(Press-News.org) URBANA, Ill. – Black Americans experience racial discrimination on a regular basis, and it is a cause of chronic and pervasive stress. It is known to contribute to elevated risk for poor mental health outcomes, but most research has focused on individuals. A new study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign looks at the interpersonal effects of discrimination on parents and their adolescent children.
“A person’s experiences with racial discrimination are not just their own but may spill over into the family and affect the mental health and perceived social support of other family members. We underestimate the impact of discrimination if we're only looking at the individual level,” said lead author Shardé Smith, associate professor in the Department of Human Development and Family Studies, part of the College of Agricultural, Consumer and Environmental Sciences at Illinois.
Smith and co-author Robyn Gobin, associate professor in the Department of Health and Kinesiology at Illinois, drew on a longitudinal Chicago neighborhood study examining the impact of social interactions and environments. Based on data from the study’s third wave, the researchers included 401 Black parent-adolescent dyads, with an average age of 15 for the children. Participants answered questions about their experiences of racial discrimination over the past year, as well as their psychological well-being and perceived family support.
Analyzing the data for patterns, Smith and Gobin identified four clusters of responses: One group in which both the parent and the adolescent reported exposure to discrimination, another group where only the parent had experienced discrimination, a third group where the adolescent but not the parent had experienced discrimination, and a fourth group where both parents and children had a low likelihood of exposure to discrimination in the past year.
Specifically, parents were likely to experience racial discrimination at work, and both adolescents and their parents were likely to experience discrimination outside of their neighborhood and when they were receiving services. Furthermore, adolescents were likely to experience racial discrimination from the police.
As expected, the researchers found interactive effects of exposure to racial discrimination, consistent with the concept of “linked lives” that indicate people’s life experiences impact their family members. Overall, parents and adolescents in the three risk groups reported more psychological distress and lower levels of family support.
However, adolescents indicated significantly less family support when their parents also experienced racial discrimination. For parents, the combined exposure to racial discrimination did not diminish their perceptions of social support any more than the other risk groups.
It’s possible that parents struggle to support their children when they are also experiencing racial discrimination themselves, or perhaps children are not reporting the experiences to their parents, the researchers noted.
“It’s important for adolescents to talk to their parents and be able to receive support in managing racial trauma. If they can’t talk about these things in their family of origin with people who really understand it, then they may be left on their own trying to manage it, which could further exacerbate the mental health challenges they might be experiencing,” Gobin stated.
The researchers did not find any differences based on demographic characteristics. This demonstrates these effects are not unique to one population, but affect people across gender identity, age, and socio-economic status, Smith said.
These findings show the importance of developing interventions to address the psychological effects of discrimination in a family context, particularly focusing on how to help adolescents receive the support they need.
“I want to highlight that the goal in an ideal world is to dismantle the systems that create the discrimination. However, given how difficult that will be over time, we still need to engage in more malleable approaches to tackle these issues. We need to make sure healing frameworks are trauma-sensitive and culturally sound, helping to capitalize on the strengths within the Black community,” Smith concluded.
The paper, “The Dyadic Effects of Racial Discrimination: Using Latent Class Analysis to Explore Patterns of Racial Discrimination Among Black Parent–Adolescent Dyads,” is published in Cultural Diversity and Ethnic Minority Psychology [DOI: 10.1037/cdp0000678].
END
Study explores effects of racial discrimination on Black parents and children
2024-08-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Wayne State University professor receives career achievement award from the Society for Health Psychology
2024-08-06
DETROIT — Mark Lumley, Ph.D., distinguished professor of psychology in Wayne State University’s College of Liberal Arts and Sciences, was recently awarded the 2024 Nathan W. Perry, Jr. Award for Career Service to Health Psychology from the Society for Health Psychology.
The Society for Health Psychology is a national nonprofit that seeks to improve the lives of individuals and society by promoting health, preventing illness and improving health care through research, practice, education, training and advocacy.
“I’m delighted and greatly honored for this recognition,” ...
Elephants on the move: Mapping connections across African landscapes
2024-08-06
URBANA, Ill. -- Elephant conservation is a major priority in southern Africa, but habitat loss and urbanization mean the far-ranging pachyderms are increasingly restricted to protected areas like game reserves. The risk? Contained populations could become genetically isolated over time, making elephants more vulnerable to disease and environmental change.
A recent study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and the University of Pretoria in South Africa demonstrates how African conservation managers could create and optimize elephant movement corridors across a seven-country ...
Youth mental health-related emergency room trips declined significantly after Illinois ended COVID-19 lockdown
2024-08-06
Social media’s rise to popularity between 2010 and 2020 has been strongly correlated with the nationwide freefall in youth mental health that characterized the 2010s. Lawmakers have put increasing pressure on the U.S. government to take social media regulation more seriously, with cases about platforms like Facebook, Instagram and X rising to the Supreme Court level.
But despite the ubiquity of social media, scientists at Northwestern Medicine and Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago found that in Illinois, youth emergency room visits and hospitalizations for depression and anxiety decreased ...
How plants become bushy, or not
2024-08-06
or many plants, more branches means more fruit. But what causes a plant to grow branches? New research from the University of California, Davis shows how plants break down the hormone strigolactone, which suppresses branching, to become more “bushy.” Understanding how strigolactone is regulated could have big implications for many crop plants.
The study was published August 1 in Nature Communications.
“Being able to manipulate strigolactone could also have implications beyond plant architecture, including on a plant’s resilience to drought and pathogens,” said senior author Nitzan Shabek, an associate professor in the UC Davis Department of ...
Research spotlight: Identifying potential new protein targets for melanoma therapeutics
2024-08-06
How would you summarize your study for a lay audience?
Some proteins, such as programmed cell death protein 1 (PD1), can stop the immune system from attacking cancer cells and, therefore, support the growth of cancer. Therapies targeting these proteins can be highly effective, but tumors can become resistant.
We applied a method to detect proteins on a single–cell level to uncover human carcinoembryonic antigen cell adhesion molecule 1 (CEACAM1) patterns in melanoma. We found that increased ...
Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation awards $5.2 million to top clinical investigators
2024-08-06
Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation awards $5.2 million to top clinical investigators
The Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation has named six new Damon Runyon Clinical Investigators. The recipients of this prestigious award are outstanding, early-career physician-scientists conducting patient-oriented cancer research at major research centers under the mentorship of the nation's leading scientists and clinicians.
The Clinical Investigator Award program was designed to increase the number of physicians capable of translating scientific discoveries into new treatments for cancer patients. Each Awardee will receive $600,000 over three years, ...
Good outcomes 10 years after surgery for ectopic bone in thoracic spine
2024-08-06
August 6, 2024 — Thoracic ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (TOPLL) is a rare condition associated with ectopic bone formation in the thoracic spine. A long-term follow-up study from Japan shows significant and lasting improvement in outcomes with posterior decompression and fixation surgery for patients with T-OPLL, reports The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Surgical treatment of T-OPLL is effective in improving neurological function, quality ...
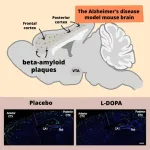
Dopamine treatment alleviates symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease
2024-08-06
A new way to combat Alzheimer’s disease has been discovered by Takaomi Saido and his team at the RIKEN Center for Brain Science (CBS) in Japan. Using mice with the disease, the researchers found that treatment with dopamine could alleviate physical symptoms in the brain as well as improve memory. Published in the scientific journal Science Signaling on August 6, the study examines dopamine’s role in promoting the production of neprilysin, an enzyme that can break down the harmful plaques in the brain that are the ...
Do your supplements contain potentially hepatoxic botanicals?
2024-08-06
Millions of Americans consume supplements that contain potentially hepatoxic botanical ingredients, according to a study from University of Michigan researchers.
Over a 30-day period, 4.7% of the adults surveyed in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey conducted from 2017 to 2020 took herbal and dietary supplements containing at least one of the botanicals of interest: turmeric; green tea; ashwagandha; black cohosh; garcinia cambogia; and red yeast rice containing products.
The resulting paper, “Estimated Exposure ...
No room for nuance in polarized political climate: SFU study
2024-08-06
Sometimes you just can’t win, and that goes double for people navigating the increasingly polarized political landscape in the United States.
Having nuanced opinions of politics in the U.S. turns out to be a very lonely, and unpopular, road, according to a recent study from a research team that includes assistant professor Aviva Phillipp-Muller from Simon Fraser University’s Beedie School of Business.
Published in the Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, the study found that people who express ambivalence about political topics – ranging from COVID-19 mask mandates, immigration and the death ...