croak, you’d be wrong. Seven newly discovered species from the tree frog genus Boophis, found across the rainforests of Madagascar, emit special bird-like whistling ...
New temperatures in two thirds of key tropical forest
2024-10-15
Two thirds of Key Biodiversity Areas (KBAs) in tropical forests are experiencing new temperature conditions as our climate changes, research shows.
KBAs identify the most important places on Earth for species and their habitats.
The new study – by Exeter, Manchester Metropolitan and Cambridge universities – assessed 30 years of temperature conditions below the forest canopy in KBAs in tropical forests worldwide.
It found that 66% of KBAs in tropical forests have recently transitioned to new “temperature regimes” (more than 40% of temperature measurements being outside the range previously recorded ...
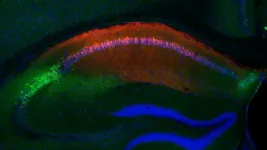
Fearful memories of others seen in mouse brain
2024-10-15
NEW YORK, NY — How do we distinguish threat from safety? It’s a question important not just in our daily lives, but for human disorders linked with fear of others, such as social anxiety or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The microscope image accompanying this press release, from the laboratory of Steven A. Siegelbaum, PhD, at Columbia’s Zuckerman Institute, displays a powerful technique scientists used to help us find an answer.
The scientists were investigating the hippocampus, a brain area that plays a key role in memory in humans and mice. Specifically, they focused on the CA2 region, which is ...
Rangers lead ground-breaking effort to monitor Uganda's lion population in critical stronghold
2024-10-15
In a new study published in Nature Communications Biology, wildlife rangers from the Uganda Wildlife Authority have demonstrated their ability to generate precise and reliable data on lion populations in Uganda’s Nile Delta, a critical stronghold for African lions.
The study reveals that wildlife rangers, a critical component of global conservation efforts but often underutilised in scientific research, can play a pivotal role in the conservation science surrounding the world’s most beloved big cat.
Rangers are effective at monitoring lions and are an underutilised resource
The study showed rangers ...
Modern mass extinction in an Ecuadorean cloud forest found to be a mirage
2024-10-15
One of the most notorious mass extinction events in modern times occurred on a hilltop in coastal Ecuador in the 1980s. Ninety species of plants known from nowhere else on Earth—many of them new to science and not yet given a name—went extinct when the last cloud forests of the Centinela range were cleared for agriculture. The cautionary tale of Centinela has long been a driving force in the fight to save the world’s rainforests. But did it really happen?
In a new study published in Nature Plants, an international team of botanists reveals that, indeed, it did not happen. The researchers – who spent years of scouring natural history museums, biodiversity databases, ...
HLA-DRB1*01:03 and severe ulcerative colitis
2024-10-15
About The Study: Among individuals with ulcerative colitis, the allele HLA-DRB1*01:03 was associated with severe ulcerative colitis requiring major operation, hospitalization, and systemic corticosteroid use compared with less severe disease. HLA-DRB1*01:03 has previously been linked to ulcerative colitis incidence. This study supports earlier, targeted genetic studies comparing patients with healthy controls reporting an association with total disease and severe disease requiring colectomy.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Marie Vibeke Vestergaard, MSc, email marievv@dcm.aau.dk.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our ...
Quantum leap in suicide prevention: Professor Philippe Courtet's visionary approach unveiled in Genomic Press Interview
2024-10-15
Montpellier, France – 15 October 2024. In a captivating Genomic Press Interview published on October 15, 2024, in the peer-reviewed journal Genomic Psychiatry (Genomic Press), Professor Philippe Courtet shares groundbreaking perspectives on suicide prevention and mental health care. As an influential PU-PH (Professeur des Universités-Praticien Hospitalier), he is a Professor of Psychiatry at the University of Montpellier, France, and head of emergency psychiatry at the University Hospital of, Professor Courtet stands at the forefront of ...
Need for streamlined miscarriage care in Canada
2024-10-15
Miscarriage, or early pregnancy loss, can have devastating emotional effects, but it is poorly managed in Canada. A review published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231489 provides guidance to physicians on how to diagnose and manage this condition and calls for referral to outpatient early pregnancy assessment clinics (EPACs) as well as a compassionate approach.
October 15 is Pregnancy and Infant Loss Remembrance Day.
Data suggest that 15%–20% of all confirmed pregnancies result in miscarriage, with ...
Traces of ancient immigration patterns to Japan found in 2000-year-old genome
2024-10-15
A joint research group led by Jonghyun Kim and Jun Ohashi of the University of Tokyo has demonstrated that the majority of immigration to the Japanese Archipelago in the Yayoi and Kofun periods (between 3000 BCE and 538 CE) came from the Korean Peninsula. The researchers analyzed the complete genome of a “Yayoi” individual and found that, among the non-Japanese populations, the results bore the most similarity to Korean populations. Although it is widely accepted that modern Japanese populations have a dual ancestry, the discovery provides insight into the details of immigration patterns to the ...
Countries that choose to do so can reduce premature death by half, researchers say
2024-10-14
DURHAM, N.C. -- Since 1970, 37 countries have cut the probability of their citizens dying before they reach age 70 in half, a milestone that signals the remarkable progress many countries have made in preventing and treating disease. But a new report argues that this goal isn’t out of reach for any country that chooses to cut its premature mortality, even those afflicted by war or poverty.
The report, published Oct. 14 by The Lancet Commission on Investing in Health, lays out a roadmap for every nation that chooses to do so to cut ...
50 by 50—How can we reduce the probability of dying before age 70 by 50% globally by 2050?
2024-10-14
A team of 50 leading international experts, the Lancet Commission on Investing in Health (CIH), explored this question, resulting in clear, actionable, and achievable measures for achieving this ambitious goal worldwide. Six of the 50 commission members are affiliated with the Bergen Centre for Ethics and Priority Setting in Health (BCEPS), a Norwegian Centre of Excellence based at the University of Bergen, Norway, including BCEPS Director and Professor Ole Frithjof Norheim, BCEPS PhD Research Fellow Sarah Bolongaita, and BCEPS-affiliated researchers Angela Chang (University ...
Research explains why some cyclists don’t wear helmets and what might convince them to wear one
2024-10-14
Copenhagen, Denmark: Wearing a helmet can prevent brain injury and deaths in cyclists, yet many do not wear a helmet. New research presented at the European Emergency Medicine Congress today (Tuesday) suggests that this is largely due to issues of convenience and comfort. [1]
The study also suggests that more adult cyclists would wear helmets if they were encouraged and incentivised to do so, for example if they were provided with a free helmet, education, and periodic reminders.
The research was presented by Dr Steven Friedman, an emergency doctor at Toronto General Hospital and associate professor at the University ...
Half of all patients with sepsis die within two years
2024-10-14
Copenhagen, Denmark: Half of all patients with sepsis admitted to an emergency medical department died within two years, according to Danish researchers investigating factors that could predict outcomes for these patients.
Dr Finn E. Nielsen, a senior scientist in the Department of Clinical Epidemiology at Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark, told the European Emergency Medicine Congress today (Tuesday) [1] that he and his colleagues examined deaths over a long follow-up period in a prospective study of 714 adult patients admitted to the emergency department with sepsis. Their findings ...
Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander adults have third highest cardiovascular death rate in the U.S.
2024-10-14
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 14 October 2024
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent. ...
Gene therapy automatically converts omega-6 to omega-3 fatty acids in the body
2024-10-14
St. Louis, MO (October 14, 2024) According to the Centers for Disease Control, nearly 20% of children and teens are considered obese. Research shows it can have a dramatic impact on a variety of health conditions, including arthritis, heart conditions and other metabolic problems, and the American Academy of Pediatrics now recommends early and intensive treatment to combat obesity. Over the last four years, Shriners Children’s St. Louis researchers have been working to develop a new way to prevent the effects of childhood obesity.
Using gene therapy, Shriners Children’s St. Louis Director of Research Dr. Farshid Guilak and Senior Scientist Dr. Ruhang Tang ...
Mpox clinical presentation, diagnostic approaches, and treatment strategies
2024-10-14
About The Study: Mpox is a viral infection transmitted primarily through close skin to skin contact that typically causes a self-resolving illness but can result in severe illness and death in immunocompromised individuals. First-line therapy is supportive care, although patients with severe mpox infection may be treated with advanced therapeutics. Mpox vaccination is effective and, if available, should be offered to individuals at risk of exposure to mpox.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jason Zucker, MD, MS, email Jz2700@cumc.columbia.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
Trends in oral and injectable HIV preexposure prophylaxis prescriptions in the US
2024-10-14
About The Study: Preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) use increased between 2013 and 2023, with generic tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine (TDF/FTC) being the most frequently prescribed medication since 2021. Injectable PrEP use was low likely because of barriers such as the high cost of stocking this expensive medication in clinics.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Laura M. Mann, PhD, MPH, email lmann@cdc.gov.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.21493)
Editor’s ...
Information about sexual and gender minority services and policies on US hospital websites
2024-10-14
About The Study: Most U.S. hospital websites explicitly included sexual and gender minority (SGM) populations in their nondiscrimination policies, but only a quarter of adult hospitals had an SGM-friendly clinician directory and provided information about SGM-related resources or hospital-based services. Pediatric hospitals more frequently posted SGM-related information than adult hospitals. Hospitals in states with more discriminatory policies were less likely to provide SGM-related information online.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Alex S. Keuroghlian, MD, MPH, email akeuroghlian@mgb.org.
To ...
Study finds use of naloxone by Good Samaritans is up, but not nearly enough
2024-10-14
Study finds use of naloxone by Good Samaritans is up, but not nearly enough
Ohio State and National Registry of EMTs research highlights importance of public’s help in opioid overdose response
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Use of a lifesaving drug to reverse opioid drug overdoses is growing, but not fast enough. That’s according to new research in JAMA Network Open from The Ohio State University College of Medicine, College of Public Health and the National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians.
In the first study of its kind, the research team looked at national use of naloxone by people without medical training to treat an opioid drug overdose.
“Naloxone ...
Risk of suicidal ideation or attempts in adolescents with obesity treated with GLP1 receptor agonists
2024-10-14
About The Study: In this study, adolescents with obesity prescribed a glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP1R) had a lower incidence of suicidal ideation or attempts compared with matched patients not prescribed GLP1R who were treated with lifestyle intervention. These results suggest a favorable psychiatric safety profile of GLP1R in adolescents. The detected reduction in hazard ratios for suicidal ideation among adolescents with obesity prescribed GLP1R suggests potential avenues for future research.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Liya Kerem, MD, MSc, email liya.em@gmail.com.
To access the ...
SARS-CoV-2 infection and new-onset type 2 diabetes among pediatric patients
2024-10-14
About The Study: In this retrospective cohort study of children and adolescents ages 10 to 19, the risk of an incident diagnosis of type 2 diabetes was greater following a COVID-19 diagnosis than in children diagnosed with other respiratory infections. Further study is required to determine whether diabetes persists or reverses later in life.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Pauline Terebuh, MD, MPH, email pdt@case.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.39444)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, ...
Recovery from COVID-19–related disruptions in cancer detection
2024-10-14
About The Study: This cross-sectional study of nationally representative registry data found that cancer incidence recovered meaningfully in 2021 following substantial disruptions in 2020. However, incidence rates need to recover further to address the substantial number of patients with undiagnosed cancer during the pandemic.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Uriel Kim, MD, PhD, MBA, email uxk13@case.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.39263)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
Smaller vial size for Alzheimer’s drug could save Medicare hundreds of millions per year
2024-10-14
Medicare could save up to 74% of the money lost from discarded Alzheimer’s drug lecanemab by the simple introduction of a new vial size that would reduce the amount of unused medication that is thrown away, new research suggests.
The researchers on the study, to be published October 14 in the peer-reviewed JAMA Internal Medicine, estimate that Medicare could waste up to $336 million annually due to discarded medication. Administered dosages are based on each patient’s body weight. But because the drug is currently available ...
[1] ... [876]
[877]
[878]
[879]
[880]
[881]
[882]
[883]
884
[885]
[886]
[887]
[888]
[889]
[890]
[891]
[892]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.