(Press-News.org) AURORA, Colo. (May 10, 2021) - Looking to safely block a gene linked to factors known to cause heart disease, scientists at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus may have found a new tool - light.
The study, published Monday in the journal Trends in Molecular Medicine, may solve a medical dilemma that has baffled scientists for years.
The gene, ANGPTL4, regulates fatty lipids in plasma. Scientists have found that people with lower levels of it also have reduced triglycerides and lipids, meaning less risk for cardiovascular disease.
But blocking the gene using antibodies triggered dangerous inflammation in mice. Complicating things further, the gene can also be beneficial in reducing the risk of myocardial ischemia and helping to repair a damaged heart.
"The scientific community is still trying to figure out a way to safely inhibit it," said the study's lead author Tobias Eckle, MD, PhD, professor of anesthesiology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine. "Now we have discovered that ANGPTL4 is a gene with a circadian pattern. It can be influenced by light."
Eckle previously discovered that light therapy can protect the heart. In this study, his team did an unbiased, whole genome array, profiling intense, light-dependent cardiac gene expressions. They found that ANGPTL4 was the top light dependent gene.
Eckle believes the gene could be manipulated by light without risking the lethal effects of blocking it entirely.
"We demonstrate that if you want to get around this problem you don't knock out the protein, you enhance the circadian amplitude by increasing its troughs and peaks," he said. "Throughout the day, you will have times of enhanced protein expression and times with lower expression."
Eckle said the gene can be activated by light therapy, a flavonoid known as nobiletin or through drug formulations.
"In fact, circadian amplitude enhancement of ANGPTL4 would be quite distinct from disabling or even overexpressing it," Eckle said. " Enhancing peaks and troughs would mean that at specific times of day, the ANGPTL4 response would be enhanced and 12 hours later the response would be even more robustly suppressed."
The discovery, Eckle said, reinforces the physiological importance of circadian rhythms as well as the light and oxygen pathways threading through the human body.
"Sunlight and oxygen are the most life-sustaining things on this planet," Eckle said. "We evolved to adapt to those two things and we have pathways throughout our body that sense them."
He said that chronotherapy, giving medications at different times of the day to maximize benefits and minimize side-effects, is a new frontier in medicine.
"The administration of any drug should be connected to a specific time of day," he said. "I believe chronotherapy is the future of medicine."
INFORMATION:
About the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus
The University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus is a world-class medical destination at the forefront of transformative science, medicine, education, and healthcare. The campus encompasses the University of Colorado health professional schools, more than 60 centers and institutes, and two nationally ranked hospitals that treat more than 2 million adult and pediatric patients each year. Innovative, interconnected and highly collaborative, together we deliver life-changing treatments, patient care, professional training, and conduct world-renowned research powered by more than $500 million in research awards. For more information, visit https://www.cuanschutz.edu END
Hamilton, ON (May 10, 2021) - It is well known that each person's gut bacteria is vital for digestion and overall health, but when does that gut microbiome start?
New research led by scientists from McMaster University and Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin in Germany has found it happens during and after birth, and not before.
McMaster researchers Deborah Sloboda and Katherine Kennedy examined prenatal stool (meconium) samples collected from 20 babies during breech Cesarean delivery.
"The key takeaway from our study is we are not colonized before birth. Rather, our relationship with our gut bacteria emerges ...
URBANA, Ill. - Sweet corn growers and processors could be bringing in more profits by exploiting natural density tolerance traits in certain hybrids. That's according to 2019 research from USDA Agricultural Research Service (ARS) and University of Illinois scientists.
But since root systems get smaller as plant density goes up, some in the industry are concerned about the risk of root lodging with greater sweet corn density. New research says those concerns are unjustified.
"Root lodging can certainly be a problem for sweet corn, but not because of plant density. What really matters is the specific hybrid and the environment, those major rainfall and wind events that set up conditions for root structural failure," says ...
WHAT: A commentary from leaders at the National Institute on Drug Abuse, part of the NIH, discusses a new study showing that an extended-release injection of buprenorphine, a medication used to treat opioid use disorder, was preferred by patients compared to immediate-release buprenorphine, which must be taken orally every day. Extended-release formulations of medications used to treat opioid use disorder may be a valuable tool to address the current opioid addiction crisis and reduce its associated mortality. The study and the accompanying commentary were published May 10, 2021 in JAMA Network Open.
It is well established that medications used to treat ...
Scientists at UC San Francisco are learning how immune cells naturally clear the body of defunct - or senescent - cells that contribute to aging and many chronic diseases. Understanding this process may open new ways of treating age-related chronic diseases with immunotherapy.
In a healthy state, these immune cells - known as invariant Natural Killer T (iNKT) cells - function as a surveillance system, eliminating cells the body senses as foreign, including senescent cells, which have irreparable DNA damage. But the iNKT cells become less active with age and other factors like obesity that contribute to chronic disease.
Finding ways to stimulate this natural surveillance system offers an alternative to senolytic ...
A new study in Current Biology from the Institute of Genomics of the University of Tartu, Estonia has shed light on the genetic prehistory of populations in modern day Italy through the analysis of ancient human individuals during the Chalcolithic/Bronze Age transition around 4,000 years ago. The genomic analysis of ancient samples enabled researchers from Estonia, Italy, and the UK to date the arrival of the Steppe-related ancestry component to 3,600 years ago in Central Italy, also finding changes in burial practice and kinship structure during this transition.
In the last years, the genetic history of ancient individuals has been extensively studied focusing on ...
Northwestern University researchers are building social bonds with beams of light.
For the first time ever, Northwestern engineers and neurobiologists have wirelessly programmed -- and then deprogrammed -- mice to socially interact with one another in real time. The advancement is thanks to a first-of-its-kind ultraminiature, wireless, battery-free and fully implantable device that uses light to activate neurons.
This study is the first optogenetics (a method for controlling neurons with light) paper exploring social interactions within groups of animals, which was previously impossible with current technologies.
The research will be published May 10 in the journal ...
There are billions of neurons in the human brain, and scientists want to know how they are connected. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Alle Davis and Maxine Harrison Professor of Neurosciences Anthony Zador, and colleagues Xiaoyin Chen and Yu-Chi Sun, published a new technique in Nature Neuroscience for figuring out connections using genetic tags. Their technique, called BARseq2, labels brain cells with short RNA sequences called "barcodes," allowing the researchers to trace thousands of brain circuits simultaneously.
Many brain mapping tools allow neuroscientists to examine a handful of individual neurons at a time, for example by injecting them with dye. Chen, a postdoc in Zador's lab, explains how their tool, BARseq, is different:
"The idea here is that instead ...
The COVID-19 pandemic has spurred genomic surveillance of viruses on an unprecedented scale, as scientists around the world use genome sequencing to track the spread of new variants of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The rapid accumulation of viral genome sequences presents new opportunities for tracing global and local transmission dynamics, but analyzing so much genomic data is challenging.
"There are now more than a million genome sequences for SARS-CoV-2. No one had anticipated that number when we started sequencing this virus," said Russ Corbett-Detig, assistant professor of biomolecular engineering at UC Santa Cruz.
The sheer number of coronavirus genome sequences and their rapid accumulation makes it hard to place new sequences on a "family ...
PHILADELPHIA-- New research performed in mice models at Penn Medicine shows, mechanistically, how the infant lung regenerates cells after injury differently than the adult lung, with alveolar type 1 (AT1) cells reprograming into alveolar type 2 (AT2) cells (two very different lung alveolar epithelial cells), promoting cell regeneration, rather than AT2 cells differentiating into AT1 cells, which is the most widely accepted mechanism in the adult lung. These study findings, published today in Cell Stem Cell, show that the long-held assumption that AT1 ...
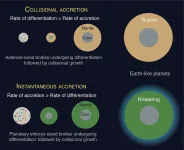
HOUSTON - (May 10, 2021) - The prospects for life on a given planet depend not only on where it forms but also how, according to Rice University scientists.
Planets like Earth that orbit within a solar system's Goldilocks zone, with conditions supporting liquid water and a rich atmosphere, are more likely to harbor life. As it turns out, how that planet came together also determines whether it captured and retained certain volatile elements and compounds, including nitrogen, carbon and water, that give rise to life.
In a study published in Nature Geoscience, Rice graduate student and lead author Damanveer Grewal and Professor Rajdeep Dasgupta show the competition between the time it takes for material to accrete into a protoplanet and the time the protoplanet ...